chap 2.4 sedimentary rocks
advertisement
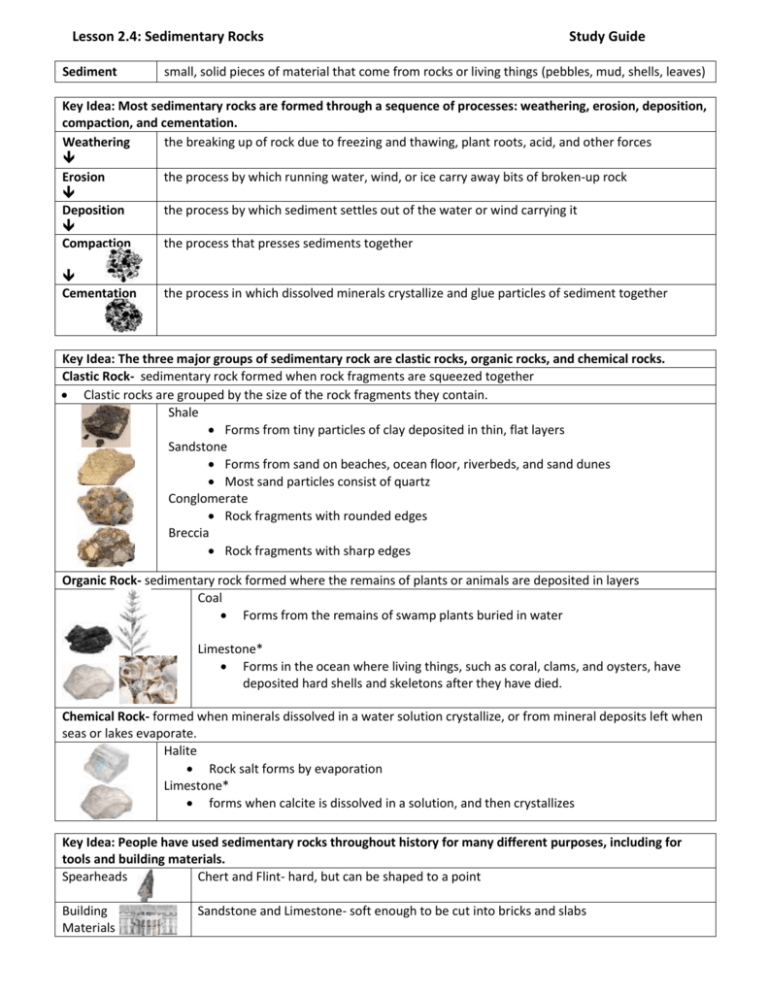
Lesson 2.4: Sedimentary Rocks Sediment Study Guide small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or living things (pebbles, mud, shells, leaves) Key Idea: Most sedimentary rocks are formed through a sequence of processes: weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction, and cementation. Weathering the breaking up of rock due to freezing and thawing, plant roots, acid, and other forces Erosion the process by which running water, wind, or ice carry away bits of broken-up rock Deposition the process by which sediment settles out of the water or wind carrying it Compaction the process that presses sediments together Cementation the process in which dissolved minerals crystallize and glue particles of sediment together Key Idea: The three major groups of sedimentary rock are clastic rocks, organic rocks, and chemical rocks. Clastic Rock- sedimentary rock formed when rock fragments are squeezed together Clastic rocks are grouped by the size of the rock fragments they contain. Shale Forms from tiny particles of clay deposited in thin, flat layers Sandstone Forms from sand on beaches, ocean floor, riverbeds, and sand dunes Most sand particles consist of quartz Conglomerate Rock fragments with rounded edges Breccia Rock fragments with sharp edges Organic Rock- sedimentary rock formed where the remains of plants or animals are deposited in layers Coal Forms from the remains of swamp plants buried in water Limestone* Forms in the ocean where living things, such as coral, clams, and oysters, have deposited hard shells and skeletons after they have died. Chemical Rock- formed when minerals dissolved in a water solution crystallize, or from mineral deposits left when seas or lakes evaporate. Halite Rock salt forms by evaporation Limestone* forms when calcite is dissolved in a solution, and then crystallizes Key Idea: People have used sedimentary rocks throughout history for many different purposes, including for tools and building materials. Spearheads Chert and Flint- hard, but can be shaped to a point Building Materials Sandstone and Limestone- soft enough to be cut into bricks and slabs