Ecology Branch of Biology that studies interactions between
advertisement
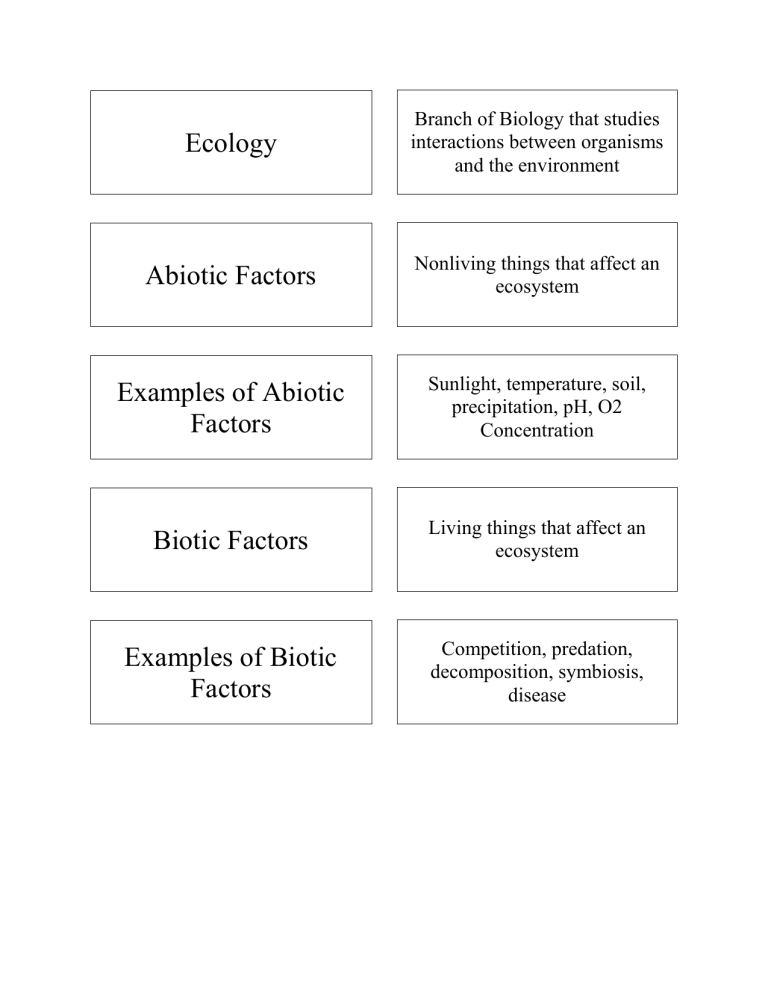
Ecology Branch of Biology that studies interactions between organisms and the environment Abiotic Factors Nonliving things that affect an ecosystem Examples of Abiotic Factors Sunlight, temperature, soil, precipitation, pH, O2 Concentration Biotic Factors Living things that affect an ecosystem Examples of Biotic Factors Competition, predation, decomposition, symbiosis, disease Population All of the individuals of one species living in a specific area Community All of the populations of different organisms living in a specific area Ecosystem All living organisms (biotic) and their physical environment (abiotic) Niche Intraspecific Interactions The full range of biotic and abiotic conditions in which an organism lives and the way it uses those conditions Interactions between individuals of the same species Interspecific Interactions Interactions between individuals of different species Neutralism A relationship between two species that interact but do not affect each other Symbiosis Relationship between organisms of different species that benefits one or both of the organisms Mutualism A symbiotic relationship between two or more species where both organisms benefit Commensalism A symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is neither benefited nor harmed Parasitism A symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is harmed Predation A relationship between organisms in which one captures and feeds on the other Competition A relationship between organisms in which they compete for limited resources Intraspecific Competition Competition between organisms of the same species Interspecific Competition Competition between organisms of different species Competitive Exclusion Principle No two species can occupy the exact same niche, in the same place, at the same time Limiting Factors When a nutrient limits the growth (productivity) of organisms in an ecosystem Exponential Growth When a population multiple by a constant factor at a constant time because of unlimited resources Logistic Growth An S shaped curved population that starts exponentially, then slows and finally stops growing Carrying Capacity The maximum number of individuals that the environment can support Producers Organisms that make their own food from inorganic compounds Autotrophs Organisms that make their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis Consumers Organisms that must obtain their food from other organisms Heterotrophs Organisms that must obtain their food from their environment Decomposers Organisms that break down the remains of dead organisms Food Chain A series of organisms though which food energy is passed How Energy Flows through an Ecosystem In a straight line through food chains Food Webs Many food chains connected at different points Effect of removing a producer from a food web Collapse of the whole system Effect of removing a consumer from a food web Increase of the individuals that the consumer eats, and reduction of the individuals which eat the consumer Primary Consumer Herbivores or omnivores that consume the producers Secondary Consumer Omnivores and carnivores that consume primary consumers Tertiary Consumer Omnivores and carnivores that consume secondary consumers Quaternary Consumer Omnivores and carnivores that consume tertiary consumers 10% Rule Only 10% of available energy, at one tropic level, is transferred to organisms at the next tropic level Pyramid of Energy Diagram which shows that the energy available to organisms decreases with each tropic level Pyramid of Biomass Diagram which shows that the total amount of living tissue (biomass) decreases with each trophic level Pyramid of Numbers Diagram which shows that the number of organisms decreases with each tropic level Carbon Cycle The movement of Carbon and Oxygen through the biosphere Nitrogen Cycle The movement of Nitrogen through the biosphere Nitrogen Fixation The process that changes free nitrogen in the atmosphere to compounds that can be used by living things Denitrification The process of breaking down nitrogen compounds into free nitrogen Ecological Succession The series of changes that occur in communities over time Primary Succession Changes that occur on surfaces where there is no soil Secondary Succession Changes that occur on surfaces where soil is already present Pioneer Species The first species to populate an area Pioneer Species in Primary Succession Lichens and Mosses Seral Communities Different communities between the pioneer species and the climax community Climax Community The mature, stable community of organisms, which is the end result of succession






