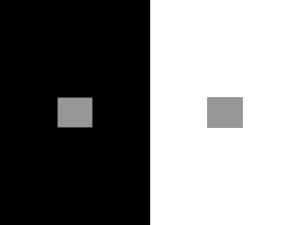PSYC2071 Week 8 Lecture notes A Visual Processing The
advertisement

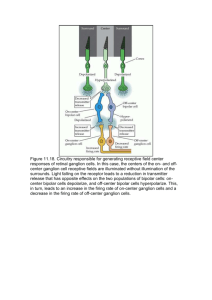
PSYC2071 Week 8 Lecture notes A Visual Processing The organization of visual in brain Parallel and hierarchical processing- in the parallel processing streams, there are sequential processing steps following a modular hierarchy. Image-based stage –Early processing: Each photoreceptor generates electrical current proportional to the amount of light falling on it. Surface Based Stage –Intermediate processing: our perceptual system is actually geared to pay attention to surfaces. This is how we arrive to our judgment of the object. Object/Category Based Stage –Late processing: Retina are a layer of matter in the eye that focus light to the photoreceptors, fovea is the only part in the eye that allows lights to hit photoreceptors directly Organisation of the Retina Optic disk is one of the most important parts of the retina, it doesn’t have any photoreceptors. It also associates with the blind spots. There are processing in the brain that fills out missing information created by blind spots. After the photoreceptors layer (Input Layer), we have bipolar cells layer (middle Processing Layer), then retinal Ganglion cells layer (Output Layer), this is known as the vertical pathways of retina. Everything in visual are made up by Modules, in the input layer there are Rod and Cone modules. In the middle processing layer it is also classified as On pathway and Off pathway (Bipolar cells). Only On pathway will be responded if lights go brighter, and Off pathway only if lights go dimmer. In the output layer, we have Magno Ganglion Cells module and Parvo Ganglion Cells module. Retinal is a light sensitive molecule A large protein Opsin is presented in both Cones (Active only during day) that produces photopsin and Rodes (Active only during night) that produces scotopsin. It is extremely hard to have both working in the same time (mesopic) Retinal Cones are divided into Red Green and Blue Visual Pigment Bleaching and Regeneration (When exposed to bright light, the ability for the eye to absorb light decreases) Cone Pigment regenerates in 6 minutes Rod Pigment takes over 30 minutes to regenerate Diseases that affect retina Macular degeneration Cholesterol builds up in the centre of your eye, fovea and small surrounding area are destroyed and it creates blind spot Retinitis pigmentosa Rods are destroyed first, night blindness. Next lecture we are going to talk about the selective types of degeneration. Lecture Notes B Middle Layer Half of Bipolar cells are specialized in increasing illuminant and half are specialized in decreasing illuminant. Bipolar cells are classified into Cone bipolar cells and Rod bipolar cells. Cone Pathway: Direct link to ganglion cells via midget and diffuse cone bipolar cells Rod Pathway: Rod bipolars: signals originating in rod photoreceptors reach the ganglion cells via an indirect route via the axon terminals of cone bipolar cells Peripheral Retinal Pathway will have convergence of 15-45 peripheral receptors to a single bipolar cell. Central Retinal Pathway will divergence, from each foveal cone to two bipolar cells. The greater convergence, the greater the overall sensitivity to light, such as the case in periphery. There is a trade off however, the resolution of telling which direction the information is coming from is weaker compare to divergence foveal cone, which is less sensitive. So far we been talking about vertical connections, there are also horizontal connections, they are providing inhibition of lateral. receptive field is very important to perceive the information as a whole, this is done through horizontal cells, which project information to each individual receptive field. • Center-Surround Receptive Fields of Ganglion Cells has Two types: – Excitatory-center-inhibitory surround: ON center-OFF surround – Inhibitory-center-excitatory surround: OFF center- ON surround they are an extension of on channel and off channel. For On center Ganglion cells, it will be extremely stimulated if light falls on it’s centre only, and no stimulation if the light falls on it’s surrounding only. And a moderate stimulation if the light covers the entire cell. For Off center Ganglion cells, the opposite happens, no stimulation if light hits centre only and extreme stimulation if light hits surroundings, and moderate stimulation if light covers the whole cell. This property of Ganglion cells ensured the spatial ability of human eyes. Lateral inhibition (above effect) provided excellent explanation to a lot of properties of human eyes such as brightness perception, the theory can be used to explain the phenomenon of Simultaneous Contrast where the two center squares reflect the same amount of light into your eyes but look different because of simultaneous contrast. It is seeing illusory brightness differences due to differences in the intensity of adjacent surrounding areas. Explained by the white surround generates more lateral inhibition, compared to the black surround The Hermann Grid where you see dark spots at an intersection of a black grid or white spot at the intersection of a white grid. Caused by superimposed surrounding of the cell to the dark boxes but not the cetre of the cell, thus causing the black spot. As well as Mach Bands, where we see the edge more sharply, such as on a color progressing picture we actually see the border of the color being darker than they really are. The edge of color means that some the surrounding field are not in the color when it’s outside the edge, that means the centre is more inhibited, makeing it more darker. Wertheimer-Benary Cross shows that we cannot just look at the theory, we need to take note that the brain functions affects our perception, the spatial belongingness that the brain recognizes the color to be in actually affect your color perception.