BI12_LG_U14 - BC Learning Network
advertisement

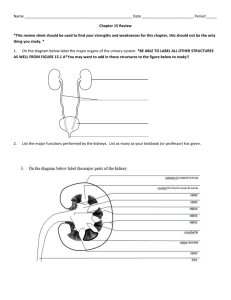
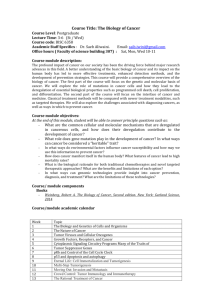
BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Unit 14 ~ Learning Guide Name:________________ INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit test. Do your best and ask questions about anything that you don't understand BEFORE you write the unit test. U14 NOTES: URINARY SYSTEM (web notes) Roles of Organs in Excretion Excretion The removal of ______________________ from the body (the useless and ____________________________________ of cellular reactions) Skin Excretes ___________________ (a solution of water, salt, and some urea) Used to ____________________________ then secretion of wastes. Increase in wastes during times of renal failure (kidney) Liver ____________________________________________ _. Yellow pigment in _________ is also formed from the breakdown of ___________ by the _________. It is then deposited in the blood and later removed by the ____________. Lungs Expiration removes ______________________ but it also results in the loss of water. Page 1 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Intestine Certain salts, such as those of _____________________ _______________________ directly into the cavity of the _____________________________________________ lining it and become part of __________________. Kidneys Excrete urine, which contains _____________________ _______________________ products of metabolism. Entrance and Exit of Water Enters: 1. Drink Water 2. Absorbed from food eaten Exits: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Exhalation Perspiration Tears (small amounts) Urination Expectorating (phlegm) Defecation Urinary System Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Kidney - ___________________________________________________ Ureters - ___________________________________________________ Bladder - ___________________________________________________ Urethra - ___________________________________________________ Parts of the Kidney When a kidney is sliced longitudinally (sagittal section), it shows 3 regions. 1. Outer granulated region called the _____________________. 2. Striated or lined layer called the _____________________. Page 2 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 3. Inner cavity called the ________________________ where urine collects. The kidney lies in the lower, dorsal port of the abdomen. They receive blood from the _________________________ to be cleaned. The wastes, to be excreted, called ______________ collects in the ________________ region of each kidney before being conducted by _________________ through the ureters down to the ___________________________. When the urinary bladder becomes full, stretch receptor trigger __________________, and the fluid is excreted via the urethra. The Nephron Microscopically, the kidney is composed of over 1 billion nephrons (or renal tubules). Various parts of the nephron align in the kidney such that: The cortex (outer region) contains: 1. ______________________________________________________________ 2. ______________________________________________________________ 3. ______________________________________________________________ The medulla (inner region) contains: 1. ______________________________________________________________ Both the cortex and medulla contain portions of the _________________________ Page 3 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Renal Artery Bring blood to the _______________ to be "cleaned". High _____________ content. Renal Veins Returns blood that is _______________. Low ____________ content, high glucose. Each nephron has its own blood supply. Including 2 capillary regions: 1. At the _____________________________. 2. Surround the rest of the ________________________________. Steps of Urine Formation 1. ________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________________________________________ 4. ________________________________________________________________ 5. ________________________________________________________________ Function of the Nephron 1. Pressure Filtration Blood enters the __________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ____________________________ water, nutrients, and wastes out of the glomerulus and into Bowman's Capsule. Large organic molecules do not exit the blood (not filtered). _________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________. Blood pressure is very important. If blood pressure is too _________, filtration will not occur. A hormone called _____________ is released from a specialized tissue in the ______________ that causes the constriction of the Glomerulus and thus, the blood pressure is increased to an adequate level. Filtered Blood Components Non-Filtered Blood Components Water Formed Elements - Blood Nutrients Cells Nitrogenous Wastes Platelets Salt (ions) Proteins Page 4 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 2. Selective Reabsorption Occurs mainly at the _____________ _____________________________. Required nutrients (glucose, amino acids, vitamins, minerals, salt molecules and some water) are reabsorbed into the peritubular capillary network. _______________ ____________________. 