Chapter 1 Math Vocabulary Properties of Addition Commutative
advertisement

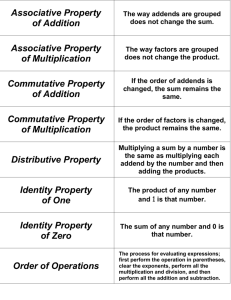
Chapter 1 Math Vocabulary Properties of Addition Commutative Property of Addition: If the order of the addends changes, the sum stays the same. Ex: 12 + 7 = 7 + 12 Associative Property of Addition: If the grouping of addend changes, the sum stays the same. Ex: 5 + (8 + 14) = (5 + 8) + 14 Identity Property of Addition – The sum of any number and 0 is that number. Ex: 13 + 0 = 13 Properties of Multiplication Commutative Property of Multiplication – If the order of the factors changes, the product stays the same. Ex: 4 x 9 = 9 x 4 Associative Property of Multiplication – If the grouping of the factors changes, the product stays the same. Ex: 11 x (3 x 6) = (11 x 3) x 6 Identity Property of Multiplication – The product of any number and 1 is that number. Ex: 4 x 1 = 4 Distributive Property – Multiplying a sum by a number is the same as multiplying each addend by the number and then adding the products. Ex: 5 x (7 + 9) = (5 x 7) + (5 x 9) The Distributive Property can also be used with multiplication and subtraction. Ex: 2 x (10 – 8) = (2 x 10) – (2 x 8) period – a group of three digits separated by commas in a multi-digit number. base – the number that is used as the repeated factor. exponent – the number that tells how many times the base is used as a factor. Ex: 103 – 10 is the base and 3 is the exponent. inverse operations – opposite operations. Ex: addition and subtraction; multiplication and division. evaluate – find the value of. order of operations – the order in which you should evaluate an expression.