Timeline 2012
advertisement

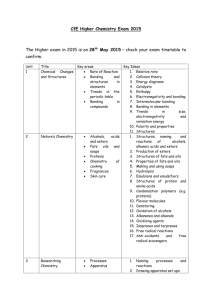
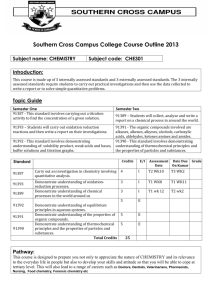
Catholic Regional College Sydenham Chemistry Timeline Unit Title : 2012 Week: School Calendar Title: Area of Study /Outcome Unit 3 Chemical Pathways Unit 4 Chemistry at Work CONTENT Assessment Term 1 1 Chemical Analysis 2 3 4 5 6 Chemical analysis in action, some case studies CH 1 Qualitative and quantitative analysis Analytical techniques utilise chemical and physical properties of substances. Overview of analytical techniques Measuring water content. Review the mole concept general gas equation, molar volume. Review determination of empirical and molecular formula. Calculations involving mass of reactants and products. Using gravimetric analysis to find the composition of a mixture. Concentration, standard solutions. Volumetric analysis; techniques and calculations. Review of acid–base chemistry. Review of pH. Indicators and pH curves. Calculations involving acid–base reactions. Acid–base titrations. Back titrations. Review of oxidation/reduction. Using oxidation numbers. Half-equations. Calculations involving redox reactions. Redox titrations. CH 2 CH 3/4 CH 4 CH 5 SAC 1A Principles of chromatography. Thin layer chromatography (TLC). High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Gas chromatography (GC). CH 6 The interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter. Overview of spectroscopic techniques. Flame colours and emission spectra. Principles and applications of atomic absorption spectroscopy. CH 7 SAC1B Catholic Regional College Sydenham Chemistry Timeline Unit Title : 2012 UV–visible spectroscopy and colorimetry; principles and applications. Principles and applications of infrared spectroscopy. CH 7 Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy—principles and applications. Principles, instrumentation, interpretation and applications of mass spectrometry. CH 8 Using a combination of techniques. Selecting an analytical techniques. Comparison of analytical techniques. Area of Study Review 7 8 9 Organic Chemical Pathways 10 11 12 13 Unit 3 Chemical Pathways Unit 4 Chemistry at Work END OF TERM ONE and EASTER Overview of bonding in carbon compounds. CH 9 Alkanes: bonding, structure, isomerism and nomenclature. Alkenes: bonding, structure, isomerism and nomenclature. Functional groups; bonding structure, isomerism and nomenclature in chloroalkanes, alkanols, carboxylic acids, amines. Reactions of alkane Reactions of alkenes. Reactions of; chloroalkanes, alkanols and carboxylic acids. CH 10/11 SAC 2 Esters; uses of esterification reactions, structure, bonding and nomenclature. (Extension polyesters) Reaction pathways. Fractional distillation. Fossil fuels, peak oil. CH 11/12 Biochemical fuels - ethanol - biodiesel - biogas. Why biofuels?. Condensation polymerisation. (General reaction mechanisms) Fats - structure of glycerol and fatty acids. - formation of triglycerides by condensation reaction. - saturated and unsaturated fats - hydrolysis of fats in the digestive system. Carbohydrates CH 12 Catholic Regional College Sydenham Chemistry Timeline Unit Title : 2012 Unit 3 Chemical Pathways Unit 4 Chemistry at Work - structure of glucose - formation of disaccharides - formation of polysaccharides 14 Proteins - amino acids - condensation reaction between amino acids, peptide bond - primary, secondary and tertiary structure of proteins. Enzymes: biological catalysts. CH 12 Proteins as disease markers. Overview of biomolecules. Function of DNA in living systems. CH 13 Structure and bonding in DNA nucleotide monomers; composition, structure and bonding, primary structure; condensation reaction between nucleotides, base sequence secondary structure; bonding between complementary base pairs; double helix tertiary structure, interaction with histones. 15 DNA and protein synthesis (brief outline only) DNA profiling, procedure and applications. Synthesis and use of aspirin. Penicillin. Proteins as medicines. Green synthesis of drugs. Developing new drugs. 