3. Water Reabsorption The body cannot afford to lose all this water. It must be reabsorbed into the blood. _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ and water follows the sodium by osmosis (to even out electrical and concentration gradients). Water is _____________________ along the entire length of the nephron. Therefore urine is concentrated. The blood in the capillaries are __________________ to the fluids in the fluid spaces. The loop of Henle creates a high osmotic pressure in the medulla. The fluid going up the distal side of the loop of Henle has a greater ______________________ of wastes and little nutrient value. 4. Tubular Excretion Occurs at the distal convoluted tubule. Excess molecules in the ______________, such as H+ ions, Histamine, Penicillin, and ammonia are secreted into the tubule from the blood, thereby helping to ___________________________________. Helps maintain blood _____. 5. Excretion Concentrated urine from the _________________________ collect and goes to the __________________________. Page 5 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Summary of Nephron Function/Urine Production YOU SHOULD GO THROUGH THE NEPHRON FUNCTION/ URINE FORMATION TUTORIAL BEFORE PROCEEDING ANY FURTHER! Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Good example of negative feedback loop. ADH - _________________ _______________________ _________________. ADH increases the permeability of the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct so that more ________________ can be reabsorbed. Therefore a decreased amount of urine results, but an increase in urine concentration. Water + Urea = Urine. ___________________________________ ________________________. Urea is a waste product in the metabolism of proteins. With more water being reabsorbed, blood volume tends to be increased. If too little water is taken in orally the _______________________________ releases a hormone into the nerve tract to the _________________________________ gland. The posterior pituitary gland releases __________ and more water is absorbed by the kidneys to maintain blood volume. Page 6 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 pH of blood is maintained by tubular excretion. If ____________________________, hydrogen ions are secreted into the nephron. Alcohol has a negative effect on ________. It sends a false message to the hypothalamus that there is too much water in the blood. ADH is not released in fact it is inhibited. Therefore _________________________________________. That is why, if you drink alcohol, you urinate a lot and become dehydrated. Aldosterone Aldosterone is a hormones which regulate the level of _________________________ _________________________ in the blood. If sodium is too low, aldosterone causes more sodium to be reabsorbed. If sodium concentration is too high the release of aldosterone is inhibited. Adrenal Cortex __________________________. The effect of this is the same as that of ADH in that __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________. Page 7 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 U14 PRACTICE: URINARY SYSTEM 1. Define excretion. (2 marks) 2. Identify the substances excreted by the following structures. (5 marks) a. sweat glands b. lungs c. liver d. kidneys e. large intestine Page 8 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 3. Label the following diagram of the urinary system and provide a brief description of the function of the structure beside each label. Please be neat (8 marks) 4. Label the following diagram of a kidney and provide a brief description of the function of the structure beside each label. You only need to label and describe the structures indicated with letters. Please be neat. (8 marks) A. B. C. D. Page 9 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 5. Describe the various ways that water enters and exits the human body. (4 marks) 6. Compare and contrast the composition of blood plasma to the composition of urine. (4 marks) 7. List the key substances that are selectively reabsorbed by the proximal convoluted tubule. (6 marks) 8. List the key substances that are excreted by the distal convoluted tubule. (4 marks) Page 10 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 9. Label the following diagram of a nephron and provide a brief description of the function of the structure beside each label. Please be neat. (16 marks) Page 11 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 10. Describe how the following events would change urine composition and output/volume: a. dehydration b. prolonged exercise and sweating c. drinking 3 liters of fluid d. excessive salt consumption e. excessive alcohol consumption 11. Explain how blood salt levels can influence blood volume and pressure. (3 marks) Page 12 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 12. Compare and contrast the role of ADH and aldosterone in regulating blood pressure. (5 marks) ~ END OF BIOLOGY 12 UNIT 14 LEARNING GUIDE ~ Page 13 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 UNIT 14 ANSWER KEY 14 PRACTICE: URINARY SYSTEM 1. Define excretion. (2 marks) = removal of metabolic wastes (undesirable byproducts of cellular activities) from the body 2. Identify the substances excreted by the following structures. (5 marks) a. sweat glands = removal of water, salt and urea (a nitrogenous byproduct of preotein metabolism) b. lungs = removal of CO2 (a byproduct or cellular respiration) c. liver = removal of old red blood cells including their pigments and nitrogenous byproducts from protein