Supplementary Tables - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement
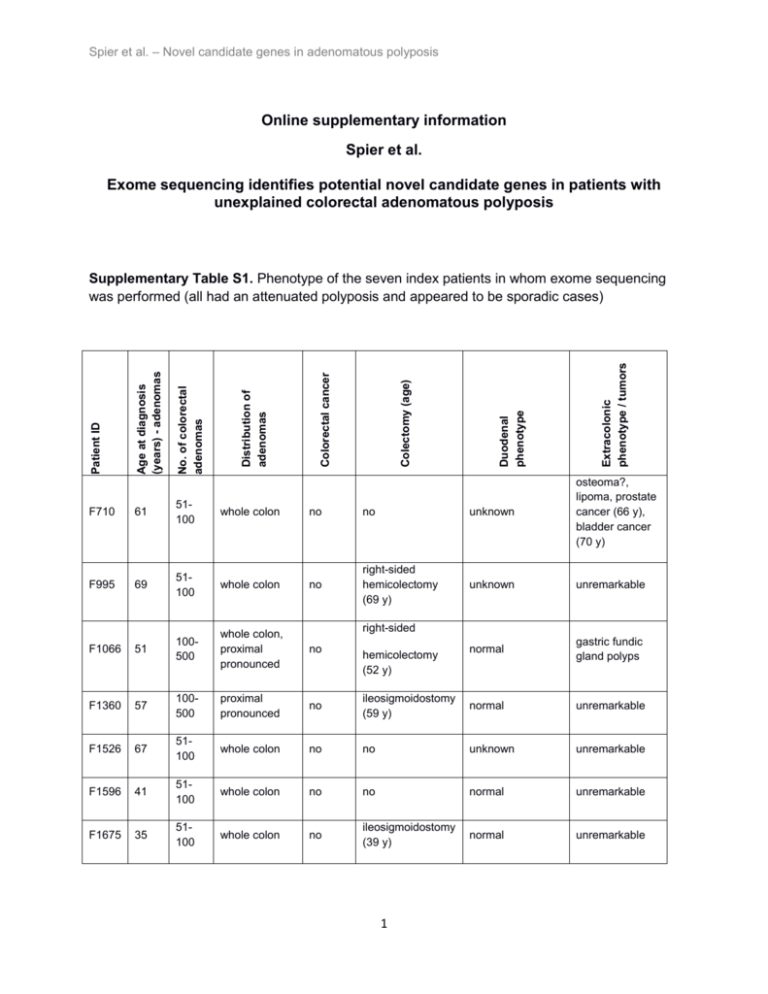
Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis Online supplementary information Spier et al. Exome sequencing identifies potential novel candidate genes in patients with unexplained colorectal adenomatous polyposis Extracolonic phenotype / tumors Duodenal phenotype Colectomy (age) Colorectal cancer Distribution of adenomas No. of colorectal adenomas Age at diagnosis (years) - adenomas Patient ID Supplementary Table S1. Phenotype of the seven index patients in whom exome sequencing was performed (all had an attenuated polyposis and appeared to be sporadic cases) F710 61 51100 whole colon no no unknown osteoma?, lipoma, prostate cancer (66 y), bladder cancer (70 y) F995 69 51100 whole colon no right-sided hemicolectomy (69 y) unknown unremarkable F1066 51 100500 whole colon, proximal pronounced no normal gastric fundic gland polyps F1360 57 100500 proximal pronounced no ileosigmoidostomy (59 y) normal unremarkable F1526 67 51100 whole colon no no unknown unremarkable F1596 41 51100 whole colon no no normal unremarkable F1675 35 51100 whole colon no ileosigmoidostomy (39 y) normal unremarkable right-sided hemicolectomy (52 y) 1 Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis Supplementary Table S2. Clinical characteristics of the validation cohort (n=191) FAP No. of patients 191 Gender (female / male) 83 / 108 Mean age at diagnosis (years) Range (years) 45 12-78 No. of colorectal adenomas < 100 adenomas 118 (62%) > 100 adenomas 31 (16%) numerous 15 (8%) multiple 27 (14%) Colorectal cancer 64 (34%) Extracolonic benign lesions * 22 (12%) Extracolonic malignancies 11 (6%) Family history ** Familial 26 (14%) Sporadic 88 (46%) Unclear (sporadic/familial) 73 (38%) Unknown 4 (2%) * gastric fundic gland polyps, congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE), desmoids, osteomas ** family history refers to the presence of colorectal polyposis in the relatives of colorectal adenomatous polyposis patients (FAP) 2 Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis Supplementary Table S3. Overall performance of the enrichment and Next Generation Sequencing process Exome sequencing of leukocyte DNA (n=7) Target size Exome sequencing of polyp DNA (n=12) 51.5 Mb (51542852 bp) Number of target regions 471155 Targeted sequencing of leukocyte DNA (validation cohort, n=191)* 0.6 Mb (622657 bp) 2163 Total reads** 80.13 million (+/- 53%) 60.09 million (+/- 35%) 3.98 million (+/- 14%) Unique mapped reads** 62.11 million (+/- 58%) 45.44 million (+/- 34%) 3.67 million (+/- 14%) GC drop out*** 16.5% (+/- 5.1%) 9% (+/- 7.4%) 2.2% (+/- 0.1%) AT drop out*** 0.2% (+/- 0.2%) 2.8% (+/- 4%) 11.6% (+/- 1.5%) Median library insert size*** 207 (+/- 58) 157 (+/- 13) 244 (+/- 6) Read length 101 (paired end) Mean on-target coverage*** 57 (+/- 31) 51 (+/- 27) 304 (+/- 44) Targets covered at depths of 10x Targets covered at depths of 20x Targets covered at depths of 30x 83.0% 80.0% 97.7% 70.0% 64.0% 96.6% 59.0% 51.0% 95.6% * the enrichment assay included a total of 140 genes, 3 of which are of relevance to the present study ** mean of each sample +/- relative standard deviation *** mean of each sample +/- absolute standard deviation 3 Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis Supplementary Table S4. Screening for the germline mutations identified in the present study in the corresponding polyp samples (“T”). T1 ZSWIM7:c.231_232del; p.Cys78Phefs*21 T2 (homozygous) T3 yes % mutant reads (number of mutant reads / coverage) 100 (27/27) yes 94 (16/17) yes 61 (28/46) DSC2: c.2686_2687dupGA; p.Ala897Lysfs*4 T1 yes 40 (18/45) T4 yes 