Structural Mechanics Course Syllabus - Civil Engineering
advertisement

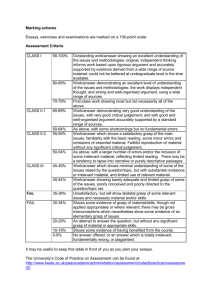
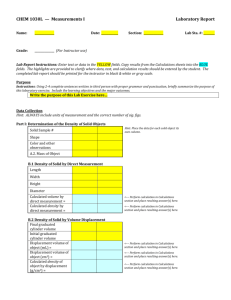
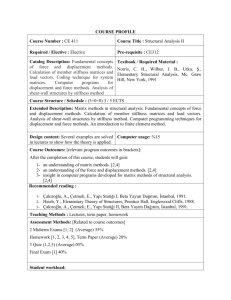
Structural Mechanics (Spring 2013) Deng, Lu; 教授楼 310;denglu@hnu.edu.cn Basic Course Information Class Hour: 64 lectures Credit: 4.0 Applicable Major: Civil Engineering Prerequisite Course: Theoretical Mechanics, Mechanics of Materials Aims Through the study of structural mechanics, students will grasp the principle and method of calculation in structure of bar system; understand the mechanical property of all kinds of structures in order to lay the groundwork for the learning of related professional courses, design and scientific research of structure. This course aims at gradually developing the ability of calculation (including calculating by hands, using brain, and using computer), innovation (including the creation of the structure forms and calculation method) and comprehensive application of structural mechanics to analyze and solve practical engineering problems. Contents and Objectives 1. Introduction • Understand study objects and tasks of this course. • Grasp selection principle of simplified structural diagram for computation. • Understand classification of structures and loads. 2. Geometrical Construction Analysis of Two Dimensional Systems • Understand the definition of geometrically stable system, geometrically unstable system, and instantaneous unstable system. • Understand the concept of rigid member, restrain, and degree of freedom. • Grasp basic construction rules of geometrically stable system and the application of the rules to analyze the geometrical construction of ordinary system and distinguish four kinds of systems: geometrically stable system with or without superfluous restraint, geometrically unstable system and instantaneous unstable system. • Understand geometrical construction characteristic of statically determinate structure and statically indeterminate structure. 3. Internal Force Calculation of Statically Determinate Structure • Understand the mechanics characteristic and calculation method of 5 common types of statically determinate structures (beam, arch, truss rigid frame and composite structure). • Proficiently master shape characteristics of internal force diagram of straight-bar and superposition method of drawing the internal force diagram. • Proficiently master internal force calculation method of multi-span statically determinate beam and be able to distinguish fundamental part and accessory part and draw internal force diagram. • Proficiently master internal force calculation method and diagram drawing of cantilevered frame, simply supported frame, 3-hinged frame and other associated frame. • Grasp discrimination method for zero bars in truss and calculation of internal force of simple truss and assigned member in associated frame using method of joint and section. Understand differences of mechanical property of all kinds of two dimensional trusses. • Grasp calculation of support reaction of three-hinged arch and internal force of assigned section and be able to draw internal force diagram. Understand concept of optional centre line of the arch. • Understand characteristic of statically determinate structure. 4. Virtual Work Principle and Structure Displacement Calculation • Understand concept of generalized force, generalized displacement, virtual work and principle of virtual work of elastic system. • Grasp unit load method and be able to establish virtual status according to the position, direction and property of the displacement. • Understand ordinary and practical formula of displacement calculation. • Proficiently master application of integral method to calculate structure displacement and graph multiplication method to calculate the displacement of beam and rigid frame. Memorize area and centroid position of common graphs. (triangle and standard quadratic parabola etc) • Understand calculation method of displacement caused by temperature change. • Understand calculation method of displacement caused by support movement. • Understand reciprocal theorem of work, displacement, support reaction and reaction-displacement. 