Energy transfer in ecosystems Summary Biology N4/5 Food chains
advertisement
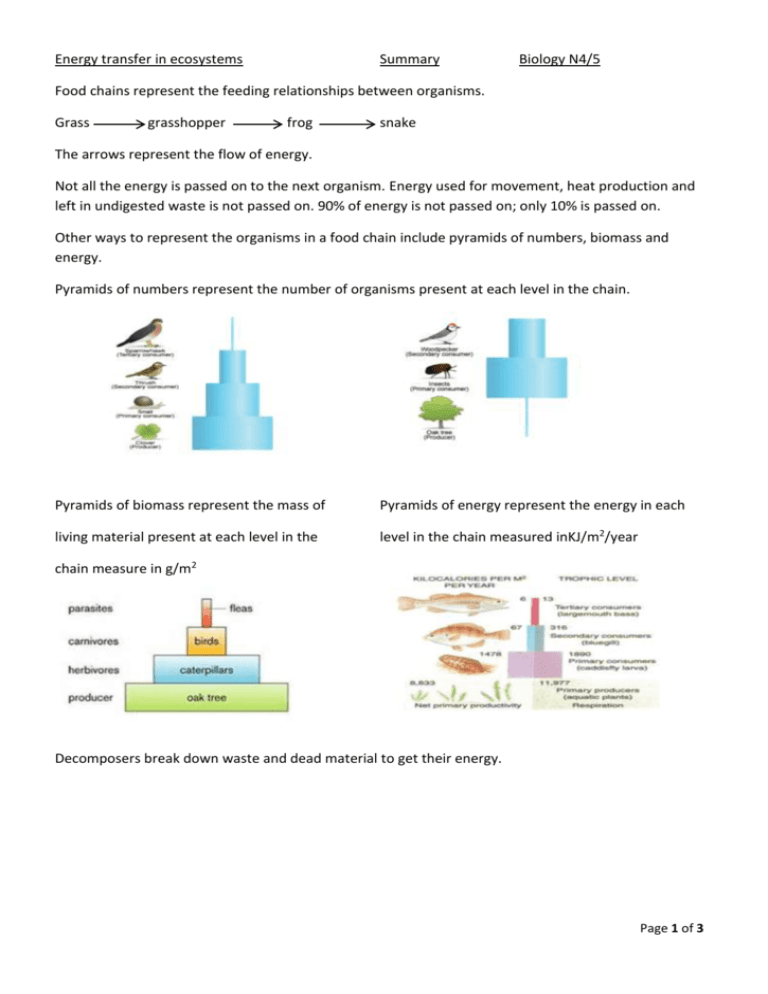
Energy transfer in ecosystems Summary Biology N4/5 Food chains represent the feeding relationships between organisms. Grass grasshopper frog snake The arrows represent the flow of energy. Not all the energy is passed on to the next organism. Energy used for movement, heat production and left in undigested waste is not passed on. 90% of energy is not passed on; only 10% is passed on. Other ways to represent the organisms in a food chain include pyramids of numbers, biomass and energy. Pyramids of numbers represent the number of organisms present at each level in the chain. Pyramids of biomass represent the mass of Pyramids of energy represent the energy in each living material present at each level in the level in the chain measured inKJ/m2/year chain measure in g/m2 Decomposers break down waste and dead material to get their energy. Page 1 of 3 Nitrogen cycle Animals and plants need nitrogen to make protein. Animals get their nitrogen by consuming plants or animals. Most plants get their nitrogen by absorbing nitrates from the soil through their roots. Some plants (legumes) like peas and clover have an association with nitrogen fixing bacteria which accumulate in nodules in their roots. These bacteria fix nitrogen from the soil in to nitrates and the plants use these as their source of nitrogen. Some free living nitrogen fixing soil bacteria also make nitrates available to plants by converting nitrogen into nitrates in the soil Nitrogenous waste (faeces and urine) along with dead organisms are decomposed by bacteria and fungi to make ammonium compounds in the soil. These ammonium compounds are converted to nitrites by nitrifying bacteria. Nitrites are further converted into nitrates by nitrifying bacteria. These nitrates are available to plants to take up through their roots. Some nitrates are converted to nitrogen by denitrifying bacteria which is returned to the atmosphere. Human influence on the nitrogen cycle Humans influence the cycle in relation to their farming and other activities. Harvesting crops removes nitrogen locked up in crops that could have gone back into the soil. To replace the nitrogen farmers add fertiliser, manure, compost or grow crops like clover. Fertilisers are man-made chemicals added to the soil. These include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K), nutrients essential for plant growth. Fertiliser bags are often labelled N:P:K with a ratio like 6:6:6 to indicate the proportions of the elements. Nitrogen is higher for leaf crops, phosphorus is higher for root crops and potassium is higher for flower and fruit crops. Page 2 of 3 Manure and compost are natural fertilisers added by farmers which release nitrates as they decompose. Clover adds nitrates as there are root nodule bacteria present in its roots that fix soil nitrogen into nitrates. The clover crop will be ploughed back into the soil. Increasing the nitrates (and other minerals) will increase the yield in the crops being grown. Excessive use of fertiliser Applying more fertilisers than the crop can use may result in some of them running off into fresh water like rivers, reservoirs and lochs when it rains. This can cause an increase in the growth of algae in the water (algal blooms) which can block out light. As the algae die and sink to the bottom they will decay. The decomposers like bacteria use up the oxygen in the water for respiration. This reduces the oxygen level which increases the deaths of invertebrates and fish. This means the water will support less life so it reduces biodiversity. Competition in ecosystems Competition occurs when organisms require the same or similar resources. Organisms compete for light, water, nutrients, space and reproductive mates. Competition can be either interspecific or intraspecific. Interspecific competition occurs between different species that require similar resources. Intraspecific competition occurs between members of the same species that require the same resources. This type of competition is often more intense as the same resources are needed. Ecosystems definitions Producers use sunlight energy to make their own food. Consumers eat other organisms to get their energy. Herbivores eat plants to get their energy. Carnivores eat animals to get their energy. Omnivores eat both plants and animals to get their energy. The number of one type of organism (species) in an ecosystem is the population. A species is defined as organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Page 3 of 3