41 (24/58) T1 PIEZO1: c.5289C>G;p.Tyr1763* T2 yes yes 50 (1/2) 71 (5/7) Patient Mutation ID F710 F995 F1526 Polyp Mutation confirmed sample in polyp sample? ID 4 Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis Supplementary Table S5. Additional information for potential pathogenic mutations identified in exome sequencing patients (n=7, shown in bold) and the validation sample (n=191). With the exception of the mutation in ZSWIM7, all mutations were heterozygous. Gene DSC2 Patient Mutation ID Type Remarks Variation Phenotype Family history Segregation F386; F929 COSMIC: 1x in large intestine, 1x in hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue); same mutation in missense patients with cardiomyopathy [1, 2]; Cadherin tandem repeat domain F386: typical (+ duodenal adenomas, osteomas, fibromas); F929: atypical F386: familial (son, daughter, sister and her son with polyps, father gastric cancer); F929: Unclear F386: no (affected sister and daughter don´t carry the mutation) F995+F1360: attenuated; F807: typical (+duodenal adenomas, retroperitoneal fibrosis) F995+F1360: unclear; F807: familial (father CRC, grandfather polyps, son polyps) F807: ? (both sons carry the mutation, one is affected, the other was not affected at the age of 24 y) c.907G>A; p.Val303Met same mutation in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy [3-5]; only 7 codons in front of regular stop codon DSC2 F995; c.2686_2687dupGA; F1360; p.Ala897Lysfs*4 F807 ins DSC2 F998 c.2701A>G;p.Arg901Gly missense penultimate codon attenuated familial? (mother CRC (61 y), deceased) not possible PIEZO1 F906 c.2104C>T;p.His702Tyr missense attenuated unclear not possible PIEZO1 F1899 c.3021C>G;p.Ile1007Met missense attenuated sporadic not possible F1909 COSMIC: mutation in adjacent codon c.5134G>A;p.Val1712Met missense (c.5131C>T;p.P1711S) in large intestine attenuated sporadic not possible PIEZO1 5 Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis PIEZO1 F1526 c.5289C>G;p.Tyr1763* PIEZO1 F1445 ZSWIM7 F710 stop 759 codons before regular stop codon attenuated sporadic not possible c.5863C>T;p.Arg1955Cys missense attenuated sporadic not possible c.231_232del; p.Cys78Phefs*21 (homozygous) attenuated unclear not possible del 6 Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis Supplementary Table S6. List of genes, which were screened for somatic mutations in adenoma samples Gene NCBI transcript ID APC NM_000038.5 BMPR1A NM_004329.2 BRAF NM_004333.4 CTNNB1 NM_001098210.1 EGFR NM_005228.3 FBXW7 NM_033632.3 KRAS NM_033360.2 MAP2K4 NM_003010.2 MLH1 NM_000249.3 MSH2 NM_000251.2 MSH6 NM_000179.2 NRAS NM_002524.4 PDGFRA NM_006206.4 PIK3CA NM_006218.2 PIK3R1 NM_181523.2 PMS2 NM_000535.5 POLD1 NM_002691.3 POLE NM_006231.2 PTEN NM_000314.4 SMAD4 NM_005359.3 STK11 NM_000455.4 TP53 NM_000546.5 7 Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis Supplementary Table S7. Histological findings of all polyp samples (“T”) and results of screening for somatic mutations in known cancer genes (cf. Supplementary Table S6). ND = not detectable. Polyp Patient sample Histology ID ID T1 F710 T2 T3 T1 tubular adenoma hyperplastic polyp? / tubular adenoma? tubular adenoma Grade of Gene dysplasia Somatic mutation % mutant reads (number of mutant reads / coverage) low grade CTNNB1 c.490G>A; p.Asp164Asn 29 (6/21) Deleterious / benign c.3469G>T; p.Glu1157* 16 (5/31) - 42 (11/26) - 32 (18/57) - 42 (26/62) - 41 (37/91) - APC low grade ND mainly low APC tubulovillous grade, adenoma partly high APC grade APC F995 T4 tubulovillous low grade adenoma APC FBXW7 T1 F1066 T2 KRAS tubular adenoma low grade tubular adenoma low grade KRAS TP53 APC T1 tubular adenoma low grade T2 T1 F1675 APC MSH2 F1526 T2 