NOUN
advertisement

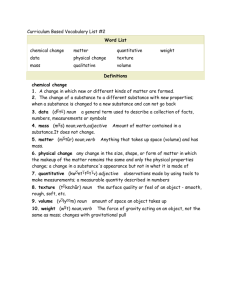
NOUN O person, place, thing, idea O Common Nouns – begin with lower case letters Ex: That’s my dog O Proper Nouns – proper names for things - begin with capital letters. Ex: My dog’s name is Coleman. O Possessive Nouns – show ownership Ex: That’s Coleman’s doghouse O Abstract Nouns – things/ideas that you can’t necessarily see or touch If it ends in –ion or –ness, it’s a noun! Ex: Coleman made the decision to stay in his doghouse. Ex: Coleman shows his happiness by wagging his tail. If it ends in –ion or –ness, it’s a noun! Directions: Write your own sentences, using at least one common noun, one proper noun, one possessive noun, and one abstract noun. Underline all nouns. ADJECTIVE O Modifies (describes) nouns (Fifi has a large bone.) and pronouns (They are curious) O Tells Which one? How many? What kind? O Includes numbers, colors, sizes, shapes O Includes the articles: a, an, the Directions: Write two sentences, underlining the adjectives. INTERJECTION O Words used to express an emotion, a protest, a command, or a greeting. O Can stand either by themselves or as part of a sentence O Mild interjections are usually separated from the rest of the sentence by a coma, but stronger ones may be followed by an exclamation mark. Examples: Wow! That’s a big pumpkin! You have homework tonight, and yes, you have to do it. O Other examples: Hello, Um, Haha Directions: Write 2 sentences using interjections not seen here. Underline the interjections. ADVERB O Modifies (describes): -Verbs (She sat quietly), -Adjectives (That sweater is really cute), -Other adverbs (We finished our homework very quickly). O Tells How? When? Where? To what extent? O Usually ends in -ly O The word Not is always an adverb Directions: Write 2 sentences using adverbs in two different ways (either modifying a verb, adjective, OR other adverb). Underline the adverbs. - PREPOSITION O Prepositions show a relationship (usually direction or time) between a noun or pronoun and some other word in the sentence. Some Examples: Across, Before, Between, During, Except, Instead of O Prepositional Phrase: Starts with a preposition and ends with a noun or pronoun. All prepositions are part of a prepositional phrase. Examples: in my car - after school - since last year O Object of Preposition: The noun/pronoun in a prep. phrase. Examples: in my car - after school - since last year Directions: Write 2 sentences using prepositions. Put parentheses around the prepositional phrases, and underline the objects of the prepositions. > Example: We rode (in my car). CONJUNCTION O A Conjunction joins (or connects) words, phrases, & clauses O 3 TYPES: 1. Coordinating – FANBOYS for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so 2. Subordinating – start dependent clauses (must be followed by a subject and verb) after, since, before, while, because, although, so that, if, when, whenever, as, even though, until, unless, etc. 3.Correlative – Come in pairs… (both/and) (not only/but also), (neither/nor), (either/or), Example: I like neither spinach nor broccoli. Directions: Write 3 sentences, each using one of the three types of conjunctions. Underline the conjunction(s) in each sentence. VERB O Shows action or expresses state of being O Action – shows action: Bob wrote a note. O Linking – links two words or ideas. Renames or describes the subject with a word in the predicate. She is my sister. She is pretty. > All the “to be” verbs (is, be, am, are, was, were, been, being) plus any verb that can take the place of a “to be” verb (appear, become, feel, grow, look, remain, seem, smell, sound, stay, taste). She = nice… She is nice. She looks nice. She seems nice. > But watch out! Some linking verbs are sometimes action verbs! Example: The bone tastes wonderful. (bone = wonderful) The dog tastes the bone. (dog ≠ bone) O Helping – “helps” another verb. > Includes all the “to be” verbs plus… will, would, can, could, shall, should, may, might, must, have, has, had, do, does, did, ought - A helping verb is ALWAYS followed by another verb (either action or linking) Spot has been digging for bones all day. digging=action Spot will be warm and cozy in his new bed. be=linking PRONOUN O Takes the place of a noun O Watch out! Some pronouns can be adjectives! O Antecedent = the noun it takes the place of - Example: Ask Kelly if Kelly got Kelly’s hair cut. => Ask Kelly if she got her hair cut O TYPES: (space these out in your flip-book for more notes later…) 1. Personal 2. Reflexive 3. Relative 4. Interrogative 5. Demonstrative 6. Indefinite