Chapter 16- Blood Plasma and the cellular elements of blood
advertisement

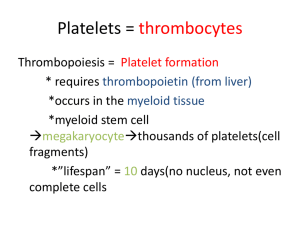
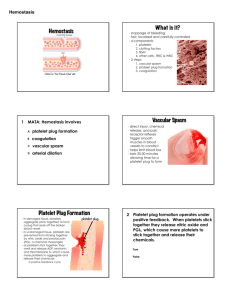
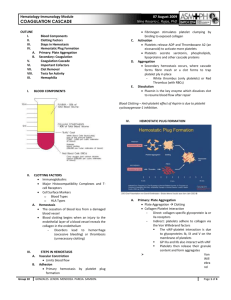
Chapter 16- Blood Plasma and the cellular elements of blood Plasma- fluid portion of the blood Plasma proteins- difference in composition from interstitial fluid Albumins- most prevalent plasma proteins, about 60% Red blood cells- erythrocytes, transport oxygen and carbon dioxide White blood cells- leukocytes, only functional cells in circulation, immune response Platelets- cell fragments of megakaryocytes, instrumental in coagulation Five types of white blood cells- lymphocytes, monocutes, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils Phagocytes- neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages- engulf and ingest foreign particles Immunocytes- lymphocytes, responsible for specific immune responses Granulocytes- basophils, eosinophils, meutrophils- contain cytoplasmic incluisions that have a granular appearance Blood cell production Bone marrow- site of pluripotent hematoporietic stem cell, develops into blood cells Hematopoiesis- synthesis of blood cells Hemoglobin- oxygen binding protein of red blood cells Interleukins- cytokines released by one white blood cell to affect another Colony stimulating factors- ability to stimulate the growth of leukocyte colonies Leukopoiesis- leukocyte production and development, regulated by CSF Thrombopoietin- a glycoprotein that regulates growth and maturation of megakaryocytes Erythropoietin- glycoprotein that regulates red blood cell production Red blood cells Hematocrit- ratio of red blood cells to plasma Morphology- ability to change shape, can provide clues for presence of disease Mean red cell volume- size of red blood cells Transferrin- transport protein in blood for iron Ferritin- storage protein for iron, mostly in liver Bilirubin- colored pigment made from remnants of heme groups Bile- secretion containing bilirubin allows excretion Jaundice- elevated bilirubin level in blood Anemia- low hemoglobin content Platelets and coagulation Hemostasis- process of keeping blood within a damaged blood vessel Platelet plug- mechanical blockage of the hole Platelet adhesion- platelets stick to exposed collagen Platelet aggregation- platelets stick to one another Tissue factor- protein phospholipid mixture, initiate third step Coagulation cascade- series of reactions, formation of fibrin Clot- reinforced platelet plug Plasmin- dissolves clot, enzyme Thrombus- blood clot that adheres to undamaged wall of blood vessel Platelet activating factor- sets up positive feedback loop by activating more platelets Thromboxane A2- vasoconstriction Prostacyclin- blocks platelet adhesion and aggregation Intrinsic pathway- begins with collagen exposure and involves proteins present in blood Extrinsic pathway- starts when damaged tissue exposes tissue factor Common pathway- joining of intrinsic and extrinsic Thrombin- enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin Plasmin- enzyme created from pasminogen by thrombin and tissue plasminogen activator Breaks fown fibrin polymers into fibrin fragments Fibrinolysis- dissolution of fibrin by plasmin Anticoagulants- prevent coagulation from taking place Heparin and antithrombin III- anticoagulants produced in body Hemophilia- coagulation disorder