View
advertisement

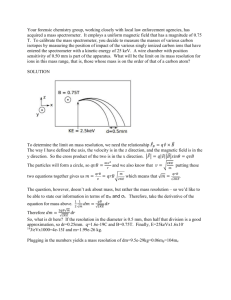
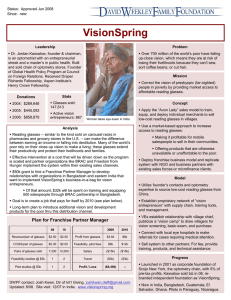
Magnetic properties of Fe2O3 -TeO2 - Bi2O3 glasses P. Sandhya Rani and R.Singh* School of Physics, University of Hyderabad, Central University P.O., Hyderabad 500046, India *corresponding author email : rsinghsp@gmail.com, Tel.: +9140 2313 4321; Fax: +9140 23010227 Abstract The glasses of composition 20Fe2O3 - (80-x)TeO2-xBi2O3 (x= 0-20mol %) were prepared by melt quenching method. Electron spin resonance (ESR) and magnetization measurements indicate the existence of short range antiferromagnetic (AFM) interactions between Fe ions which increases with increase in Bi2O3 content in these glasses. Keywords: Oxide glasses, Electron Spin Resonance , magnetic interactions, susceptibility. Introduction The study of the magnetic properties of oxide glasses with transition metal (TM) ions gives useful information on the valence states and magnetic interactions between TM ions in a vitreous matrix, as well as on the distribution mode of magnetic ions in the glass network. Electron spin resonance (ESR) spectra show distinct resonance lines for the paramagnetic ions involved in structural units of well-defined symmetry and those connected in clusters [1]. Experimental The glasses of composition 20Fe2O3 - (80-x)TeO2xBi2O3 (x = 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 mol %) were synthesized by melt quenching method. Amorphous nature of the ascast samples was confirmed from XRD studies. The ESR spectra of the samples were recorded on Joel XBand ESR spectrometer. The magnetization (M) measurements were done using model 7400 Lake Shore Cryotronics Magnetometer. Fig.1.ESR spectra for the glass samples at room temperature (293K). fig.2. Two straight lines fit as per Curie-Weiss law with change of slope at ~ 200K are obtained. The Curie temperature (θc) is negative for both the linear fit regions. The lower value of θc are obtained for Bi2O3 doped glasses in 80 < T < 200 temperature range. The data indicates that magnetic interactions between the iron ions in the present glasses are predominantly antiferromagnetic. The interaction increases with the addition of Bi2O3 in the glass matrix. However, as the temperature decreases below 200 K the interaction weakens in the Bi2O3 doped glasses. Results and discussion Fig 1 shows ESR spectra of the present glass system at room temperature. All the compositions show broad resonance centered at g ~ 2.0 with resonance line width ΔHpp = 325 ± 25 mT. The intensity J (≈ I∆HPP2) of ESR signal decrease with increase in Bi2O3 content. With the addition of Bi2O3, the Fe3+ ions convert into Fe2+ ions leading to increased antiferromagnetic interaction and decrease in J value. In these glasses the isolated Fe ions are not detected. All Fe ions are coupled antiferromagnetically in the form of clusters (dimers or triads). The addition of Bi2O3 does not change the cluster formation and create isolated Fe ions. The M and susceptibility (χ) decrease with increase in Bi2O3 content The inverse of susceptibility (-1) versus T plots for various glass samples are shown in Fig.2. H/M vs. T plots for the glass samples. References [1] P. Sandhya Rani and R. Singh, Electron spin resonance and magnetization studies of ZnO-TeO2Fe2O3 glasses, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 74 (2013) 338343.