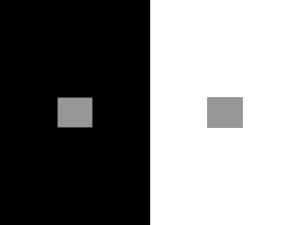Powerpoint file - How Your Brain Works
advertisement

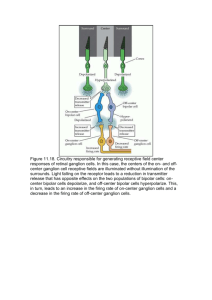
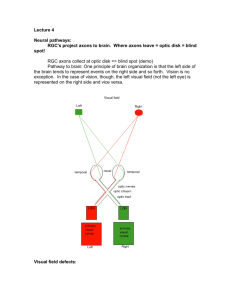
Seeing Things 1 Eye and Brain How Your Brain Works - Week 3 Dr. Jan Schnupp jan.schnupp@dpag.ox.ac.uk HowYourBrainWorks.net Light Wavelength A Optics of the Eye B Eye and Retina The Blind Spot Retinotopy • Adapted from drawings by Ramon y Cajal The Optic Pathway: eye, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract, thalamus, optic radiation, visual cortex Rene Descartes, Retinotopy and the Seat of the Soul Photoreceptors • The human eye has ca. 10 million rods and ca 120 million cones Phototransduction • Light activated rhodopsin (R) activates G-protein (G) which in turn activates phosphodiesterase (PDE) which cleaves cGMP which closes cGMP-gated Na+ channel. • What does any of this have to do with carrots? Absorption Spectra • The three different types of cones and the rods have slightly different opsins which are sensitive to different wavelengths. • “Trichromacy” theory. Sensitivity of Receptors Rod and Cone Distribution Retinal Wiring • Photoreceptors • Horizontal cells • Bipolar cells • Amacrine cells • Retinal ganglion cells Centre –Surround Receptive Fields Photoreceptors Horizontal Cell - - ++ + + -- - - Bipolar Cell Retinal Ganglion Cell On-centre and off-centre Receptive Fields • Lateral inhibition provided by photoreceptor ribbon synapses, horizontal cell synapses and amacrine cells Lateral inhibition for contrast (edge) detection RGC receptive fields as “spatial frequency filters” Difference of Gaussians Model of Retinal Ganglion Cells • The centre-surround structure of Retinal Ganglion Cells turns them into “spatial frequency filters”. Larger RGC receptive fields are tuned to “coarsely grained” structure in the visual scene, while smaller RFs are tuned to fine grain structure. Convolving a Penny with DoGs • The picture of an American cent (left) seen through large (middle) or small (right) difference of Gaussian receptive fields. The Fovea Eye muscles Eye movements • • Eye-movement traces while a subject explores a picture of the bust of Nefertiti. From "Eye Movements and Vision" by A. L. Yarbus; Plenum Press, New York; 1967 Dan Simmons’ visual attention task • Count the number of passes of the white team Colour opponency Colour Opponency The Colour Wheel Yellow-Blue Red Green Why Colour Vision Does Not Work Well in Poor Light surround centre Cone mosaics • Cone mosaics for four different individuals Colour blindness Red-green channel broken Blue-yellow channel broken M cells and P cells • 90% P cells • 5% M cells • 5% non-M non-P Projections to the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus The Stepping Feet Illusion • http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/mot_feet_lin /index.html • What is going on here? • M cells are colour blind, but very sensitive to brightness (luminance) contrast. • P cells are R-G opponent • Non-M non-P cells are Y-B opponent • Only M cells project to the motion processing streams in the brain.