Review Sheet for Mitosis and Meiosis Answer Key
advertisement

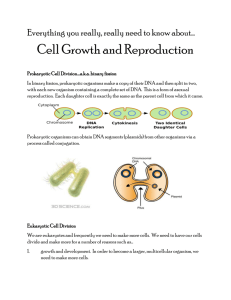
Name _____________________________________ Date ______________________ Period _________ Review for Mitosis & Meiosis Test Mitosis 1. What are the 4 phases of the cell cycle? What happens during each phase? a. G1 – cells increase in size and synthesize new proteins and organelles b. S – the chromosomes are replicated c. G2 – many of the organelles and molecules needed for mitosis are produced d. M – the division of the nucleus and the cell 2. Why do cells need to divide? They get too big and don’t have enough DNA to function properly and cannot transport wastes and nutrients across the membrane efficiently 3. What happens to the volume compared to the surface area as the cell gets bigger? The volume increases faster than the surface area 4. What are the 4 phases of mitosis (in order!)? What happens during each phase? a. Prophase – nucleoli disappear, chromosomes condense and become visible, nuclear membrane disappears, spindle forms b. Metaphase – the chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers and line up at the equator (middle) c. Anaphase – the centromere splits and the sister chromatids move to opposite poles d. Telophase – nucleoli reappear, nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes, chromosomes uncoil 5. What happens during Interphase? Which phases of the cell cycle make up Interphase? The cell grows, chromosomes are copies, and the cell prepares for mitosis. Interphase is made up of the G1, S, and G2 phases. 6. What happens during cytokinesis? When does cytokinesis begin? Division of the cytoplasm; the cell divides into two cells. Cytokinesis begins during telophase. 7. What is the spindle? What does it do? The spindle is the structure made up of spindle fibers. It attaches to the chromosomes and then pulls them apart. 8. What are centrioles? Where are they located in the cell during mitosis? Small structures found in animal cells. They move to the poles of the cell during mitosis. 9. Label the centromere and the sister chromatids on the chromosome below. centromere sister chromatid 10. Explain cell-to-cell contact and how it controls cell growth. When cells come in contact with other cells they stop growing/dividing. 11. What are cyclins? What role do they serve in the cell cycle? Cyclins are proteins that control the cell cycle. 12. What structure associated with cell division is only found in an animal cell? What structure associated with cell division is only found in a plant cell? Animal = centrioles Plant = cell plate 13. What is cancer? Uncontrolled cell growth 14. What is a tumor? A cluster of cancer cells 15. When during the cell cycle are the chromosomes visible? During the M phase 16. Be familiar with the diagram of the cell cycle from your notes. Be able to label the different sections of the diagram. Meiosis 17. What (specifically) is being made during meiosis? Gametes – sperm and eggs 18. If an organism has 16 chromosomes in one of its body cells, how many chromosomes would its sex cells have? 8 19. What is crossing over? Draw an example to show crossing-over. Crossing over is when pieces of homologous chromosomes overlap. 20. When does crossing-over occur during Meiosis? Prophase I 21. Gametes are haploid/diploid. (circle the correct answer) 22. What does haploid mean? One of each chromosome (half the diploid number) 23. What does diploid mean? Two of each chromosome 24. What is a tetrad and when does it form? A tetrad is 4 sister chromatids of a homologous pair of chromosomes. It forms during prophase I. 25. What is a stem cell? Why is it useful in medicine? Unspecialized cells that can become specialized under certain conditions. Could eventually be used to treat spinal cord injuries or other injuries/diseases that damage cells. 26. Be able to describe the steps of Meiosis. 27. Know the table that compares Mitosis and Meiosis. (From the Meiosis Powerpoint)