Nagel Social Studies Unit 1
advertisement

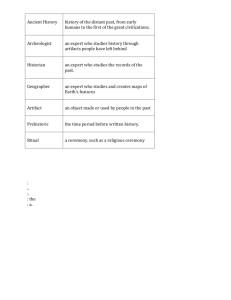
Social Studies Grade 6 Unit 1 Unit 1- Human Beginnings Essential Standards – H.1.3, H.2.3, G&EL.1.1, G&EL.1.2, G&EL.1.3, G&EL.1.4, G&EL.2.1, C&G.1.1, C&G.1.4, E&FL.1.1, E&FL.1.2, C.1.1, C.1.3 HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY CULTURE Unit Overview In this unit, students will examine the origins of human society. Students should develop an understanding of the role of paleontologists, archaeologists, and anthropologists in the context of social studies and prehistory. Students should be able to analyze the origins of human society and trace its transition from nomadic hunter-gatherer cultures to agrarian civilizations, including the introduction and subsequent developments of tools and agricultural technology. Generalizations 1. Anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists work together to create our understanding of prehistoric cultures since the defining trait of prehistory is its lack of a writing system. 2. The development and use of tools enabled the nomadic hunter-gatherers to settle into a more agrarian civilization, which in turn led to the creation of villages and permanent settlements. 3. Essential resources such as access to food, water, and shelter are necessary for a society to thrive. Essential Questions 1. What is social studies? Why do we study it? 2. How do anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists work together to create our modern understanding of the prehistoric era? 3. How did the development of tools lead to more stable societies? 4. What caused the transition from nomadic societies to agrarian civilizations? 5. What are the most essential resources for a society to thrive? 6. How are the Stone and Bronze Ages similar and different? 7. How are Cro-Magnons and Neanderthals similar and different? 8. What is the Neolithic Revolution, and how did it impact the cultures of the Prehistoric Era? Unit Vocabulary Agrarian Homo sapiens Nomadic Anthropologist Human community Origin Archaeologist Hunter-gatherer Paleolithic cave painting Artifact Ice Age Paleontologist Bronze Age Innovation Prehistoric Clovis Location Resources Cro-Magnon Migration Scarcity Decline Neanderthal Social studies Hominid Neolithic Revolution Stone Age Donald Johanson Lucy Key People Mary and Louis Leakey Unit 4 Classical Civilizations 1 Social Studies Grade 6 Unit 1 Unit 1- Goals What do students need to KNOW? What do students need to be able to DO? A working definition of social studies Define “social studies” The reasons we study history Explain the reasons for studying history What anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists do How anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists work together to create an understanding of a prehistoric culture Explain what anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists do Analyze how they work together to create an understanding of a prehistoric culture Identify the tools developed during the Prehistoric Era Analyze the impact of tool development and use on the cultures of that time period Explain why many nomadic societies settled into agrarian civilizations The timeline of tool development from the Prehistoric Era The impact of tool development and use on the cultures of that time period Why many nomadic societies settled into agrarian civilizations The essential resources necessary for a society to thrive The defining characteristics of the Stone Age and the Bronze Age Identify the essential resources necessary for a society to thrive The defining characteristics of Cro-Magnons and Neanderthals Identify the characteristics of the Stone Age and the Bronze Age The causes and effects of the Neolithic Revolution Compare and contrast the Cro-Magnons and Neanderthals Analyze the causes and effects of the Neolithic Revolution I Can… Statements I Can… define “social studies.” I Can… explain the reasons we study history. I Can… explain what anthropologists, archaeologists, and paleontologists do. I Can… analyze how these people work together to create an understanding of a prehistoric culture. I Can… identify the tools developed during the Prehistoric Era. I Can… analyze the impact of tool development and use on the cultures of that time period. I Can… explain why many nomadic societies settled into agrarian civilizations. I Can… identify the essential resources necessary for a society to thrive. I Can… identify the characteristics of the Stone Age and the Bronze Age. I Can… compare and contrast the Cro-Magnons and Neanderthals. I Can… analyze the causes and effects of the Neolithic Revolution. Unit 4 Classical Civilizations 2 Social Studies Grade 6 Unit 1 Unit 1- Essential Standards HISTORY H.1.3 Use primary and secondary sources to interpret various historical perspectives. H.2.3 Explain how innovation and/or technology transformed civilizations, societies, and regions over time (e.g., agricultural technology, weaponry, transportation, and communication). GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY G&EL.1.1 Explain how the physical features and human characteristics of a place influenced the development of civilizations, societies, and regions (e.g., location near rivers and natural barriers, trading practices, and spread of culture). G&EL.1.2 Explain the factors that influenced the movement of people, goods, and ideas and the effects of that movement on societies and regions over time (e.g., scarcity of resources, conquests, desire for wealth, disease, and trade). CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT C&G.1.1 Explain the origins and structures of various governmental systems (e.g. democracy, absolute monarchy and constitutional monarchy). C&G.1.4 Compare the role (e.g. maintain order and enforce societal values and beliefs) and evolution of laws and legal systems (e.g. need for and changing nature of codified system of laws and punishment) in various civilizations, societies and regions. ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY E&FL.1.1 Explain how conflict, compromise, and negotiation over the availability of resources (natural, human and capital) impacted the economic development of various civilizations, societies and regions (e.g. competition for scarce resources, unequal distribution of wealth and the emergence of powerful trading networks). E&FL.1.2 Explain how quality of life is impacted by economic choices of civilizations, societies and regions. CULTURE C.1.1 Analyze how cultural expressions reflected the values of civilizations, societies and regions (e.g., oral traditions, art, dance, music, literature, and architecture). C.1.3 Summarize systems of social structure within various civilizations and societies over time (e.g. Roman class structure, Indian caste system and feudal, matrilineal and patrilineal societies). G&EL.1.3 Compare distinguishing characteristics of various world regions (e.g., physical features, culture, political organization, and ethnic make-up). G&EL.1.4 Explain how and why civilizations, societies and regions have used, modified and adapted to their environments (e.g., invention of tools, domestication of plants and animals, farming techniques and creation of dwellings). G&EL.2.1 Use maps, charts, graphs, geographic data and available technology tools to draw conclusions about the emergence, expansion, and decline of civilizations, societies, and regions. Academic Vocabulary: agrarian, artifact, Stone Age, Bronze Age, Neolithic Revolution, anthropologist, archaeologist, paleontologist Unit 4 Academic Vocabulary: resources, agrarian, hunter-gatherer, nomadic, Neolithic Revolution, migration, location, scarcity Academic Vocabulary: agrarian civilization, nomadic culture Classical Civilizations Academic Vocabulary: domestication, innovation, scarcity Academic Vocabulary: cuneiform, domestication, agricultural innovation, resources, cave paintings, community, artifact 3 Social Studies Grade 6 Unit 1 Unit 1- Common Core Standards READING WRITING CMS CCSS Power Standards: CMS CCSS Power Standards: R.6-8.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources. W.6-8.1 Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. R.6-8.10 Read and comprehend history/social studies texts in the grade 6 text complexity band independently and proficiently. W.6-8.2 Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes. Additional Reading Standards: Additional Writing Standards: R.6-8.2. Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of the source distinct from prior knowledge or opinions. W.6-8.4 Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. R.6-8.6 Identify aspects of a text that reveal an author’s point of view or purpose (e.g., loaded language, inclusion or avoidance of particular facts). R.6-8.7 Integrate visual information (e.g., in charts, graphs, photographs, videos, or maps) with other information in print and digital texts. W.6-8.5 With some guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on how well purpose and audience have been addressed. W.6-8.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. R.6-8.8 Distinguish among fact, opinion, and reasoned judgment in a text. R.6-8.9 Analyze the relationship between a primary and secondary source on the same topic. Unit 4 Classical Civilizations 4 Social Studies Grade 6 Unit 1 Unit 1- Concepts with Subtopics Aligned to Unit Generalizations HISTORY GEOGRAPHY & ENVIRONMENTAL LITERACY CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL LITERACY H.1.3, H.2.3 G&EL.1.1, G&EL.1.2, G&EL.1.3, G&EL.1.4, G&EL.2.1 C&G.1.1, C&G.1.4 E&FL.1.1, E&FL.1.2 Time: Era 1-2, may touch the beginning of Era 3 Ice Age Stone Age Bronze Age Paleolithic Mesolithic Neolithic Location: (absolute and relative) Olduvai Gorge Africa Fertile Crescent Asia Europe Indus River Valley Yellow River Valley Leadership: Government Structure: Military Innovation: Citizenship: Rules and Laws: Historical Figures: Mary Leakey Louis Leakey Place: (physical & human characteristics) Fertile soil Mountainous Access to resources River valleys Economic Development Division of labor Trade Development of agriculture Population growth Access to resources leading to exploration, conquest, and settlement Technological Developments: Agricultural Tools Communication Cultural Developments: Nomadic cultures Agrarian cultures Connections to Today: Archaeologists Paleontologists Anthropologists Natural Resources: Stone Bronze Wood Metal Water Animals Food sources—huntergatherer to agrarian Irrigation Agriculture The need for all these things stems from the development of permanent civilizations: As people live together in closer proximity and as population grows due to agricultural and technological developments, communities expand and eventually develop the need for leaders, social structures, military, citizenship, and rules and laws. Quality of Life Population growth Surplus of food due to agricultural developments CULTURE C.1.1, C.1.3 People: Cro-Magnon Neanderthal Hominids Lucy Australopithecine Homo habilis Homo erectus Homo sapiens Cultural Expression: Cave paintings Artifacts Tools Religion Art Social Structure Settling of nomadic cultures into agrarian civilizations Division and specialization of labor Formalized religion Movement: Nomads Hunter-gatherer Neolithic Revolution Migration settlement Unit 4 Classical Civilizations 5 Social Studies Grade 6 Unit 1 Unit 1- Assessment Options: W1- Literacy Common Core Power Standard: Writing Arguments Choose the resource that you think is most important for a society to continue to thrive. Write a paragraph from the point of view of that resource. The paragraph should justify why you as the resource are more essential to a society than other resources. Use a minimum of three accurate details that support your claim based on informational texts (pictures, maps, articles, artifacts and primary sources). W2- Literacy Common Core Power Standard: Writing Informative Texts Create a comic strip that illustrates the transition from nomadic societies to permanent communities. Demonstrate the causes for this transition by including relevant information about environment, tools, geography and people based on informational text (pictures, maps, political cartoons, artifacts, articles and primary sources). R1/R10- Literacy Common Core Power Standard: Reading Closely Over Time with a Variety of Texts Pictures of tools and cave paintings, available in the History Alive! Resource materials Newspaper articles about the discoveries at Olduvai Gorge Unit 4 Classical Civilizations 6