here
advertisement

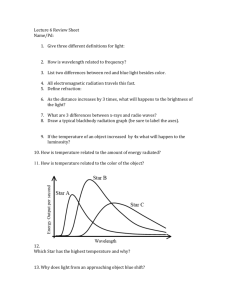
Science 9 Honours Caitlin S Summative Assessment (with answers) – Stars 1. What is a star? /1 A: It is a luminous sphere of plasma and gas that is held together by its own gravity. 2. What is the full name of an H-R Diagram? /1 A: Hertzsprung – Russel Diagram 3. What does the H-R Diagram measure? /2 A: It measures effective temperature, spectral class, absolute magnitude, luminosity compared to sun. 4. What are the names of the spectral classes? /1 A: O, B, A, F, G, K, M 5. What is the relationship between spectral classes and spectral types? /2 A: Each spectral class is divided into 10 types. They are shown with the numbers 0-9. 0 is the hottest and 9 is the coolest. 6. Where are stars formed? Provide a definition. /2 A: they are formed inside stellar nebulas or stellar nurseries. A stellar nebula is a cloud of hydrogen and helium gas and dust in space. 7. How are protostars created? /2 A: it starts inside a stellar nebula. The clouds eventually collapse and that’s what forms protostars. 8. What does it mean to be a main- sequence star? /2 A: It means a star where all of the energy of a star is from hydrogen being fused in the core. 9. In the star life cycle, do red giants form before or after planetary nebuluas? /1 a. Before b. After A: a. Before 10. How are red giants formed? /1 A: they are formed when a star runs out of hydrogen full in its core. All of the hydrogen has been fused into helium. Science 9 Honours Caitlin S 11. What happens to the core when all of the helium in the core has fused? /1 A: The core contracts and energy increase from burning in the shells. This causes the outer layers to expand. 12. What is the difference between absolute and apparent magnitude? /2 A: Absolute magnitude is the brightness of an object if it were to be seen at a certain distance from the earth. Apparent magnitude refers to the brightness of an object as it appears from earth. It is judges using its original distance. 13. What is left over once all of the planetary shells have been shed? /1 A: the core is left over which would be called a white dwarf star. 14. Define high-mass stars /2 A: Form quickly and have short lives. It refers to certain group of spectral classes. Grand total /20