Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
advertisement

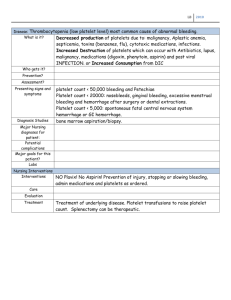
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology Thirteenth Edition Gerard J. Tortora • Bryan H. Derrickson Chapter 19 The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Copyright © 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Plasma (55%) Red blood cells (45%) Buffy coat, composed of white blood cells and platelets (a) Appearance of centrifuged blood Whole blood 8% Proteins 7% Blood plasma 55% Other fluids and tissues 92% Water 91.5% Albumins 54% Globulins 38% Fibrinogen 7% All others 1% Electrolytes Nutrients Gases Formed elements 45% Regulatory substances Other solutes 1.5% Waste products PLASMA (weight) SOLUTES Platelets 150,000–400,000 Neutrophils 60–70% White blood cells 5000–10,000 Red blood cells 4.8–5.4 million Lymphocytes 20–25% Monocytes 3–8% Eosinophils 2–4% Basophils 0.5–1.0% BODY WEIGHT VOLUME FORMED ELEMENTS (number per μL) (b) Components of blood WHITE BLOOD CELLS White blood cell Platelet Red blood cell SEM 3500x (a) Scanning electron micrograph White blood cell (leukocyte—neutrophil) Blood plasma Red blood cell (erythrocyte) Platelet White blood cell (leukocyte—monocyte) LM (b) Blood smear 400x Key: Key: Progenitor cells Colony-forming unit—erythrocyte CFU–Meg Colony-forming unit—megakaryocyte CFU–GM Colony-forming unit—granulocyte macrophage CFU–E Precursor cells or "blasts" Formed elements of circulating blood Tissue cells Pluripotent stem cell Myeloid stem cell Lymphoid stem cell CFU–E CFU–Meg Proerythroblast Megakaryoblast CFU–GM Eosinophilic myeloblast Basophilic myeloblast Myeloblast Monoblast B lymphoblast NK lymphoblast Eosinophil Basophil Neutrophil Monocyte T lymphocyte B lymphocyte (T cell) (B cell) Natural killer (NK) cell T lymphoblast Nucleus ejected Reticulocyte Red blood cell (erythrocyte) Megakaryocyte Platelets (thrombocytes) Granular leukocytes Mast cell Agranular leukocytes Macrophage Plasma cell 8μm Surface view Sectioned view (a) RBC shape Beta polypeptide chains (globins) Heme Iron (Fe2+) Alpha polypeptide chains (globins) (b) Hemoglobin molecule (c) Iron-containing heme Circulation for about 120 days 7 3 Reused for protein synthesis Amino acids Globin 4 2 Heme Red blood cell death and phagocytosis Biliverdin Bilirubin 9 Bilirubin 11 10 Kidney 13 Urobilin Macrophage in spleen, liver, or red bone marrow 12 Bilirubin Urobilinogen Bacteria Feces Liver Small intestine + Globin + Vitamin B12 + Erythopoietin 8 Erythropoiesis in red bone marrow Key: in blood Stercobilin Urine Fe3+ Ferritin Transferrin 1 Transferrin 6 5 Fe3+ Fe3+ Large 14 intestine in bile Some stimulus disrupts homeostasis by Decreasing Oxygen delivery to kidneys (and other tissues) Receptors Kidney cells detect low oxygen level Input Increased erythropoietin secreted into blood Control center Proerythroblasts in red bone marrow mature more quickly into reticulocytes Output Return to homeostasis when oxygen delivery to kidneys increases to normal Increased erythropoietin secreted into blood Effectors Larger number of RBCs in circulation Increased oxygen delivery to tissues LM all 1600x (a) Eosinophil (b) Basophil (c) Neutrophil (d) Lymphocyte (e) Monocyte Interstitial fluid Blood flow Neutrophil Endothelial cell Rolling Sticking Squeezing between endothelial cells Key: Selectins on endothelial cells Integrins on neutrophil Neutrophils Eosinophils Lymphocytes Basophils Monocytes Red Blood Cells (RBCs) or Erythrocytes Lymphocytes Neutrophils Monocytes Eosinophils Basophils Platelets (thrombocytes) Red blood cell Platelet Collagen fibers and damaged endothelium 1 Platelet adhesion Collagen fibers Liberated ADP, serotonin, and thromboxane A2 2 Platelet release reaction Collagen fibers Platelet plug 3 Platelet aggregation Platelet Red blood cell Fibrin threads SEM 1445x (a) Early stage SEM 900x (b) Intermediate stage Fibrin threads Red blood cell SEM 3400x (c) Late stage showing red blood cells trapped in fibrin threads (a) Extrinsic pathway (b) Intrinsic pathway Tissue trauma Blood trauma Tissue factor (TF) Damaged endothelial cells expose collagen fibers Damaged platelets Activated XII Ca2+ Activated platelets Ca2+ Platelet phospholipids Activated X V 1 Activated X Ca2+ Ca2+ PROTHROMBINASE V (c) Common pathway Prothrombin (II) Ca2+ THROMBIN XIII 2 Ca2+ Fibrinogen (I) Activated XIII Loose fibrin threads STRENGTHENED FIBRIN THREADS 3 BLOOD TYPE TYPE A TYPE B A antigen B antigen Anti-B antibody Anti-A antibody TYPE AB TYPE O Both A and B antigens Neither A nor B antigen Red blood cells Plasma Neither antibody Both anti-A and anti-B antibodies Rh– mother Placenta First Rh+ fetus Anti-Rh antibodies Second Rh+ fetus Rh+ antigens (a) First pregnancy (b) Between pregnancies (c) Second pregnancy Anti-A serum Untreated blood Treated with anti-A serum Anti-B serum Treated with anti-B serum Blood type A B AB O Sickled Normal Crenated SEM 1665x Red blood cells