Sample Assignment 1(a)
advertisement

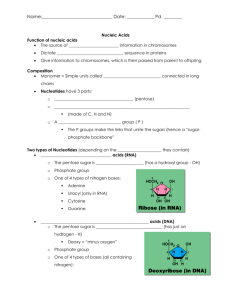
U5: Genetics T2(b): Molecular Biology From Gene to Protein A7(a): Cracking the Genetic Code The RNA Codon Name _________________________________________________ Period _____ Date _______________________ Objective: To construct an explanation based on reasoning for how the structure of nucleic acids determines the structure of proteins. I. Anticipatory Set (Warm-up) An example of a code is binary code, used in computer science. Computers communicate in binary language, using just 1s and 0s. People communicate through text, based on characters. For computers and people to talk to one another, one language must be translated to the other. Different combinations of two digits, 1 and 0, arranged in blocks of eight, can be used to represent the different characters. For example, the combination 01000001 codes for upper case “A”. A total of 28 = 256 combinations are available for characters, more than are needed. 1. There are ____ binary digits, 1 and 0. 2. There are at least ____ characters that need to be coded for. 3. In computer science, different combinations of ____ 1s and 0s can represent each of a possible _____ characters. U5: Genetics A7(a): Cracking the Genetic Code T2(b): Molecular Biology The RNA Codon From Gene to Protein 4. Using the handout key, translate the following message from binary to text: 01000100010011100100000100100000011010010111001100100000011101000 11010000110010100100000011000110110111101100100011001010010000001 101111011001100010000001101100011010010110011001100101 5. Information encoded in binary language can be ____________________________ into text. II. Background Biologists suspected that the information encoded in nucleic acids is translated into proteins, which do the work of the cells. Just as binary code is made of long chains of 1s and 0s, ______________________ are made of long chains of nucleotides. Just as text is made of long chains of characters, ______________________ are made of long chains of amino acids. There were 4 types of nucleotides that needed to code for 20 types of amino acids. The puzzle was to figure out (a) how many combinations of nucleotides represented each of 20 amino acids and (b) how many nucleotides were in each combination. U5: Genetics T2(b): Molecular Biology From Gene to Protein A7(a): Cracking the Genetic Code The RNA Codon Sample DNA sequence: AAATCGGGAAATGGCAGTACCAATAGCACA TTTAGCCCTTTACCGTCATGGTTATCGTGT Complementary RNA sequence: Protein sequence: Phe-Ser-Pro-Leu-Pro-Ser-Try-Leu-Ser-Cys U5: Genetics T2(b): Molecular Biology From Gene to Protein A7(a): Cracking the Genetic Code The RNA Codon III. Activity: Using Reasoning to Crack the Code 1. There are _____ types of nucleotides found in nucleic acids. 2. There are _____ types of amino acids found in protein. A. Hypothesis 1: A single nucleotide codes for each amino acid 3. If 1 nucleotide codes for 1 amino acid, then a total of 41 = _____ amino acids can be coded for. Example: A 4. Does this coding scheme work? Explain. B. Hypothesis 2: A combination of 2 nucleotides codes for each amino acid. 5. Write out each unique pair of nucleotides below. Hint: Arrange the nucleotides on the lab bench in groups of 2 until you have all possible unique combinations. Example: AA 6. There are 42 = _____ unique combinations of nucleotide pairs. Each pair of nucleotides can represent each of _____ amino acids. 7. Does this coding scheme work? Explain. U5: Genetics T2(b): Molecular Biology From Gene to Protein A7(a): Cracking the Genetic Code The RNA Codon C. Hypothesis 3: A combination of 3 nucleotides codes for each amino acid. 8. Write out each unique triplet of nucleotides below. Hint: Arrange the nucleotides on the lab bench in groups of 3 until you have all possible unique combinations. Example: AAA 9. There are 43 = _____ unique combinations of nucleotide triplets. Each triplet of nucleotides can represent each of _____ amino acids. 10. Does this coding scheme work? Explain. D. Hypothesis 4: A combination of 4 nucleotides codes for each amino acid. 11. There are ______ = ______ unique combinations of nucleotide quadruplets. Each quadruplet of nucleotides can represent each of _____ amino acids. U5: Genetics A7(a): Cracking the Genetic Code T2(b): Molecular Biology The RNA Codon From Gene to Protein 12. Does this coding scheme work? Is it necessary to have this many combinations? Explain. IV. Drawing Conclusions Using Argument from Reasoning 13. Construct an explanation based on reasoning for how the structure of nucleic acids could determine the structure of proteins. In your answer, a. Identify the building blocks of nucleic acid and protein and describe how they are arranged. b. Identify the best hypothesis that explains how nucleic acids code for proteins: c. Explain why this is the best hypothesis. d. Explain why the other hypotheses are not the best. Image Sources: http://www.biotopics.co.uk/JmolApplet/jcontentstable.html http://www.commons.wikimedia.org