metabolism (further processed out of blood by kidneys) d. kidneys = production of urine which contains multiple waste products from cellular metabolism e. large intestine = excrete excess salts including of calcium and iron 3. Label the following diagram of the urinary system and provide a brief description of the function of the structure beside each label. Please be neat (8 marks) Page 14 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 4. Label the following diagram of a kidney and provide a brief description of the function of the structure beside each label. You only need to label and describe the structures indicated with letters. Please be neat. (8 marks) A. C. D. E. 5. Describe the various ways that water enters and exits the human body. (4 marks) - Enter by drinking and food consumption - Exits by exhalation, perspiring, tears, expectorating (spitting), defecation and urination 6. Compare and contrast the composition of blood plasma to the composition of urine. (4 marks) - Plasma should be ~ 90% water and contain a variety of proteins, salts, nutrients (including glucose) and wastes (especially if it has not been recently processed through the kidneys - Urine should be mostly water and contain some salts, pigments from old red blood cells, nitrogenous wastes, other metabolic wastes yet it should lack proteins and nutrients (such as glucose) 7. List the key substances that are selectively reabsorbed by the proximal convoluted tubule. (6 marks) - Nutrients such as amino acids, glucose, vitamins, mineral and salts as well as some water 8. List the key substances that are excreted by the distal convoluted tubule. (4 marks) - Excess hydrogen ions, histamine, antibiotics such as penicillin if they are being taken, ammonia (a nitrogenous byproduct of protein metabolism) Page 15 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 9. Label the following diagram of a nephron and provide a brief description of the function of the structure beside each label. Please be neat. (16 marks) G. Renal arteriole carrying unfiltered (dirty) blood into nephron F. Glomerulus = knot of capillaries where pressure filtration occurs forcing water, nutrients and waste out of blood of glomerulus and into Bowman's (glomerular) capsule E. Bowman's capsule = collects filtrate from the glomerulus H. Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) = selective reabsorption of nutrients such as glucose, salts, minerals and amino acids back into blood from filtrate B. Descending Arm of Loop of Henle = pump salt out of tubule creating an osmotic gradient C. Ascending Arm of Loop of Henle = water exits tubule following the osmotic gradient created by the salt such that it can be reabsorbed into the blood I. Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) = tubular excretion where excess hydrogen ions, histamine, ammonia and antibiotics such as penicillin are excreted from the blood into the tubule J. Peritubular Caplillary Network = where salt and water is reabsorbed from tubule/tissue into blood D. Renal venule carrying filtered blood A. Collecting duct = collects concentrated urine from multiple nephrons Page 16 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 10. Describe how the following events would change urine composition and output/volume: a. Dehydration = less urine, more concentrated b. prolonged exercise and sweating = less urine, more concentrated c. drinking 3 liters of fluid = more urine, less concentrated d. excessive salt consumption = less urine, more concentrated as high blood salt leads to water retention e. excessive alcohol consumption = more urine, less concentrated as alcohol interferes with the antidiuretic hormone (ADH) such that less water is reabsorbed from the urine into the blood 11. Explain how blood salt levels can influence blood volume and pressure. (3 marks) = high blood salt levels create blood that is hypertonic to urine such that more water is reabsorbed into the blood, this increases blood volume which in turn increases blood pressure. 12. Compare and contrast the role of ADH and aldosterone in regulating blood pressure. (5 marks) = both ADH (antidiuretic hormone) and aldosterone are released in response to low blood pressure and lead to feedback mechanisms that help to increase blood pressure however they are released from different areas of the body in response to different triggers =ADH is released by the pituitary gland when the hypothalamus detects a high blood salt concentration which is indicative of low blood pressure (recall concentration = salt/water and if you decrease the volume of water you have a high salt concentration, low blood volume and low blood pressure), ADH then targets the DCT and collecting duct such that more water is reabsorbed from the urine into the blood thereby increasing blood volume and pressure = Aldosterone is released by the adrenal gland when low blood pressure is detected by the kidney; when the kidney detects low blood pressure it releases renin which converts inactive angiotensin into active angiotensin I and II; angiotensin II causes the blood vessels of the kidney to constrict thereby raising the local blood pressure; Angiotensin II also causes the adrenal glands to release aldosterone which causes the kidneys to increase salt and water reabsorption from the urine into the blood thereby increasing blood volume and pressure throughout the entire body Page 17 of 17