Gilberts: Renal Function
advertisement
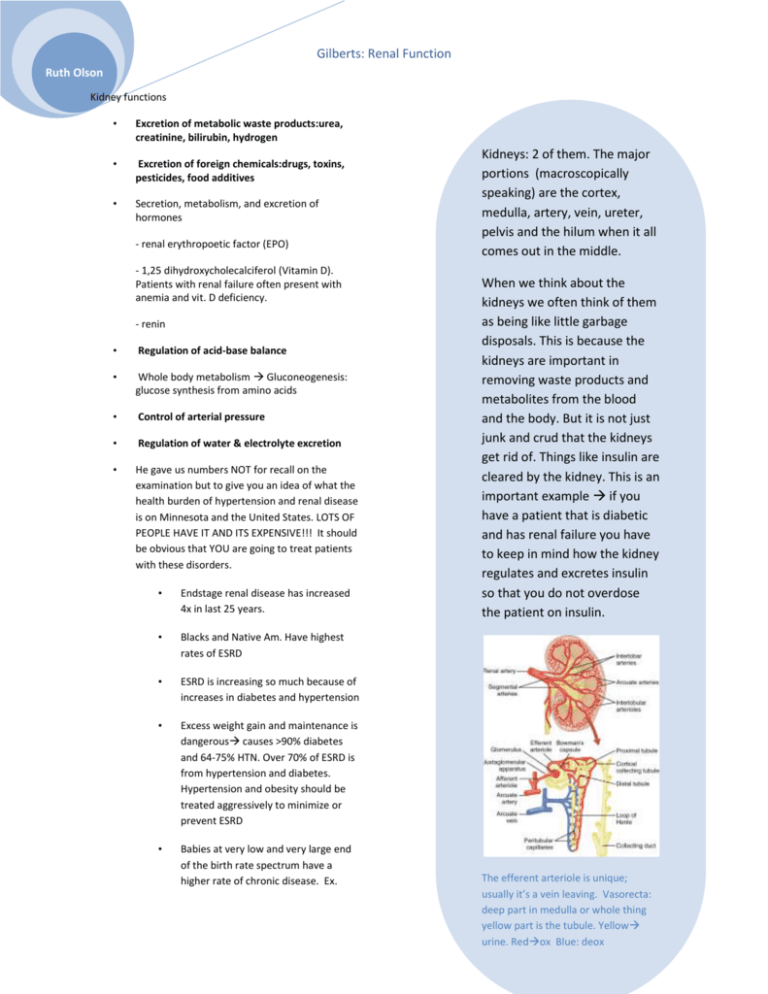
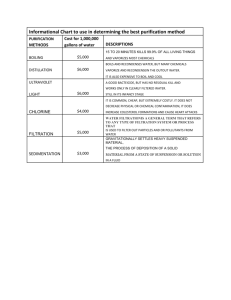
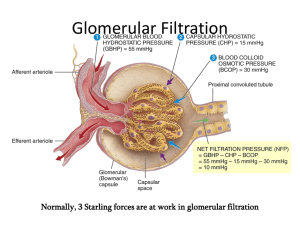
Gilberts: Renal Function Ruth Olson Kidney functions • Excretion of metabolic waste products:urea, creatinine, bilirubin, hydrogen • Excretion of foreign chemicals:drugs, toxins, pesticides, food additives • Secretion, metabolism, and excretion of hormones - renal erythropoetic factor (EPO) - 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol (Vitamin D). Patients with renal failure often present with anemia and vit. D deficiency. - renin • Regulation of acid-base balance • Whole body metabolism Gluconeogenesis: glucose synthesis from amino acids • Control of arterial pressure • Regulation of water & electrolyte excretion • He gave us numbers NOT for recall on the examination but to give you an idea of what the health burden of hypertension and renal disease is on Minnesota and the United States. LOTS OF PEOPLE HAVE IT AND ITS EXPENSIVE!!! It should be obvious that YOU are going to treat patients with these disorders. • Endstage renal disease has increased 4x in last 25 years. • Blacks and Native Am. Have highest rates of ESRD • ESRD is increasing so much because of increases in diabetes and hypertension • Excess weight gain and maintenance is dangerous causes >90% diabetes and 64-75% HTN. Over 70% of ESRD is from hypertension and diabetes. Hypertension and obesity should be treated aggressively to minimize or prevent ESRD • Babies at very low and very large end of the birth rate spectrum have a higher rate of chronic disease. Ex. Kidneys: 2 of them. The major portions (macroscopically speaking) are the cortex, medulla, artery, vein, ureter, pelvis and the hilum when it all comes out in the middle. When we think about the kidneys we often think of them as being like little garbage disposals. This is because the kidneys are important in removing waste products and metabolites from the blood and the body. But it is not just junk and crud that the kidneys get rid of. Things like insulin are cleared by the kidney. This is an important example if you have a patient that is diabetic and has renal failure you have to keep in mind how the kidney regulates and excretes insulin so that you do not overdose the patient on insulin. The efferent arteriole is unique; usually it’s a vein leaving. Vasorecta: deep part in medulla or whole thing yellow part is the tubule. Yellow urine. Redox Blue: deox Gilberts: Renal Function Ruth Olson Pima tribe, Aboriginese, UK, US. Prenatal care is important in long term health • Kidney is fully formed but not fully functional at the time of birth Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) Early nephron deficit and HTN: HTN damages nephrons 130 120 110 100 90 Excretion = Filtration –Reabsorption + Secretion Filtration : somewhat variable, not selective (except for proteins; also things bound to praren’t filtered either), avg 20% of renal flow Reabsorption : highly variable and selective. Most electrolytes (e.g. Na+, K+, Cl-) and nutritional substances (e.g. glucose) are almost completely reabsorbed; most waste products (e.g. urea)poorly reabsorbed Secretion : highly variable; important for rapidly excreting some waste products (e.g. H+), foreign substances (including drugs), and toxins 80 70 60 500 550 600 650 700 750 3 Glomerulus number (x10 ) Nephron # decreases as we age. After 40, 10% loss for every ten years. Nephron loss is accelerated in uncontrolled diabetic and hypertensive patients, leading to renal disease. Drugs are removed by filtration and excretion Here we have diagrammed the 3 steps to urine formation. 