Trachte-Fungal
advertisement

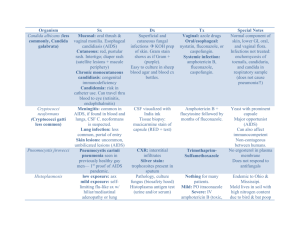
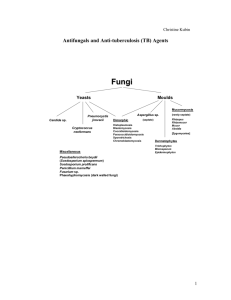
Trachte: Antifungals Causes of fungal infections: Superinfection from using broad spectrum Abx Use of immunosuppressive agents, which body’s host-defense mechanisms Diseases that resistance to infection Tx depends on: Immune status of patient Resistance considerations CNS involvement Systemic vs superficial Basis for Selective Toxicity: ergosterol is the major membrane lipid in fungi (in mammals: cholesterol) Severity of the infection Antifungals: Used for systemic / deep or superficial mycoses? Systemic / Deep Superficial (mostly topical / sometimes systemic) Amphotericin B, Flucytosine, Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Voriconazole, Capsofungin Nystatin, Amphotericin B, Terbinafine, Griseofulvin, Miconazole, Ketoconazole, Clotrimazole Drug Amphotericin B (Polyene) Flucytosine MOA Alters sterol-containing cell membranes: bind sterol, form pores in lipid bilayer Ergosterol > cholesterol Selectivity: Host cells don’t take flucytosine Host cells don’t convert flucytosine to 5-fluorouracil Spectrum Systemic CIDAL (in absence of cell growth) STATIC @dose Toxicity Nephro (80%) GFR (can be permenant w/dose. w/new drugs that contain lipids) Resistance -Acquired=less common -Fungi with ability to synth ergosterol -Mutant fungi w/ quantities of other sterols Cardiotox: w/rapid infusion (give slow) < AmpB Other: chills/fever, BP, delirium, N/V, thrombophlebitis Reversible neutropenia and occasional thrombocytopenia Nausea Skin rashes, eosinophilia Intolerable in AIDS pts Combo of AmpB and Flucytosine: Resistance. Synergistic / Additive effect Amphotericin B activity may allow more uptake of flucytosine The dose of Amphotericin B can be lowered and decrease nephrotoxicity from Amph B. Amphotericin B may enhance the toxicity of flucytosine by impairing its renal excretion Route: CNS Pen: Toxicity: Spectrum: Resistance: uptake and conversion to 5fluorouracil and 5-FUMP (use in combo w/other drugs) AmpB Flucytosine IV No > > < Oral Yes < < > Distrib/Elim Absorption: GI: bad CNS: bad w/IV, give intrathecal. Slow renal excret. Long tissue ½ life Oral. Goes to CNS. Kidney excretion. No metabolism Renal Impaired: no change modify dose Caspofungin = echinocandin MOA: Blocks the synthesis of Beta (1,3)-d-glucan (polysaccharide part of fungi cell wall) Uses: Candidiasis, invasive aspergillosis SE: fever, rash, nausea, vomiting and phlebitis at the injection site AZOLES: MOA: Inhibit the fungal enzyme sterol 14-alpha-demethylase, a microsomal cytochrome P450 - dependent enzyme system o Impaired biosynthesis of ergosterol for the cytoplasmic membrane o Leads to accumulation of 14-alpha-methyl sterols and disruption of the phospholipids in the fungal membrane o Resistance via multiple mechanisms Selective Toxicity: Differential requirement for ergosterol. Greater affinity for fungal rather than human cytochrome P450 enzymes Consequences of inhibition of human cytochrome P450 enzymes o Interfere with biosynthesis of adrenal and gonadal steroid hormones Gynecomastia (abnormal development of male mammary glands), infertility and menstrual irregularities o Potential for drug interactions: Alters the metabolism of other drugs Imidazoles Ketoconazole Clotrimazole Miconazole Econazole Butoconazole Oxiconazole Sulconazole Triazoles Fluconazole Itraconazole Voriconazole Terconazole With systemic administration: •Triazoles are more slowly metabolized than imidazoles, thus longer duration of action •Triazoles have less effect on human sterol synthesis than do imidazoles •Triazoles are replacing use of imidazoles, especially in systemic infections Imidazoles (Keto = prototype) = Most effective during active fungal growth Fewer adverse effects than Amphotericin B Orally available. Doesn’t penetrate the CNS. Liver metabolism (toxicity) Dose dependent decrease in serum testosterone, gynecomastica, menstrual irregularities No longer drug of first choice in systemic fungal infections Triazoles = Itraconazole, Fluconazole, Voriconazole More slowly metabolized Less effect on human sterol synthesis V: Best activity against Aspergillus, but drug interactions F: Penetrates CNS. Fewer drug interactions In General: Imidazoles and triazoles (‘azoles’) are better tolerated than Amphotericin B and Flucytosine. The 'azoles' may decrease effectiveness of Amphotericin B by inhibiting ergosterol synthesis and decreasing the binding of Amphotericin B. The ‘azoles’ are replacing Amphotericin B and Flucytosine in many situations. In general, Amphotericin B and Flucytosine are used when more aggressive treatment is needed. Superficial Infections: AZOLES: Miconazole, Ketoconazole, Clotrimazole, (Not metronidazole d/t interactions w/EtOH) Polyenes: Nystatin, AmpB (not absorbed from skin/mucous membranes; no AE/resistance) Terbinafine: MOA: Inhibits squalene epoxidase, leading to accumulation of squalene which is toxic to the fungi (thus fungicidal) o Given orally for superficial infections, also used topically. Binds to keratin and protects the skin from infection fungal toenail infections. AE rare. Pneumocystis jiroveci lung infections: Treat with Trimethoprim & sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) - Trimetrexate is another effective agent Organism does not possess a folate transporter. Very susceptible to folate metabolism inhibitors Antifungal Drug Classes Class MOA Allylamin Inhibits squalene epoxidase (blocks ergosterol synth) Azole Impairs ergosterol synth Echinocandin Impairs B 1,3 glucan synthesis Nucleoside analog Impairs Pyrimidine metabolism Polyene Binds to ergosterol, prevents cell wall growth Drugs Terbafine Ketoconazle. Fluconazole. Itraconazole. Voriconazole Caspofungin Flucytosine AmpB deoxycholate. AmpB colloidal dispersion. AmpB lipid complex. Liposomal ampB Treatment of invasive fungal infections: Aspergillosis: Voriconazole, Lipid AmpB, Caspofungin Candidiasis: Fluconazole (esophagus, blood). Caspofungin, AmpB deoxycholate (esophagus & blood, refr to Fluc) Cryptococcosis: AmpB / lipid AmpB + flucytosine (meninges) Febrile neutropenia: liposomal AmP, voriconazole.