16 CH 14 Area of Study Review 17 18 Semester 1 Ends June 6 Year 12 Orals Yr 11 Exams Year 11/12 Exams GAT 14 June REVISION AND CONSOLIDATION EXAM WEEK WORK SAC 3 Catholic Regional College Sydenham Chemistry Timeline 2012 Unit Title : Unit 3 Chemical Pathways Unit 4 Chemistry at Work UNIT 4 CHEMISTRY AT WORK Industrial Chemistry Everyday examples of fast and slow reactions. CH 15 Chemical reactions involve breaking and making bonds. Chemical energy, enthalpy, exothermic and endothermic reactions, ΔH notation. Energy profile diagrams, activation energy. 1 Semester 2 commences CH 15 Factors affecting the rate of reaction; surface area, concentration, temperature, catalysts Explanation in terms of collision theory. Catalysts. Examples of incomplete and reversible reactions. CH 16 Dynamic nature of chemical equilibrium. 2 Equilibrium law expression. Equilibrium law calculations. Le Chatelier’s principle; effect of changing concentration, pressure, volume, temperature, and addition of a catalyst. Competing equilibria (Extension). Equilibrium overview Term 3 3 4 Kw CH 17 Relative concentrations of H3O+ and OH– in acidic, neutral and basic solutions. Definition of pH, calculations involving pH. Effect of temperature on pH. Acidity constants expression Ka and acid strength; calculations involving Ka Buffers (extension) Chemical industry overview. CH 18 Operational issues; optimum conditions, yield, energy, costs. Health and safety issues; dangerous goods, hazardous substances, MSDS. Waste management, origin and fate of industrial chemicals. Waste management practices. Principals of green chemistry revisited. Community concerns. Siting a chemical plant; factors for consideration (Extension) SAC 1A and SAC 1B Catholic Regional College Sydenham Chemistry Timeline Unit Title : 2012 5 Unit 3 Chemical Pathways Unit 4 Chemistry at Work Uses of sulfuric acid. CH 21 Contact process, reactions, equilibrium and rate considerations, optimal operational conditions. Waste management, green chemistry considerations. Health and safety Area of Study Review 6 Supplying and Using Energy 7 8 9 Energy usage. Energy converters. Fossil fuels, use and reserves - coal - oil - natural gas sustainability of fossil fuels. CH 23/24 Nuclear energy, fission reactions, waste, advantages and disadvantages; reserves Biochemical fuels, biogas, ethanol, bio-diesel. CH 24 Other renewable energy sources. Comparison of energy sources. Revise energy of chemical reactions and bond energies; ΔH notation. CH 25 Introduction to thermochemical equations. Calculations involving thermochemical equations. Energy and temperature rise. Heats of reaction; solution and bomb calorimetry, calibration of calorimeter. Calculations. Heat of combustion; comparison of energy of fuels The Daniell cell; reactions, movement of electrons and ions; CH 26/27 half-cells, salt bridge. Cell Equations. (Half and Full equations.) Electrochemical series; relative oxidising and reducing strengths; standard conditions. Potential difference. Predicting redox reactions, limitations of predictions. Primary cells, examples and applications, anode and cathode reactions. Examples, zinc carbon dry cell, alkaline cells, silver–zinc button cell, lithium cells. SAC 2 Catholic Regional College Sydenham Chemistry Timeline 2012 10 Unit Title : Unit 3 Chemical Pathways Unit 4 Chemistry at Work Secondary cells, e.g. lead–acid accumulator, CH 27 nickel cadmium and nickel hydride cells. Application; anode and cathode reactions Reactions involved in recharging secondary cells. What are fuel cells? Types of fuel cells and their applications. Anode and cathode reactions involving fuel cells. Advantages and disadvantages of fuel cells. Electrolysis as a non-spontaneous reaction. CH 28 Principles of electrolysis, e.g. simple electroplating cell. Faraday’s first and second laws, and calculations to determine mass metal deposited, current, charge and time. Competing electrode reactions. CH 28 Production of chemicals from electrolysis of : (i) molten electrolytes, e.g. sodium, aluminium (ii) aqueous electrolytes, e.g. chlorine, sodium, copper 11 12 Term 4 13 Modified Timetable Yr 12 Compulsory Trial Exams 14 Revision Exam practice EXAM REVISION EXAM REVISION 15 16 Area of Study review Melbourne Cup Holidays Exams commence EXAM REVISION EXAM REVISION FOR CHEMISTRY CONTINUES SAC 3