1 GFR (filtration: goes on at glomerular capillaries), 2, tubular reab (tubule peritubular capillaries) sorption which as about 99% of all solutes (Na, CL, glucose, Amino acids) then tubular secretion (tubular capillaries tubule.) 180 L per day filtered. About 99% of filtrate is absorbed into peritubular capillaries. Creatinine: important clinical indicator of renal function: filtered and excreted. Steady state in physiology: ex. If you go on a high salt diet, excretion will increase to get rid of extra Na2+ Gilberts: Renal Function Ruth Olson Glomerular Filtration Rate (the essence of kidney function) = 125 ml/min =180 L/day Plasma volume is filtered 60 times per day. This allows are body to regulate things more Glomerular filtrate composition is about the same as plasma, except for large proteins Filtration fraction (GFR / Renal Plasma Flow) = 0.2 (i.e. 20% of plasma is filtered) There is a flomerular capillary filtration barrier (which is neg. charged.) • assessment and monitoring of known renal disease • Eating lots of protein also increases GFR, but that is a transient effect. • “Is the dipstick OK?” : dipstick protein tests may not be very accurate: “trace” results can be normal & positives must be confirmed by quantitative laboratory test. Microalbuminuria • Effects of size and charge on filterability Definition: urine excretion of > 30 but < 150 mg albumin per day • Causes: early diabetes, hypertension, glomerular hyperfiltration • Prognostic Value: diabetic patients withmicroalbuminuria are 10-20 fold morelikely to develop persistent proteinuria Things that are polycationic filter MUCH better than anionic things, reguardless of size. There are rare conditions where basement membrane loses its charge; this doesn’t show up with histological evaluation! Clinical importance of Proteinuria • early detection of renal disease in at-risk patients • hypertension: hypertensive renal disease • diabetes: diabetic nephropathy • pregnancy: gestational proteinuric hypertension (pre-eclampsia) • annual “check-up”: renal disease can be silent Bowman’s capsule colloid osmotic pressure is usually zero. Net filtration is normally 10 mmHg. The importance of the values: this is much higher than you have in normal capillary beds. You don’t want that in your skeletal muscle that’s edema. Normal Values: GFR = 125 ml/min Net Filt. Press = 10 mmHg Kf = 12.5 ml/min per mmHg, or 4.2 ml/min per mmHg/ 100gm (400 x greater than in most tissues) Gilberts: Renal Function Ruth Olson This is only about 8 weeks of obesity. This is reversible in dogs if weight loss is achieved. BM gets much more thick in obesity. Dogs respond to diet the same way we do. When they go on a low fat diet, the hyperfiltration stops. Autoregulation: In other places: match delivery and demand at local tissue sights. In kidney, there is far more delivery of nutrients than needed for renal metabolism. Autoregulation here is more about helping regulate renal function and excretion of what you want to get rid of. In kidney disease, there is a loss of the ability to autoregulate. This is why renal disease is a slippery slope; progression is dangerous and prevents autoregulation. No autoregulation of urine flow. Gilberts: Renal Function Ruth Olson Both of these are mediated by a hormone acting on smooth muscle. Normally sympathetic activation does not have an effect on GFR, but it does in situations like hemorrhage. 