Grade 4 - Science (revised 8/16/15)
advertisement
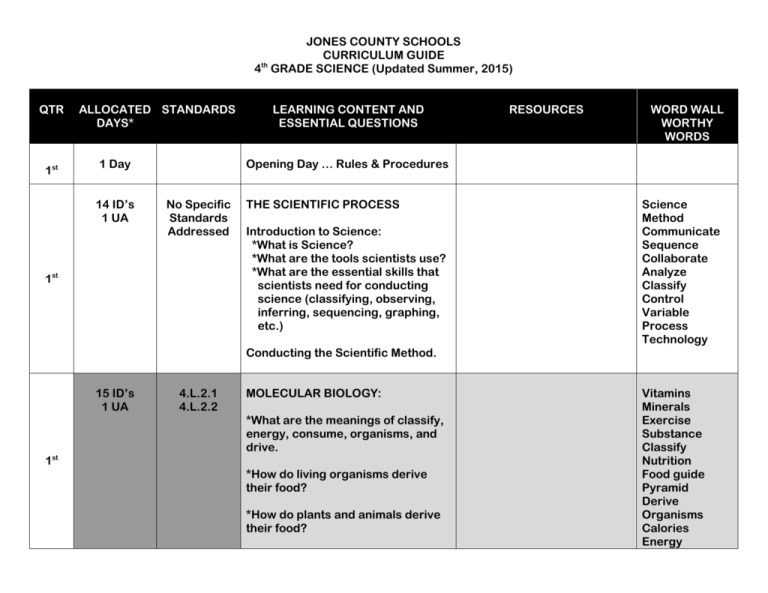
JONES COUNTY SCHOOLS CURRICULUM GUIDE 4th GRADE SCIENCE (Updated Summer, 2015) QTR 1st ALLOCATED STANDARDS DAYS* 1 Day 14 ID’s 1 UA LEARNING CONTENT AND ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS RESOURCES WORD WALL WORTHY WORDS Opening Day … Rules & Procedures No Specific Standards Addressed 1st THE SCIENTIFIC PROCESS Introduction to Science: *What is Science? *What are the tools scientists use? *What are the essential skills that scientists need for conducting science (classifying, observing, inferring, sequencing, graphing, etc.) Science Method Communicate Sequence Collaborate Analyze Classify Control Variable Process Technology Conducting the Scientific Method. 15 ID’s 1 UA 1st 4.L.2.1 4.L.2.2 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: *What are the meanings of classify, energy, consume, organisms, and drive. *How do living organisms derive their food? *How do plants and animals derive their food? Vitamins Minerals Exercise Substance Classify Nutrition Food guide Pyramid Derive Organisms Calories Energy *What are the meanings of vitamins, minerals, exercise, development, essential, healthy, body systems, and maintenance? *What is the role of vitamins for humans? Dietary Consume Ingest Supplements Maintenance Body systems *What foods do humans find vitamins and minerals in? *What is the importance of exercise to humans? 15 ID’s 1 UA 4.E.1.1 4.E.1.2 EARTH & THE UNIVERSE: *What are the meanings of rotation, revolve, revolution, lights rays, seasons, and axis. *How long does a rotation and revolution take of the Earth. *How do the seasons occur? 1st *What are the meanings of phases, waxes, wanes, new moon, first quarter, full moon, last quarter, repeat, visible portion, shadow) (Extensions: eclipse) *What are the four phases of the moon? *How is the moon’s appearance determined and what is the time frame for this? Orbit Axis Phases Waxes Wanes New Moon First Quarter Full Moon Last Quarter Rotates Revolves Shadow Seasons Eclipse Visible Portion Revolution Rotation 15 ID’s 1 UA 4.E.2.1 4.E.2.2 4.E.2.3 EARTH HISTORY: *What are the meanings of fossils, molds, casts, preserved, evidence, lithosphere, Earth’s surface, Earth’s crust, weathering, landslide, earthquake, volcanic eruption. *Why are fossils important as evidence of Earth’s history? *What are some ways that fossils share characteristics? *How are organisms of the past similar or different to organisms of today? 2nd *How do living organisms today leave fossil or fossil-like evidence? *How do fossils provide indications of environmental conditions from the past? *How has the surface of Earth changed over time? *Describe the difference between drastic, slow, and rapid changes on Earth’s surface. *What are the natural occurrences that can shape the surface of Earth. *Describe the effect of water on rocks on Earth’s surface. Fossil Molds Casts Preserved Weathering Landslide Earthquake Volcanic Eruption Organisms Characteristics Evidence Earth’s surface Lithosphere Drastic Rapid Gravity Pressure Crust 25 ID’s 1 UA 4.L.1.1 4.L.1.2 4.L.1.3 4.L.1.4 ECOSYSTEMS: *What is the meaning of behavior, population, habitats, organism, environment, beneficial, harmful, response, surviving, advantageous, frequented, decreased, disease, scenario, stressed, reduced, instinct, recycling, adapt, habitat, variation. *Why do some plants and animals survive well in some environments and other do not. 2nd *What are some advantageous situations in different environments? Disadvantageous? *What are the needs of an animal? *What affect does the five senses have within an environment? *What are instinctive behaviors that helps an animal survive? *Explain the relationship between the brain and survival in in an environment. *How do animals/human adapt to live in an environment. *Distinguish between learned and innate adaptations. Behavior Population Habitats Adapt Instinct Ecology Organisms Environment Beneficial Harmful Response Survival Advantageous Frequented Scenario Adaptations Habitat Variation Senses Preserve Conserve Exhibit 20 ID’s 1 UA 4.P.2.1 4.P.2.2 4.P.2.3 MATTER: PROPERTIES & CHANGE *What is the meaning of attract, reaction, properties, hardness, conduct, dissolve, evaporate, color luster, streak, cleavage, Moh’s Hardness Scale, mineral, composition, metamorphic, igneous, sedimentary, particles, classify, transformed. *What are the observable properties of matter? 3rd *How are samples of matter described? *How do you test for hardness, flexibility, ability, conduction, magnetism in samples of matter? *What tests can be used to identify minerals? Composition Metamorphic Igneous Sedimentary Properties Hardness Luster Streak Cleavage Color Moh’s Hardness Scle Evaporate Dissolve Reaction Attract Flexibility Mineral Classify Particles Transformed Conduct Rock cycle *How are rocks classified? *What is the processes involved in the rock cycle? 20 ID’s 1 UA 3rd 4.P.3.1 4.P.3.2 4.P.3.3 ENERGY: CONSERVATION & TRANFORMATION *What is the meaning of light, heat, sound, electrical, energy. *How does energy flow in a circuit? Light Energy Sound Energy Heat Energy Electrical Energy Magnetic Energy *What energy is generated from within a circuit? *How does light travel and what can happen to light? 20 ID’s 1 UA 4.P.1.1 4.P.1.2 FORCES & MOTION *What is the meaning of magnet, north pole, south pole, metal, attract, repulsion, force field, discharge, electricity, electric charge. *What is the effect of a magnet and materials made of iron? 4th *How can you identify the force field of a magnet? *How does electric charges work on an object? *Provide an example of changes in electrical charges. 4th 4th 20 ID’s 1 UA END OF YEAR REVIEW NORTH CAROLINA FINAL EXAM, (if needed) Motion Change Thermal Circuit Transfer Refraction Reflection Absorption Medium Iron Electricity Electric charge Metal Force field Repulsion Discharge Magnet North pole South pole Attraction Magnetism *ALLOCATED DAYS ID = Instructional Days UA = Unit Assessment (via SchoolNet or Discovery Education)