5. Force Method • Understand concept of statically indeterminate structure. • Grasp determination method of degree of indeterminacy and selection of fundamental structure. • Understand equation of force method and its physical significance • Proficiently master internal force calculation of statically indeterminate beam and rigid frame under loading and be able to draw bending moment diagram. • Grasp internal force calculation of statically indeterminate truss, composite structure, framed bent and arch under loading. • Understand calculation of statically indeterminate structure under temperature change and support movement. • Grasp application of symmetry to simplify calculation of symmetrical fundamental structure in force method. • Grasp displacement calculation of statically indeterminate structure. • Understand characteristic of statically indeterminate structure. 6. Displacement Method • Understand basic concept of displacement method. • Grasp determination of the number of unknown joint rotation displacement and independent joint translation displacement and selection of fundamental structure. • Understand equation of displacement method and its physical significance. • Memorize shape-constant and load-constant of common statically determinate single-span beams with uniform section. • Grasp calculation of statically indeterminate frame under loading. • Grasp application of symmetry to apply half-structure to simplify calculation in displacement method. • Grasp principle and method of direct application of equilibrium to establish equation of displacement method. 7. Influence Line • Understand concept of moving load and definition of influence line. • Grasp application of static method to draw influence line of certain value. • Grasp application of kinematics method to draw influence line of certain value. • Grasp application of influence line to acquire influence value under given load. • Grasp method to locate the most unfavorable load position of statically determinate structure under moving load and solving method of absolute maximum of bending moment and drawing of envelope diagram of internal force of simply supported beam. • Understand the most unfavorable load position and envelope diagram of internal force of continuous beam under uniform load. 8. Matrix Displacement Method • Understand basic concept of matrix displacement method and local coordinate system of element and global coordinate system of structure. • Grasp transfer matrix between two coordinate systems and memorize element stiffness matrix of local coordinate system. • Proficiently master forming principle and method of structure stiffness matrix (pre-treatment method). Understand Post-treatment method. • Grasp processing method of non-joint load. • Grasp procedure of calculation of all kinds of structures using matrix displacement method. 9. Dynamical Calculation of Structure • Understand significance of dynamical calculation, classification of dynamic load, task of dynamical calculation and principle and method of dynamical calculation. Grasp method to determine dynamical degree of freedom of elastic system. • Proficiently master free vibration and forced vibration of system of single degree of freedom. • Proficiently master free vibration of system of multiple degrees of freedom. Understand orthogonality of normal modes. • Understand forced vibration of system of multiple degrees of freedom. Arrangement and Pattern of Teaching Structural Mechanics is a skill-based course. The priority of learning is class-teaching. Exercise and discussion class must be no less than 8 lectures. The overall plan is 64 lectures for the first semester, covering the first 6 chapters. (See specific plan below at Allocation of Lectures). Student’s in-after class time spending ratio of 1:2 is recommended. Allocation of Class Hour Chapter 1. Introduction (2 lectures) Chapter 2. Geometrical Construction Analysis of Two Dimensional Systems (6 lectures) Chapter 3. Internal Force Calculation of Statically Determinate Structure (14 lectures) Chapter 4. Virtual Work Principle and Structure Displacement Calculation (12 lectures) Mid-term Exam: covering the first 4 chapters (2 lectures) Chapter 5. Force Method (14 lectures) Chapter 6. Displacement Method (12 lectures) Review: All materials in the 6 chapters (2 lectures) Exam All exams will be closed book. Evaluation and Grade Final grade of this course consists of the following elements: • Attendance: 5% • Homework: 15%. (NO credit will be given to homework submitted after the due date) • Mid-term Exam: 25% • Quiz and Project: 15% • Final Exam: 40% Textbook 《Structural Mechanics》, 1st edition, Bao Shihua, Gong Yaoqing, Wuhan University of Technology Press, 2006. Reference Book •《结构力学》 (上、下册) (第四版) ,包世华,辛克贵编,武汉理工 大学出版社,2012。 •《结构力学》 (上、下册) (第四版) ,杨茀康、李家宝编,高等教育 出版社,1998 年。 •《结构力学》 (上、下册) (第三版) ,龙驭球、包世华编,高等教育 出版社,1994 年。