File
advertisement

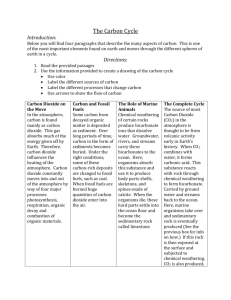
Project 2 ABC Biodegradable: a material capable of being decomposed by bacteria or other living organisms and thereby avoiding pollution Carbon dioxide: The gas thought to cause global warming. Made from one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. Carbon footprint: The amount of CO2 we each emit every year taking into account transport, electricity use and the products we buy. Carbon cycle: How carbon moves between the atmosphere, plants, animals and the soil. DEF Fossil fuels: Coal, oil Climate change: Long term and gas, formed from the fossilization of changes in global animals and plants temperatures- evidence Decomposer: Bacteria suggests that the earth is or fungi - organisms getting hotter. Combustion: ‘Burning’ - fuel that consume (eat) dead organisms. + oxygen → water + carbon dioxide. Condensation: The process of changing from gas to liquid. Consumer: 1) A person who buys things 2) An organism that consumes (eats) another organism GHI Global warming: Long term changes in global temperatures- evidence suggests that the earth is getting hotter. Glacier: Large permanent sheets of ice. JKL MNO P Photosynthesis: When plants use the sun’s energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (plant food) and oxygen. Pollution: the presence in or introduction into the environment of a substance which has harmful or poisonous effects. QR STU Sustainable: something that can be maintained/not run out. Respiration: When living things release energy from food. This requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide and water as waste products. VWXYZ Project 1 ABC Closed loop system: A system where everything is recycled and reused, nothing gets ‘lost’ or ‘wasted’ (natural systems are usually closed loop e.g. water cycle) Combustion: ‘Burning’ fuel + oxygen → water + carbon dioxide. Condensation: The process of changing from gas to liquid. Consumer: 1) A person who buys things 2) An organism that consumes (eats) another organism Consumer Product: An item that can be bought in a shop. Cradle-to-cradle design: An item designed specifically so that it can be recycled easily. DEF Fossil fuels: Coal, oil and gas, formed from the fossilization of animals and plants Evaporation: Process of changing from liquid to a gas. Decomposer: Bacteria or fungi - organisms that consume (eat) dead organisms. Downcycling: When a product is used to make something of less value than that of the original product. GHI Global warming: Long term changes in global temperatures- evidence suggests that the earth is getting hotter. Glacier: Large permanent sheets of ice. JKL Linear system: Systems where by not everything is reused. Current manufacturing systems are linear as most waste ends up in landfill. Landfill: the disposal of waste material by burying it MNO Natural materials: Materials that exist naturally e.g. rock, bone, plant litter. Malleable: A material that can be bange and bent into shape without shattering (metals are malleable) PQR Pollution: the presence in or introduction into the environment of a substance which has harmful or poisonous effects. Respiration: When living things release energy from food. This requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide and water as waste products. Recycling: Reusing materials. STU Technical materials: ‘Man-made’ materials, non-biodegradable Toxic: chemicals that can be poisonous to living organisms. Technical materials often make the soil toxic. Sustainable: something that can be maintained/not run out. Upcycling: When a product is used to make something of a greater value than that of the original product. VWXYZ Water cycle: How water molecules are cycled between land, air and sea/lakes etc. Waste: A product or material that is no longer useful or required. Biodegradable A material capable of being decomposed by bacteria or other living organisms Carbon dioxide The gas thought to cause global warming. Made from one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. Carbon footprint The amount of CO2 we each emit every year taking into account transport, electricity use and the products we buy. Carbon cycle How carbon moves between the atmosphere, plants, animals and the soil. Climate change Long term changes in global temperaturesevidence suggests that the earth is getting hotter. Combustion ‘Burning’ - fuel + oxygen → water + carbon dioxide. Condensation The process of changing from gas to liquid. Consumer 1) A person who buys things 2) An organism that consumes (eats) another organism Fossil fuels Coal, oil and gas, formed from the fossilization of animals and plants Power station A place where electricity is produced - often through the burning of fossil fuels e.g. coal, oil, or nuclear. Solar energy Capturing energy from the sun for other uses e.g. heating. Decomposer Bacteria or fungi organisms that consume (eat) dead organisms, breaking them down. * Global warming Long term changes in global temperaturesevidence suggests that the earth is getting hotter. Glacier Large permanent sheets of ice. Pollution The presence in or introduction into the environment of a substance which has harmful or poisonous effects. Respiration When living things release energy from food. This requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide and water as waste products. Sustainable Something that can be maintained/not run out. Photosynthesis ENERGY! ENERGY! When plants use the sun’s energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (plant food) and oxygen. Biodegradable Carbon dioxide Carbon footprint Carbon cycle Climate change Combustion Condensation Consumer Fossil fuels Power station Solar energy Decomposer * Global warming Glacier Pollution Respiration Sustainable ENERGY! Photosynthesis A material capable of being decomposed by bacteria or other living organisms The gas thought to cause global warming. Made from one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. The amount of CO2 we each emit every year taking into account transport, electricity use and the products we buy. How carbon moves between the atmosphere, plants, animals and the soil. Long term changes in global temperatures- evidence suggests that the earth is getting hotter. ‘Burning’ - fuel + oxygen → water + carbon dioxide. The process of changing from gas to liquid. 1) A person who buys things 2) An organism that consumes (eats) another organism Coal, oil and gas, formed from the fossilization of animals and plants A place where electricity is produced - often through the burning of fossil fuels e.g. coal, oil, or nuclear. Capturing energy from the sun for other uses e.g. heating. Bacteria or fungi - organisms that consume (eat) dead organisms, breaking them down. Long term changes in global temperatures- evidence suggests that the earth is getting hotter. Large permanent sheets of ice. The presence in or introduction into the environment of a substance which has harmful or poisonous effects. When living things release energy from food. This requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide and water as waste products. Something that can be maintained/not run out. ENERGY! When plants use the sun’s energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (plant food) and oxygen.