INSTRUCTIONS TO AUTHORS FOR THE PREPARATION
advertisement
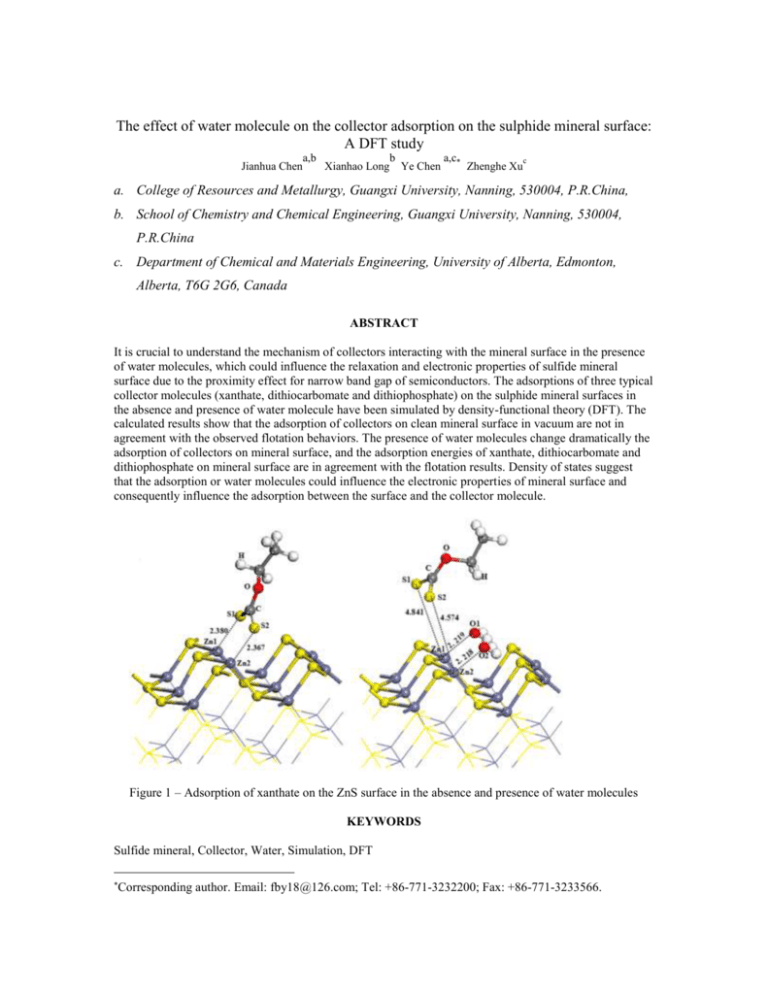
The effect of water molecule on the collector adsorption on the sulphide mineral surface: A DFT study Jianhua Chen a,b b a,c c Xianhao Long Ye Chen Zhenghe Xu a. College of Resources and Metallurgy, Guangxi University, Nanning, 530004, P.R.China, b. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning, 530004, P.R.China c. Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, T6G 2G6, Canada ABSTRACT It is crucial to understand the mechanism of collectors interacting with the mineral surface in the presence of water molecules, which could influence the relaxation and electronic properties of sulfide mineral surface due to the proximity effect for narrow band gap of semiconductors. The adsorptions of three typical collector molecules (xanthate, dithiocarbomate and dithiophosphate) on the sulphide mineral surfaces in the absence and presence of water molecule have been simulated by density-functional theory (DFT). The calculated results show that the adsorption of collectors on clean mineral surface in vacuum are not in agreement with the observed flotation behaviors. The presence of water molecules change dramatically the adsorption of collectors on mineral surface, and the adsorption energies of xanthate, dithiocarbomate and dithiophosphate on mineral surface are in agreement with the flotation results. Density of states suggest that the adsorption or water molecules could influence the electronic properties of mineral surface and consequently influence the adsorption between the surface and the collector molecule. Figure 1 – Adsorption of xanthate on the ZnS surface in the absence and presence of water molecules KEYWORDS Sulfide mineral, Collector, Water, Simulation, DFT Corresponding author. Email: fby18@126.com; Tel: +86-771-3232200; Fax: +86-771-3233566.