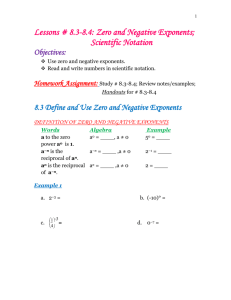
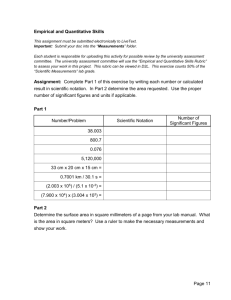
Grade Level: 8 Subject: Mathematics Unit Topic: Radicals and
advertisement

Grade Level: 8 Subject: Mathematics Standard(s): (bold the priority standards) Unit Topic: Radicals and Integer Exponents Explanations and Examples: Length of Unit: 3 Weeks 8.EE.1 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, 32 × 3–5 = 3–3 = 1/33 = 1/27. 8.EE.1 Integer (positive and negative) exponents are further used to generate equivalent numerical expressions when multiplying, dividing or raising a power to a power. Using numerical bases and the laws of exponents, students generate equivalent expressions. 8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. 8.EE.2 Students recognize that squaring a number and taking the square root √ of a number are inverse operations; likewise, cubing a number and taking the cube root 3 are inverse operations. This understanding is used to solve equations containing square or cube numbers. Equations may include rational numbers such as x2 = 1 /4, x2 = 4 /9 or x3 = 1/8 (NOTE: Both the numerator and denominators are perfect squares or perfect cubes.) Students recognize perfect squares and cubes, understanding that non-perfect squares and non-perfect cubes are irrational. Students understand that in geometry a square root is the length of the side of a square and a cube root is the length of the side of a cube. The value of p for square root and cube root equations must be positive. 1Retrieved from www.corestandards.org, p.3, Introduction: Common Core State Standards for Mathematics. Revised 6/2013 8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. For example, estimate the population of the United States as 3 times 108 and the population of the world as 7 times 109, and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger. 8.EE.4 Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific Page 2 of 7 8.EE.3 Students express numbers in scientific notation. Students compare and interpret scientific notation quantities in the context of the situation. If the exponent increases by one, the value increases 10 times. Students understand the magnitude of the number being expressed in scientific notation and choose an appropriate corresponding unit. For example, 3 x 108 is equivalent to 30 million, which represents a large quantity. Therefore, this value will affect the unit chosen. 8.EE.4 Students use laws of exponents to multiply or divide numbers written in scientific notation. Additionally, students understand scientific notation as generated on various calculators or other technology. Revised 6/2013 notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. Students can convert decimal forms to scientific notation and apply rules of exponents to simplify expressions. In working with calculators or spreadsheets, it is important that students recognize scientific notation. Students should recognize that the output of 2.45E+2 3 is 2.45 x 1023 and 3.5E-4 is 3.5 x 10-4. Students enter scientific notation using E or EE (scientific notation), * (multiplication), and ^ (exponent) symbols. Concepts:(What students need to Skills:(What students need to be able to do) Blooms / DOK Levels: know) Apply 2/1 Integers Generate 1/3 Exponents Evaluate 4/3 Square root Estimate 2/2 Cube root Express 1/2 Solution Perform 2/1 Equation Choose 1/3 Rational number Interpret 4/4 Perfect Cubes Perfect Squares Irrational Power of 10 Operations Scientific Notation Decimal Expansion Essential Questions: (Open-ended questions that the students Corresponding Big Ideas: (Foundational understandings that should be able to answer by the end of the unit) students need to discovered by the end of the unit) How is equivalency shown in Algebra? Large numbers that have factors that are repeated can be written as a product of powers. Why is it helpful to write numbers in different ways? Scientific notation allows for easy recognition of the How are square and cube roots related? magnitude of values for comparison purposes. How can you develop and use the properties of integer Mathematical operations can be performed efficiently exponents? on numbers written in scientific notation. How do you add, subtract, multiply, and divide using scientific Students become much more adept at learning new notation? concepts when they are provided opportunities to How do you estimate and compare irrational numbers? interact with the content from different vantage points. What are the similarities and differences between a number Calculations involving expressions with exponents can written in scientific notation and the calculator notation of the be solve more efficiently by using properties of powers. number shown on a screen? Page 3 of 7 Revised 6/2013 What is the difference between an exact value and an approximate value? Vocabulary: Mathematical Practices: Resources: (Practices in bold are to be emphasized in the Integers Engage NY unit.) http://www.engageny.org/sites/default/files Exponents /resource/attachments/g8-m1-module Square Root 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in overview-and-assessments.pdf Cube Root solving them. ALEX Lesson Plans Solution 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. http://alex.state.al.us/lesson_view.php?id= Equation 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the 26292 Rational Number reasoning of others. PBS.org Perfect Cubes 4. Model with mathematics. http://www.pbs.org/teachers/mathline/con Perfect Squares 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. cepts/space2/activity3.shtm Irrational Numbers 6. Attend to precision. WALCH Education Power of 10 7. Look for and make use of structure. Center on Disability Studies Operations 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated Scientific Notation reasoning. Assessment for Learning: (How do you know the student has mastered the standards? Include both Pre and Post Assessments) Pre-Assessment and Scoring Rubric Radicals and Integer Radicals and Integer Exponents Pre-Unit Assessment.docx Exponents Pre-Assessment Scoring Rubric.docx Post-Assessment and Scoring Rubric Radicals and Integer Radicals and Integer Exponents Post-Unit Assessment.docx Exponents Post-Assessment Scoring Rubric.docx Engaging Learning Experiences Task The Laws of Exponents http://alex.state.al.us/lesson_vi ew.php?id=26292 Page 4 of 7 Description: (Standards addressed, Blooms / DOK Levels, links to rubric, resources, instructional strategies, etc.) Suggested Length of Time Standards Addressed: 8.EE.1 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. Blooms Level/DOK 5/2 61 – 90 Minutes Revised 6/2013 The Laws of Exponents.pdf Around the World in 0.1345 Seconds Web Quest http://www.webquest.hawaii.ed u/kahihi/webquests/math/grade 7/MA7.1.2world/intro.php The Capacity of the Planets http://www.pbs.org/teachers/m athline/concepts/space2/activit y3.shtm The Capacity of the Planets.pdf Rubric/Resources Rubric included in attachments on website Standards Addressed: 8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. 8.EE.4 Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. Blooms Level/DOK 2/2 Rubric/Resources Rubric for final project included in Web Quest Standards Addressed: 8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. 8.EE.4 Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. Blooms Level/DOK 2/2 Rubric/Resources Answer Key Attached 60 Minutes 20 Minutes The Capacity of the Planets Answer Key.pdf Page 5 of 7 Revised 6/2013 Exponents and Scientific Notation Station Rotation Standards Addressed: 8.EE.1 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, 32 × 3–5 = 3–3 = 1/33 = 1/27. Exponents and 8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to Scientific Notation Station Rotation.pdf equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. 8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. 8.EE.4 Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. Blooms Level/DOK 3/2 Rubric/Resources All needed resources and rubrics included in Document Integer Exponents and Standards Addressed: Scientific Notation 8.EE.1 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, 32 × 3–5 = 3–3 = 1/33 = 1/27. Integer Exponents 8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to and Scientific Notation.pdf equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. 8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. 8.EE.4 Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. Page 6 of 7 60 Minutes 2 – 60 Minute Classes Revised 6/2013 Blooms Level/DOK 3/3 Rubric/Resources All needed resources and rubrics included in attachment Page 7 of 7 Revised 6/2013