CHART Time Traveler Activity
advertisement

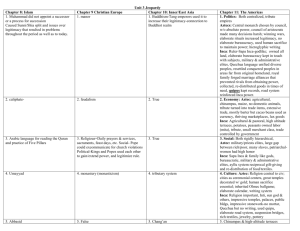
Name ____________________________________________ CHART Chapters 10-13 Theme Chapter 10 Chapter 11 Inner & East Asia 600-1200 CE Peoples &Civ’s of the Americas 1. Interaction between humans and the environment. 2. Development and interaction of cultures. 3. State-building, expansion, and conflict Chapter 12 Mongol Eurasia & Its Aftermath Chapter 13 Tropical Asia & Africa 1200-1500 CE Sui – Grand Canal created to unify China’s 2 major rivers Tang – Expansion westward along the Silk Road; growth of Chang’an Song – Unified N. & S. Song Dynasties; Japan –Small area; settled in mountainous area Vietnam – Settled along Red & Mekong River Korea – Mountainous; Silla&Koryo Maya – S. Mexico; Guatemala; Belize; Tikal/Chichen Itza Aztec – Central Mexico Tenochitlan/floating city/military conquests Inca – S. America/Andes/Cuzco; military conquests; Inca Trail/roads Tropical environment (The tropics) Monsoons & heavy rainfall Domestication of animals & plants in tropical areas Construction of irrigation canals & water systems Abundant minerals (Gold, Iron, Copper) Trans-Saharan trade route Indian Ocean trade route Tang – Influenced by Buddhism because of the success of the Silk Road & Emperor adoption; Confucianism ok Song – Neo-Confucianism; Buddhism influence decreases; astronomical clock; movable type; gunpowder; paper $$$; junk; Going Upriver at the Qingming Festival Japan – The Tale of Genji (Murasaki) & The Pillowbook Diaries (SeiShonagon) ALL 3 Polytheistic Maya – Religious sacrifices; Quetzalcoatl; Religion & astrology linked; develop a calendar system; predict the movement of the planets; 3 level cosmos; pyramids; Mayan ballgame Aztec –Religious sacrifices of conquered people; Huitzilopochtli/Tlaloc; pyramids Inca – Inti (Sun god); emperor (Son of the Sun); Temple of the Sun; Sacrifice of animals/textiles; Maya – Tikal (capital); rulers served as priests; central govt., military conquest & battles important Aztec –Tenochitlan (capital); tribute system imposed on conquered people & keeps empire stable; military expansion; central govt., warrior-based Inca –Cuzco (capital); expansion thru military conquest; central govt; bureaucracy; ayllu Spread of Islam – through Islamic merchants (TransSaharan trade; the Hajj; Mansa Musa’s Hajj; Timbuktu; Ibn Battuta; SE Asia) Spread of Christianity – Ethiopia (steles) – Coptic Christianity Important technology – Camel Saddle; Indian Ocean Dhow; building of Great Zimbabwe; writings & travels of Ibn Battuta; Benin Bronzes; Timbuktu Mosque; Church of St. George W. Africa – Kings (Mansa Musa/Sundiata in Mali) turned into Islamic states Swahili Coast – Great Zimbabwe (Stone Enclosures; city-states) Delhi Sultanate – Islamic-run state in India; led by kings/sultans; Raziya (only female leader); foreign rulers/alien status; alienated Hindu customs, but eventually allowed Hindus in their administration Maya – elevated fields/terraces for agriculture; conquered peoples public work projects Aztec – Chinampas (Floating Gardens); Tenochitlan markets for trading and selling of goods/food; Tribute System, Tribute System!!! $$$-less economy, barter system preferred Inca – Terraced fields on hill/mountainsides; canals; waru-waru farming system; potatoes; Tribute system; Inca Trail/Roads unified trade; trade controlled by govt.; Quechua language Maya –King Priests Merchants/Artisans Peasants/Workers Aztec – King Priests/Warriors Merchants/Artisans Peasants Inca – King Priests Warriors Merchants/Artisans Peasants; Chosen Women of the Emperor or Virgins of the Sun – servants of the Incan Emperor Africa (Trans-Saharan trade – used by Ibn Battuta; items traded heavily were gold & salt; link of trade between Great Zimbabwe & Saharan traders; major cities along trade routes, i.e. Timbuktu; Gold & Salt trade make Ghana & Mali powerful; trade ran from N to S & viceversa; Swahili & Indian Ocean trade – use of the Arab Dhow; trade relations between India & China) Indian Ocean Trade (linked Africa, India & China; allows for spread of Buddhism & Islam into SE Asia; used by Ibn Battuta Tang – Emperor Li Shimin& Empress Wu Zhao; Buddhism influenced; conflict between Buddhism & Confucianism; An Lushan Rebellion Song – Neo-Confucianism; Civil-service exam perfected Japan – Feudal System; Fujiwara/KamakaraShogunate; Kamikaze winds def. Mongols 4. Creation, expansion and interaction of economic systems Sui – Grand Canal expands trade within China; tributary system Tang – Silk Road; spread of Buddhism; Xuanzhang travels between China & India Song – Tributary system; “Flying Money”/Paper $$$; Going Upriver at the Qingming Festival; Chinese internal economy & trade thrives; trade or share knowledge of gunpowder to M. East/Persia; Economic growth; urban growth; Vietnam –Champa Rice given as tribute to Song 5. Development and transformation of social structures Tang/Song – Patriarchal; subordination of women; footbinding to upper class women; women could be educated; women’s property passed on to her husband; women could not remarry if divorced or widowed Japan –The Tale of Genji & The Pillowbook provide accounts of daily life in the court & demonstrates learning of women; Samurai; Women only allowed to communicate in Japanese, not Chinese; Men both languages High percentage of slavery in Africa, Asia, & India Patriarchal society placed women as inferior to men Indian upper-caste (class) women practiced SATI (throwing yourself on deceased husbands burning body Overall, female status based on her male master (father, husband, or owner); women not permitted to play roles in commerce/trade, administration or religion Expectation for women – farming, child rearing, cooking, spinning. Islam helped social status of women; others became slaves or concubines Name: _________________________________ Period: _____ Unit 3 (600-1450 CE) Chapters 10-13 I. Interaction between humans and the environment o Migration o Patterns of settlement o Technology o Demography and disease II. Development and interaction of cultures o Religion o Belief systems, philosophies, and ideologies o Science and technology o The arts and architecture III. State-building, expansion, and conflict o Political structures and forms of governance o Empires o Nations and Nationalism o Revolts and Revolution o Regional, transregional, and global structures and organizations AP Themes Chart Ch. 10 Inner & East Asia 600-1200 CE Tang, Song, Korea and Japan Ch. 11 Peoples & Civilizations of the Americas Ch. 12 Mongol Eurasia & Its Aftermath 1200-1500 CE IV. Creation, expansion, and interaction of economic systems o o o o o Maya, Aztec, and Inca Genghis Khan, The Rise of the Mongols, Yuan and Ming Ch. 13 Tropical Asia & Africa 1200-1500 CE Mansa Musa, Indian Ocean Trade, Islamic Africa V. Agriculture and pastoral production Trade and commerce Labor systems Industrialization Capitalism and socialism Development and transformation of social structures o Gender roles and relations o Family and kinship o Racial and ethnic constructions o Social and economic classes