PH-101 Student Learning Outcomes - University of Louisville Public
advertisement

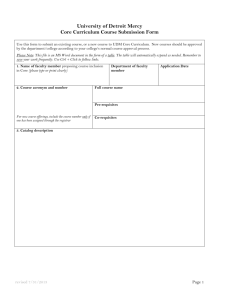
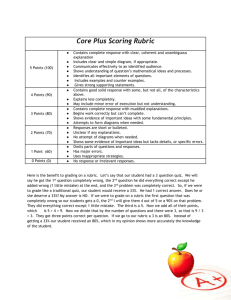
PH-101 Student Learning Outcomes General Education Mission “The General Education Program at the University of Louisville fosters active learning by asking students to think critically, to communicate effectively, and to understand and appreciate cultural diversity. Specifically, students will establish foundations in the following content areas: Arts and Humanities, Mathematics, Natural Sciences, Oral Communication, Social and Behavioral Sciences, and Written Communication. Additionally, in the competency area, students will acquire an understanding of Cultural Diversity through work in the content areas.” PH-101 Objectives and Outcomes The following two sections are extracted from the PH-101 syllabus. Neither is what is needed, but Course Objectives At the conclusion of the course, the successful student is able to: Understand and describe the key features of the historical development of public health as a domain of specialized knowledge and public policy. Analyze and differentiate the concept of population health from medical, nursing, dental, and other health care activities. Understand and discuss the concepts of prevention, detection, control of infectious and chronic conditions, health disparities, and global health. Apply the basic principles of epidemiology. Analyze the impact of behavior, socioeconomic status, and culture on health. Evaluate the importance of cultural diversity in assessing health status and outcomes. Understand and describe the impact and control of environmental factors on health. Evaluate the role of governmental and non-governmental institutions in shaping population health outcomes. Formulate what it means to foster a healthy society both locally and globally. General Education Learning Outcomes Social and behavioral sciences are concerned with understanding human behavior, human interactions, human environment, and the related social structures and forms. Students who satisfy this requirement demonstrate that they are able to do all of the following: 1 1. Communicate an understanding of how social science knowledge is established and how and why it changes over time. Outcome (specify how this course meets the outcome stated above) Understand and describe the key features of the historical development of public health as a domain of specialized knowledge and public policy. Analyze and differentiate the concept of population health from medical, nursing, dental, and other health care activities. Evaluate the importance of cultural diversity in assessing health status and outcomes. Understand and discuss the concepts of prevention, detection, control of infectious and chronic conditions, health disparities, and global health. Assessment (means of assessment such as essays, quizzes, tests, homework, journals, group projects, class discussion, research papers, field work, service learning, independent study, etc.) Five-minute summaries (critical thinking, effective communication; see description and rubric in syllabus) Examinations (understanding of issues of cultural diversity included in exams 2 and 3 based on readings and discussions in classes 12-18 and 2028, respectively) Essay (critical thinking, effective communication; see description and rubric in syllabus) Journal (critical thinking, effective communication, understanding of issues of cultural diversity; see description and rubric in syllabus) 2. Evaluate evidence and apply it to solving problems through social science methods. Outcome (specify how this course meets the outcome stated above) Understand and discuss the concepts of prevention, detection, control of infectious and chronic conditions, health disparities, and global health. Apply the basic principles of epidemiology. Analyze the impact of behavior, socioeconomic status, and culture on health. Evaluate the importance of cultural diversity in assessing health status and outcomes. Understand and describe the impact and control of environmental factors on health. Assessment (means of assessment such as essays, quizzes, tests, homework, journals, group projects, class discussion, research papers, field work, service learning, independent study, etc.) Examinations (understanding of issues of cultural diversity included in exams 1, 2, and 3 based on readings and discussions in classes 1-10, 1218, and 20-28, respectively) 2 Essay (critical thinking, effective communication; see description and rubric in syllabus) Journal (critical thinking, effective communication, understanding of issues of cultural diversity; see description and rubric in syllabus) 3. Communicate an understanding of a body of social science knowledge and its disciplinary perspective. Outcome (specify how this course meets the outcome stated above) Formulate what it means to foster a healthy society both locally and globally. Analyze and differentiate the concept of population health from medical, nursing, dental, and other health care activities. Evaluate the importance of cultural diversity in assessing health status and outcomes. Understand and discuss the concepts of prevention, detection, control of infectious and chronic conditions, health disparities, and global health. Assessment (means of assessment such as essays, quizzes, tests, homework, journals, group projects, class discussion, research papers, field work, service learning, independent study, etc.) Examinations (understanding of issues of cultural diversity included in exams 1, 2, and 3 based on readings and discussions in classes 1-10, 1218, and 20-28, respectively) Essay (critical thinking, effective communication; see description and rubric in syllabus) Journal (critical thinking, effective communication, understanding of issues of cultural diversity; see description and rubric in syllabus) 3