Part I
advertisement
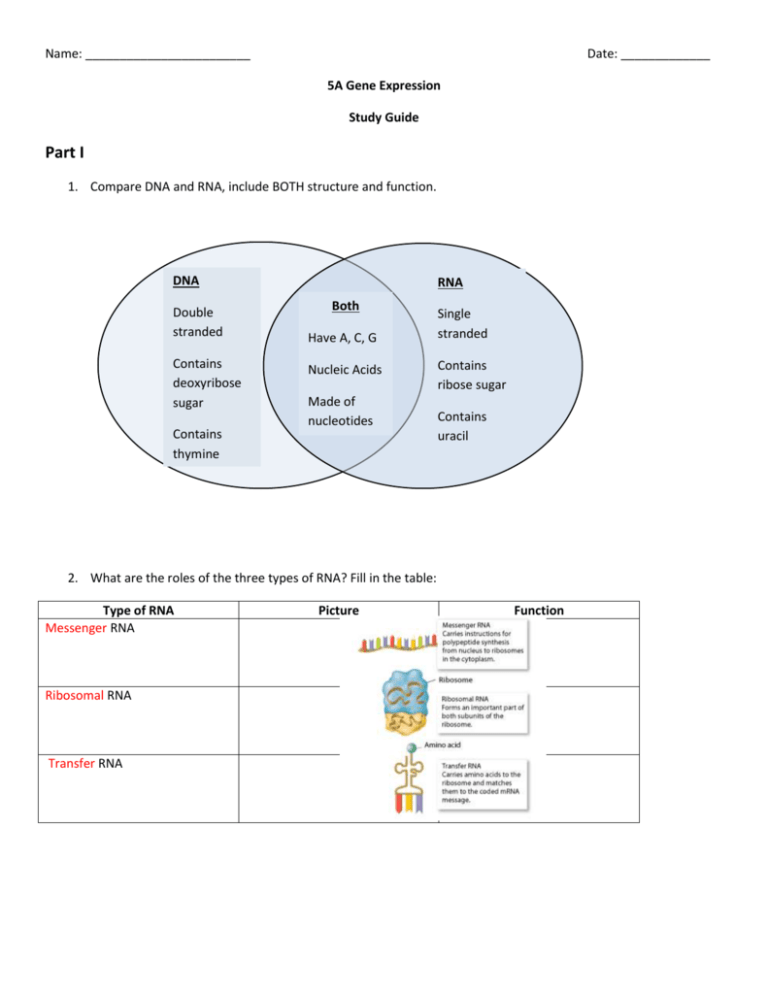
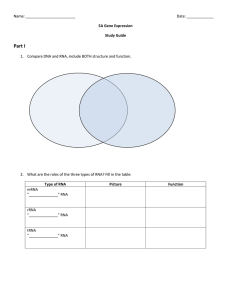
Name: ________________________ Date: _____________ 5A Gene Expression Study Guide Part I 1. Compare DNA and RNA, include BOTH structure and function. DNA Double stranded Contains deoxyribose sugar Contains thymine RNA Both Have A, C, G Nucleic Acids Made of nucleotides Single stranded Contains ribose sugar Contains uracil 2. What are the roles of the three types of RNA? Fill in the table: Type of RNA Messenger RNA Ribosomal RNA Transfer RNA Picture Function Use the following gene to complete the tasks below: DNA/gene T A C T T C G G A A T A G C A A C T Transcribe the gene into mRNA ____AUG___|____AAG____|____CCU_____|_____UAU____|______CGU___|____UGA___ Translate the mRNA into a polypeptide _____Met__|____Lys_____|_____Pro_____|_____Tyr_____|_____Arg_____|____stop____ What are the tRNA anticodons that match with the mRNA codons? _____UAC__|____UUC____|_____GGA_____|_____AUA___|_____GCA____|_____ACU__ 3. Complete the following table: Location Starting Molecule Product nucleus DNA mRNA Ribosome mRNA Polypeptide (protein) Transcription Translation 4. What enzyme allows for transcription to occur? ______RNA Polymerase______ 5. What is the first codon read on an mRNA strand called? __Start Codon___ What three letters make this codon? ____AUG____ 6. What is the codon called that tells the ribosome that the polypeptide is complete? ____Stop Codon___ 7. tRNAs bring in the correct amino acids according to the message in the mRNA. This happens because each tRNA has an ___anticodon____ that pairs with a specific ____codon____ on the mRNA. 8. What types of bonds connect the amino acids in the polypeptide? _____peptide_______ 9. Use the word bank to label the diagram below: mRNA tRNA start codon stop codon anticodon ribosome polypeptide tRNA polypeptide anticodon ribosome mRNA Start codon Stop codon 10. Think!! a. A mRNA strand with 66 nucleotides codes for a polypeptide __22___ amino acids in length. b. A protein 300 amino acids in length was made from an mRNA strand ___900____ nucleotides in length. Part II 1. What are the three types of gene mutations? __substitution, insertion, deletion__________________________ 2. Create each of the gene mutations one at a time using the gene below. EACH TIME MAKE THE MUTATION AT THE 4TH BASE. Show how it will affect the resulting polypeptide. Original Gene: TAC GTG AAC GCA Transcribe the original: AUG CAC UUG CGU Translate the original: His Leu Arg Met Substitution Insertion Deletion Gene with mutation Resulting mRNA Resulting polypeptide 3. Which two gene mutations are frameshift mutations? ___insertion and deletion_____________________ 4. Why are these more problematic types of mutations? ____These shift all the nucleotides over, and change all the codons after the mutation, therefore changing all the amino acids in the resulting polypeptide. ___________ 5. Describe each of the chromosomal mutations shown below: - ___A section of the chromosome is missing____ -___A section of a chromosome is copied twice (doubled)____________________________ -____Two sections of a chromosome switch places_________________________ -____A section or sections of one chromosome moves to another chromosome__________ 6. Why can some mutations be helpful, others harmful, and others make no difference at all? ____Helpful mutations lead to better functioning proteins, harmful mutations lead to non-functioning proteins, mutations in the third nucleotide of a triplet can potentially have no effect on the protein if the codon still translates to the same amino acid. ____________________________________________________________ 7. Roughly how much of the DNA codes for protein? ___2%__What is the rest of the DNA called? _Non-coding___ 8. What does it mean for a certain gene to be “turned on”? ______If a gene is turned on it is actually being expressed, meaning that its message will be transcribed and translated into a protein. _____________ 9. Turning on and off genes allows cells to ___specialize_________ (have a certain job role).