Name Definition How does this event occur? What are the hazards
advertisement
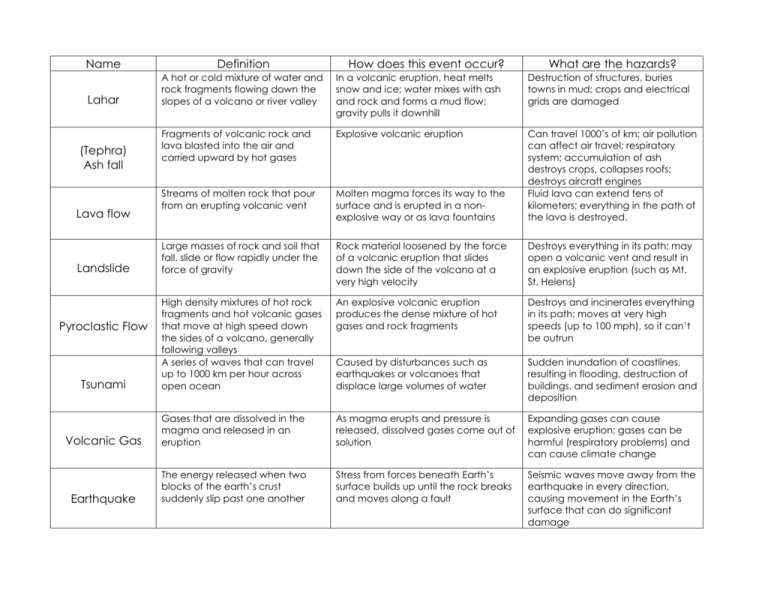
Name Definition Lahar A hot or cold mixture of water and rock fragments flowing down the slopes of a volcano or river valley In a volcanic eruption, heat melts snow and ice; water mixes with ash and rock and forms a mud flow; gravity pulls it downhill Destruction of structures, buries towns in mud; crops and electrical grids are damaged Fragments of volcanic rock and lava blasted into the air and carried upward by hot gases Explosive volcanic eruption Streams of molten rock that pour from an erupting volcanic vent Molten magma forces its way to the surface and is erupted in a nonexplosive way or as lava fountains Can travel 1000’s of km; air pollution can affect air travel; respiratory system; accumulation of ash destroys crops, collapses roofs; destroys aircraft engines Fluid lava can extend tens of kilometers; everything in the path of the lava is destroyed. Large masses of rock and soil that fall, slide or flow rapidly under the force of gravity Rock material loosened by the force of a volcanic eruption that slides down the side of the volcano at a very high velocity Destroys everything in its path; may open a volcanic vent and result in an explosive eruption (such as Mt. St. Helens) High density mixtures of hot rock fragments and hot volcanic gases that move at high speed down the sides of a volcano, generally following valleys A series of waves that can travel up to 1000 km per hour across open ocean An explosive volcanic eruption produces the dense mixture of hot gases and rock fragments Destroys and incinerates everything in its path; moves at very high speeds (up to 100 mph), so it can’t be outrun Caused by disturbances such as earthquakes or volcanoes that displace large volumes of water Sudden inundation of coastlines, resulting in flooding, destruction of buildings, and sediment erosion and deposition Volcanic Gas Gases that are dissolved in the magma and released in an eruption As magma erupts and pressure is released, dissolved gases come out of solution Expanding gases can cause explosive eruption; gases can be harmful (respiratory problems) and can cause climate change Earthquake The energy released when two blocks of the earth’s crust suddenly slip past one another Stress from forces beneath Earth’s surface builds up until the rock breaks and moves along a fault Seismic waves move away from the earthquake in every direction, causing movement in the Earth’s surface that can do significant damage (Tephra) Ash fall Lava flow Landslide Pyroclastic Flow Tsunami How does this event occur? What are the hazards?