Unit 3 Jeopardy
advertisement

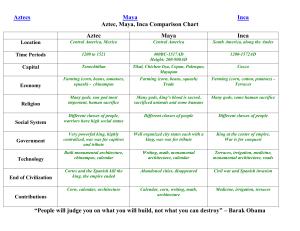
Unit 3 Jeopardy Chapter 10: Inner/East Asia 1. Buddhism-Tang emperors used it to increase their legitimacy-connection to Buddhist realm Chapter 8: Islam 1. Muhammad did not appoint a successor or a process for succession Caused Sunni/Shia split and issues over legitimacy that resulted in problems throughout the period as well as to today. Chapter 9 Christian Europe 1. manor 2. caliphate- 2. feudalism 2. True 3. Arabic language for reading the Quran and practice of Five Pillars 3. Religious=Daily prayers & services, sacraments, feast days, etc. Social- Pope could excommunicate for church violations Political-Kings and Popes used each other to gain/extend power, and legitimize rule. 3. True 4. Umayyad 4. monastery (monasticism) 4. tributary system 5. Abbasid 5. False 5. Chang’an Chapter 11: The Americas 1. Politics: Both centralized, tribute empires Aztecs: Central monarch chosen by council, w/o absolute power, council of aristocrats made many decisions harsh; winning wars, elaborate rituals increased legitimacy, no elaborate bureaucracy, used human sacrifice to maintain power; hieroglyphic writing Inca: Ruler-Sapa Inca-godlike; owned all land, elaborate bureaucracy kept in touch with subjects, military & administrative elites, Quechua language unified diverse peoples, resettled conquered peoples in areas far from original homeland, royal family forged marriage alliances that prevented rivals from obtaining power, collected, re-distributed goods in times of need, quipus kept records, road system reinforced Inca power. 2. Economy: Aztec: agricultural, chinampas, maize, no domestic animals, tribute turned into trade items, extensive trade, mostly barter but cacao beans used as currency, thriving marketplaces, lux goods Inca: Agricultural & pastoral, high altitude terraces, potatoes, peasants owned labor (mita), tribute, small merchant class, trade controlled by government 3. Social: Both rigidly hierarchical, Aztec: military/priests elites, large gap between rich/poor, many slaves, patriarchalwomen had high honor Inca: Sapa Inca & family like gods, bureaucratic, military & administrative elites, ayllu system reciprocal gift-giving and re-distribution of food/textiles. 4. Culture: Aztec: Religion central to civ; cities as ceremonial centers, great temples decorated w/ gold; human sacrifice essential; inherited Olmec ballgame; elaborate calendar, writing system Inca: Religion important, Inti, sun god & others, impressive temples, palaces, public bldgs, impressive stonework-no mortar, Quechua but no writing, used quipu, elaborate road system, suspension bridges, rich textiles, jewelry, pottery 5. Chinampas & high-altitude terraces 6. Islamic Spain, al-Andalus Blended Roman, Germanic, Jewish, Arab, and Berber traditions. 6. False-food production was not a role of the Church. 6. Buddhists and women 7. True-Muslim women had rights of divorce and could own property. 7. True 8. True 9. True-eventually conquered Constantinople in 1453 8. West=fragmented kingdoms under various Kings like Clovis and Charlemagne that depended on feudal system of mutual obligations East=Centralized bureaucracy-Byzantine Emperor had absolute power. 9. investiture controversy 10. Both Christian, West-romance languages; East-Greek derivations 7.gunpowder, moveable type, credit, water wheels, astronomical clocks, medicine, fractions, magnetic compass etc. 8. footbinding 9. Europe=contract Japan=moral obligation 10. Ghana, Mali 11. civil and commercial law based on Qura’n and hadith 12.False Chapter 13: Tropical Asia & Africa 1. Legal scholar 2. monsoons Chapter 14: Latin West 1. Magna Carta 2. False 3. True 3. True 4.False 3. India= brutal conquest Africa=peaceful conversion 4, Islam 5. Both were nomadic, military societies 5. local irrigation projects 6. Japan 6. prosperous, independent city-states 8. False. 9. True True 10. Chapter 12: The Mongols 1. Thriving trade-Pax Mongolica 2. Disease 7. True 6. Aztecs: Cortez with help from enemies, believed Cortez was a god prophesized to return, assistance from Malinche who interpreted Smallpox, horses, weapons, guns Inca: already weak from civil war and disease that had already arrived ahead of Pizzaro, superior weapons, etc. Road system 4. warming temps, fewer epidemics, tech innovations: plow, horse collar, etc. 5. 3-field system increased fertility Expansion into new agricultural lands; draining swamps, clearing forests 6. end of serfdom in most places, growth of industry, ie, millers, iron mining/making, guilds, banking, investment, urban jobs 7.humanism, ethics, education, increased literacy, painting, sculpture, architecture 8. True 9.intense artistic & intellectual activityItalian and Northern Europe Rebirth of Greco-Roman culture 10. Mansa Musa Possible DBQ’s: Rise of Cities in the Post-Classical Era Significance and Impact of Mongol Expansion and Rule in Eurasia during 13th and 14th centuries Patterns of Trade 1000-1450 ce Chapter 15: Maritime Revolution 1. Zheng He 2. Ming, trade, tribute, display power, curiosity, Indian Ocean, East Africa, huge treasure ships 3. 4. 5. Treaty of Todesillas 6. Ming Dynasty 7. True 8. What do you think? 9. Muslim, Greeks, 10. military force