2. Also important in HTN: ACE inhibitors are percribed which prevents AT II formation. If a person already has a deterioration in renal function it can be problematic blocking AT II formation. Pgs, in particular, Prostacyclin(PC) is a VD. It will inc GFR and BF. If you block PC, the opposite can happen. NSAIDs can cause severe decreases in GFR in patients with cirrhosis (as indicated by creatine clearance.) Gilberts: Renal Function Ruth Olson RENAL AUTOREGULARION: On top: RAP: steady state: 100. Place a clamp on renal artery: BP dec to 80. Also, dec in GRF (acute). RAP remains at 80, but because of autoregulatory mechanisms, GFR and Bf will recover back to normal. If you increase BP to kidney, inc GFR and BF (acute) but autoregulatory mechanisms will cause them to recover. Fxns of renal BF • Structure of the juxtaglomerular apparatus: Macula Densa: Tubular-glomerular feedback: Involves delivery of Na2+ to distal tubules. The macula densa measure Na2+ delivery (not Na2+ concentration) in the distal tubule (we don’t know how.) To deliver enough plasma to kidneys for glomerular filtration • To deliver nutrients to kidney so that the renal cells can perform their functions (only about 20% of renal blood flow needed for this function) Ang II blocade impairs GFR autoregulation: you need a higher arterial P to get a given GFR. Gilberts: Renal Function Ruth Olson Questions: 1. 12. T/F The macula densa measures Na2+ concentration in the distal tubule Creatinine undergoes a. Filtration b. Filtration and complete reabsorption c. Filtration and partial reabsorption d. Filtration and secretion 2. Inulin undergoes a. Filtration b. Filtration and complete reabsorption c. Filtration and partial reabsorption d. Filtration and secretion 3. Glucose undergoes a. Filtration b. Filtration and complete reabsorption c. Filtration and partial reabsorption d. Filtration and secretion 4. Sodium chloride undergoes a. Filtration b. Filtration and complete reabsorption c. Filtration and partial reabsorption d. Filtration and secretion 5. Amino acids undergo a. Filtration b. Filtration and complete reabsorption c. Filtration and partial reabsorption d. Filtration and secretion 6. Organic acids and bases undergoe a. Filtration b. Filtration and complete reabsorption c. Filtration and partial reabsorption d. Filtration and secretion 7. Which races have the highest rates of ESRD a. Whites b. Native Americans c. Asian Americans d. Blacks 8. T/F All nephron loss is due to aging 9. What are causes of microalbuminuria? a. early diabetes, b. hypertension c. glomerular hyperfiltration d. All of the above 10. In what special case does sympathetic activation have an effect on GFR? 11. Fill in the chart below: Answers 1. a 7.b, d 2.a 8.F 3. c 9. D 4.b 5.c 10.Hemorrhage 6.d 11. 12. F. The macula densa measures Na2+ delivery, NOT Na2+ concentration