T3 tubular adenoma tubular adenoma tubular adenoma tubular adenoma In silico prediction tools (SIFT / PolyPhen2) APC low grade MSH2 c.2626C>T; p.Arg876* c.4612delG; p.Glu1538Asnfs*27 c.3049delA; p.Asn1017Metfs*5 c.4385_4386delAG; p.Ser1465Trpfs*3 c.1393C>T; p.Arg465Cys c.38G>A; p.Gly13Asp c.804C>G; p.Asn268Lys c.35G>A; p.Gly12Asp c.694C>T;p.Arg232* c.4221delT; p.Ser1407Argfs*8 c.589A>G; p.Lys197Glu c.4233delT; p.Ser1411Argfs*4 c.589A>G; p.Lys197Glu 42 (28/67) Deleterious / prob. dam. Deleterious / poss. dam. Deleterious / prob. dam. Deleterious / benign - 37 (30/82) - 48 (23/48) Deleterious / prob. dam. 30 (27/90) - 35 (49/139) 17 (32/184) 11 (6/55) 22 (46/211) 39 (29/74) low grade CTNNB1 c.97T>C;p.Ser33Pro 20 (6/30) low grade Deleterious / prob. dam. Deleterious / prob. dam. ND low grade CTNNB1 c.104T>G;p.Ile35Ser 44 (17/39) 8 Deleterious / prob. dam. Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis Suppl. Fig. S1 (a) Heterozygous DSC2 germline mutation c.2686_2687dupGA;p.Ala897Lysfs*4 in patient F995 (exome sequencing data, reverse sequence). (b) Sanger sequencing of the corresponding region (reverse sequence). 9 Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis Suppl. Fig. S2 (a) Homozygous ZSWIM7 mutation c.231_232del;p.Cys78Phefs*21 in patient F710 (exome sequencing data, reverse sequence). (b) Sanger sequencing of corresponding region (reverse sequence). 10 Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis Suppl. Fig. S3 (a) PIEZO1 mutation c.5289C>G;p.Tyr1763* in patient F1526. The variant seemed to be homozygous in exome sequencing data with low read depth of 7x (reverse sequence). (b) Sanger sequencing of corresponding region revealing the mutation as heterozygous (reverse sequence). 11 Spier et al. – Novel candidate genes in adenomatous polyposis REFERENCES 1. Garcia-Pavia P, Syrris P, Salas C, Evans A, Mirelis JG, Cobo-Marcos M, Vilches C, Bornstein B, Segovia J, Alonso-Pulpon L, Elliott PM: Desmosomal protein gene mutations in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy undergoing cardiac transplantation: a clinicopathological study. Heart (British Cardiac Society) 2011, 97(21):1744-1752. 2. Andreasen C, Nielsen JB, Refsgaard L, Holst AG, Christensen AH, Andreasen L, Sajadieh A, Haunso S, Svendsen JH, Olesen MS: New population-based exome data are questioning the pathogenicity of previously cardiomyopathy-associated genetic variants. Eur J Hum Genet 2013, 21(9):918-928. 3. Syrris P, Ward D, Evans A, Asimaki A, Gandjbakhch E, Sen-Chowdhry S, McKenna WJ: Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy associated with mutations in the desmosomal gene desmocollin-2. Am J Hum Genet 2006, 79(5):978-984. 4. De Bortoli M, Beffagna G, Bauce B, Lorenzon A, Smaniotto G, Rigato I, Calore M, Li Mura IE, Basso C, Thiene G, Lanfranchi G, Danieli GA, Nava A, Rampazzo A: The p.A897KfsX4 frameshift variation in desmocollin-2 is not a causative mutation in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Eur J Hum Genet 2010, 18(7):776782. 5. Fressart V, Duthoit G, Donal E, Probst V, Deharo JC, Chevalier P, Klug D, Dubourg O, Delacretaz E, Cosnay P, Scanu P, Extramiana F, Keller D, Hidden-Lucet F, Simon F, Bessirard V, Roux-Buisson N, Hebert JL, Azarine A, Casset-Senon D, Rouzet F, Lecarpentier Y, Fontaine G, Coirault C, Frank R, Hainque B, Charron P: Desmosomal gene analysis in arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy: spectrum of mutations and clinical impact in practice. Europace : European pacing, arrhythmias, and cardiac electrophysiology : journal of the working groups on cardiac pacing, arrhythmias, and cardiac cellular electrophysiology of the European Society of Cardiology 2010, 12(6):861-868. 12