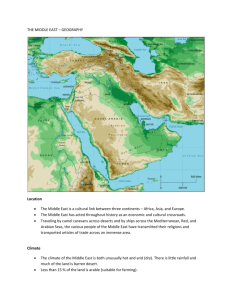
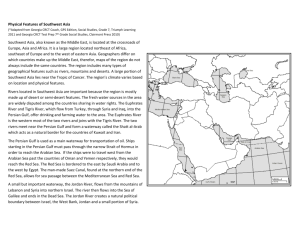
Middle East Physical Features Definitions
advertisement

Atlas Mountains A system of ranges and plateaus of northwest Africa extending from southwest Morocco to northern Tunisia between the Sahara Desert and the Mediterranean Sea and rising to 4,167.8 m (13,665 ft). the Ahaggar, are a highland region in central Sahara, or southern Algeria, along the Tropic of Cancer. Hindu Kush A mountain range of southwest Asia extending more than 805 km (500 mi) westward from northern Pakistan to northeast Afghanistan. It is crossed by several high-altitude passes used as invasion and trade routes since ancient times. The highest elevation is Tirich Mir, 7,695.2 m (25,230 ft), in Pakistan. Taurus Mountains A range of southern Turkey extending about 563 km (350 mi) parallel to the Mediterranean coast. It rises to 3,736.6 m (12,251 ft) and has important mineral deposits. Zag·ros Mountains (zăg′rəs) A range of western Iran forming the western and southern borders of the central Iranian plateau and rising to 4,550.6 m (14,920 ft). Arabian Sea The northwest part of the Indian Ocean between Arabia and western India. It has long been an important trade route between India and the West. Black′ Sea′ n. a sea between Europe and Asia, bordered by Turkey, Romania, Bulgaria, Ukraine, Georgia, and the Russian Federation. Caspian Sea - a large saltwater lake between Iran and Russia fed by the Volga River; the largest inland body of water in the world Dead Sea (dĕd) A salt lake, about 397 m (1,300 ft) below sea level, between Israel and Jordan. It is one of the saltiest bodies of water known and is the lowest point on the surface of the earth. Red Sea n 1. (Placename) a long narrow sea between Arabia and NE Africa, linked with the Mediterranean in the north by the Suez Canal and with the Indian Ocean in the south Gulf of Oman - an arm of the Arabian Sea connecting it with the Persian Gulf Persian Gulf n 1. (Placename) a shallow arm of the Arabian Sea between SW Iran and Arabia: linked with the Arabian Sea by the Strait of Hormuz and the Gulf of Oman; important for the oilfields on its shores Gulf of Aden - arm of the Indian Ocean at the entrance to the Red Sea Mediterranean Sea n 1. (Placename) a large inland sea between S Europe, N Africa, and SW Asia: linked with the Atlantic by the Strait of Gibraltar, with the Red Sea by the Suez Canal, and with the Black Sea by the Dardanelles, Sea of Marmara, and Bosporus; many ancient civilizations developed around its shores Suez Canal - a ship canal in northeastern Egypt linking the Red Sea with the Mediterranean Sea Strait of Hormuz - a strategically important strait linking the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman The Tigris River /ˈtaɪɡrɪs/ is the eastern member of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, Encyclopædia Britannica Get involvedShare Euphrates River, Turkish Fırat Nehri, Arabic Nahr al-Furāt, river, Middle East. The longest river in Southwest Asia, it is one of the two main constituents of the Tigris-Euphrates river system. The river rises in Turkey and flows southeast across Syria and through Iraq. Formed by the confluence of the Karasu and the Murat rivers in the high Armenian plateau The Nile (Arabic: ال ن يل, an-Nīl; Ancient Egyptian: Iteru & Ḥ'pī; Coptic Egyptian: ⲫⲫⲫⲫⲫ, P(h)iaro; Amharic: ዓባይ?, ʿAbbai) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa, generally regarded as the longest river in the world.[ The Arabian Desert is located in Western Asia. It is a vast desert wilderness stretching from Yemen to the Persian Gulf and Oman to Jordan and Iraq. It occupies most of the Arabian Peninsula, with an area of 2,330,000 square kilometers search Coordinates: 20°N 50°E20°N 50°E Rub' al Khali ()ال رب ع ال خال ي sand desert Sand dunes in the Rub' al Khali. Saudi Arabia, Oman, Countries United Arab Emirates, Yemen Length Width 1,000 km (621 mi) 500 km (311 mi) The Rub' al Khali (Arabic: لاخل لبرلاar-Rubʿ al-Ḫālī ,[note 1] "the empty quarter") or Empty Quarter is the largest sand desert in the world,[1] encompassing most of the southern third of the Arabian Peninsula The Sahara (Arabic: ال ك برى ال صحراء, aṣ-Ṣaḥrāʾ al-Kubrā , 'the Great Desert') is the world's hottest desert, and the third largest desert after Antarctica and the Arctic.[1] At over 9,400,000 square kilometres (3,600,000 sq mi), it covers most of North Africa, making it almost as large as China or the United States. The Syrian Desert (Arabic: ال شام ب ادي ة, bādiyat ash-shām), also known as the Syro-Arabian desert is a combination of steppe and true desert that is located in the northern Arabian Peninsula covering 200,000 square miles (over 500,000 square kilometers) of the region of Syria. The desert is very rocky and flat