(Nick`s)Essential Biology 3.3 & 7.1 DNA Structure HL
advertisement

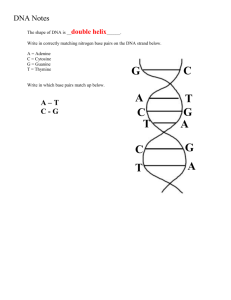
Essential Biology 3.3 & 7.1: DNA Structure (HL Only) Resources: http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com/bis-ib-diploma-programme-biology/02-the-double-helix/dnastructure-and-replication-inc-ahl-71-72/ 1. Draw and label the structure of a simplified single nucleotide, including sugar, phosphate and base. A C G T C C G T 2. Complete the table below to show the pairings of the bases in DNA: Purine Pyramidine A- Adenine T- Thymine C- Cytosine G- Guanine 3. Where would one find the base uracil? Uracil replaces Thymine in RNA. 4. In the space below, draw a single strand of three nucleotides, naming the bonds between them and showing the correct relative position of these bonds. Stephen Taylor A H T C H G T H A G H C A H T Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 3.3 & 7.1: DNA Structure (HL Only) 5. Define the term double helix. A pair of parallel helices intertwined about a common axis. 6. In the space below, draw a section of DNA, showing two anti-parallel strands of three nucleotides. Label the bonds which hold the bases together as well as the correct complementary base pairs. Also include the 3’ and 5’ linkages (and ends), and the distinction between purines and pyramidines. 7. Explain the relevance of the following in the double-helix structure of DNA: a. Complementary base pairing The complimentary base pairings ensure that there are no mistakes made when copying or transcribing DNA. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 3.3 & 7.1: DNA Structure (HL Only) b. Hydrogen bonds Hydrogen bonds are used to hold together the nitrogen bases. c. Relative positioning of the sugar-phosphate backbone and the bases The sugar phosphate backbone is Hydrophilic so it is positioned on the outside. Nitrogenous bases are very reactive so are protected on the inside. 8. In the space below, draw the structure of a simplified nucleosome, including the H1 linker and histone proteins. 9. Nucleosomes allow the DNA to be supercoiled. a. What is the approximate length of the DNA strand in one chromosome? The length is about 2 meters. b. During which phase of the cell cycle is DNA most likely to be supercoiled? It is during metaphase that the DNA will be supercoiled. c. Outline how nucleosomes help regulate transcription. Nucleosomes help regulate transcription through promoters. 10. Distinguish between unique or single-copy genes and highly repetitive sequences: Single-copy genes Highly-repetitive sequences Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 3.3 & 7.1: DNA Structure (HL Only) 1.5% of genome makes polypeptides. 3% codes for on/off gene switches. Contains exons and introns. Makes up about 5-45% of the genome. Once called “junk” DNA. Also known as satellite DNA, each repeated sequence can be 5-300 base pairs. HRS’s are used in genetic fingerprinting. 11. Distinguish between introns and exons in eukaryotic genes. Exons are coded regions and Introns are non-coded regions which are edited out. 12. The discovery of the structure of DNA earned a Nobel Prize for Watson, Crick and Wilson. Read the resources at the Nobel Prize website: http://nobelprize.org/educational_games/medicine/dna_double_helix/readmore.html How is it a good example of the following: a. Internationalism in science? b. Cooperation in science? c. Competition in science? 13. What was the role of Rosalind Franklin in the process of the discovery of the structure of DNA and why was she not included in the Nobel Prize? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 3.3 & 7.1: DNA Structure (HL Only) Wilson, Crick and Watson got their ideas from her data. She did not receive a Nobel prize as she died in 1958, however it was discovered that she was never nominated for it. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com