Nursing Care Plan
advertisement
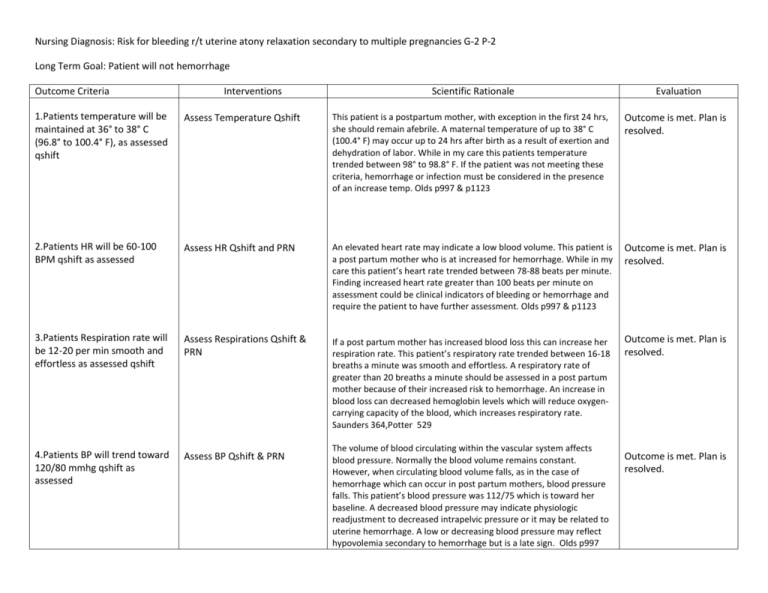
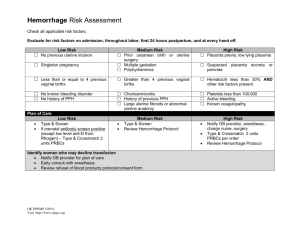
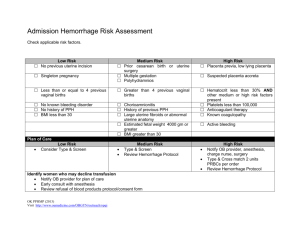
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for bleeding r/t uterine atony relaxation secondary to multiple pregnancies G-2 P-2 Long Term Goal: Patient will not hemorrhage Outcome Criteria Interventions Scientific Rationale Evaluation 1.Patients temperature will be maintained at 36° to 38° C (96.8° to 100.4° F), as assessed qshift Assess Temperature Qshift This patient is a postpartum mother, with exception in the first 24 hrs, she should remain afebrile. A maternal temperature of up to 38° C (100.4° F) may occur up to 24 hrs after birth as a result of exertion and dehydration of labor. While in my care this patients temperature trended between 98° to 98.8° F. If the patient was not meeting these criteria, hemorrhage or infection must be considered in the presence of an increase temp. Olds p997 & p1123 Outcome is met. Plan is resolved. 2.Patients HR will be 60-100 BPM qshift as assessed Assess HR Qshift and PRN An elevated heart rate may indicate a low blood volume. This patient is a post partum mother who is at increased for hemorrhage. While in my care this patient’s heart rate trended between 78-88 beats per minute. Finding increased heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute on assessment could be clinical indicators of bleeding or hemorrhage and require the patient to have further assessment. Olds p997 & p1123 Outcome is met. Plan is resolved. 3.Patients Respiration rate will be 12-20 per min smooth and effortless as assessed qshift Assess Respirations Qshift & PRN If a post partum mother has increased blood loss this can increase her respiration rate. This patient’s respiratory rate trended between 16-18 breaths a minute was smooth and effortless. A respiratory rate of greater than 20 breaths a minute should be assessed in a post partum mother because of their increased risk to hemorrhage. An increase in blood loss can decreased hemoglobin levels which will reduce oxygencarrying capacity of the blood, which increases respiratory rate. Saunders 364,Potter 529 Outcome is met. Plan is resolved. 4.Patients BP will trend toward 120/80 mmhg qshift as assessed Assess BP Qshift & PRN The volume of blood circulating within the vascular system affects blood pressure. Normally the blood volume remains constant. However, when circulating blood volume falls, as in the case of hemorrhage which can occur in post partum mothers, blood pressure falls. This patient’s blood pressure was 112/75 which is toward her baseline. A decreased blood pressure may indicate physiologic readjustment to decreased intrapelvic pressure or it may be related to uterine hemorrhage. A low or decreasing blood pressure may reflect hypovolemia secondary to hemorrhage but is a late sign. Olds p997 Outcome is met. Plan is resolved. Potter 536 Outcome Criteria 5. The fundus will decrease one fingersbreadth daily, assessed qshift Interventions Scientific Rationale Assess Fundus height qshift and Assessing the height of the fundus gives information about the prn progress of involution. Although postpartum hemorrhage often occurs within hours of birth, a delayed hemorrhage can occur due to subinvolution which is failure to return to normal size. This patient’s fundus was progressing well 2 fingerbreadths below this umbilicus on second day post partum. Olds 1008,1120 Evaluation Outcome is met. Plan is resolved. This patient’s fundus was firm which indicates that the uterine muscles are contracted and bleeding will not occur. Her fundus was also midline. The fundus can deviate from midline when bladder is full because enlarged bladder pushes uterus aside. During postpartum period because of diuresis the bladder may fill more rapidly than normal, putting the woman at risk for uterine atony and hemorrhage. Olds 1008 Outcome is met. Plan is resolved. The postpartal woman has an increased bladder capacity, swelling and bruising of the tissues around the urethra, decreased sensitivity to fluid pressure and decreased sensation to bladder filling. A full bladder may also increase the tendency of the uterus to relax by displacing the uterus and interfering with contractility, leading to hemorrhage. This patient voided as needed, urine output average 60 ml/hr while in my care. Olds p997 Outcome is met. Plan is resolved. Evaluation of lochia is necessary not only to determine the presence of hemorrhage but also to assess uterine involution. Persistent discharge of lochia rubra indicates subinvolution or late postpartum hemorrhage. This patient is day 2 postpartum has a moderate amount of lochia with earthy small and no clots. Length of lochia rubra phase lasts longer then generally assumed. Olds p993 Outcome is met. Plan is resolved. 6. The fundus will remain firm and midline qshift as assessed Assess fundal firmness and position qshift & PRN 7. Patient will void 30ml per/hr as assessed qshift Assess urine output qshift 8. Patients lochia will trend toward lighter amount of flow and color with no clots and earthy odor assessed q shift Assess Lochia q shift and prn Outcome Criteria 9. Patient will verbalize trends in lochia q shift Interventions Teach patient trends in lochia q shift Scientific Rationale Length of lochia rubra phase lasts longer then generally assumed usually after patient is out of the hospital. This patient is 2 days post partum and has a moderate flow of lochia rubra and will be discharge, it is important for her to understand the trend of lochia so she is able to determine if there are any complications. Flow and color should get lighter and there should be no clots present or odor. If the character of the lochia returns to bright red bleeding, excessive amount, or clots she should contact her healthcare provider because this is indicative of hemorrhage. She should address fouls smalls with hcp as well. Olds p993 p1050 Evaluation Outcome is met. Plan is resolved. 10. Patient hemoglobin will trend toward 12-16 g/dl assessed as ordered Monitor Hemoglobin values as ordered Hemoglobin levels may be difficult to interpret in the first 2 days after birth because of the changing blood volume. This blood loss in the first 24 hrs accounts for half of the RBC blood volume gained during the course of pregnancy. This patient had a vaginal birth and average blood loss for this is 200-500 ml. This patient’s hemoglobin before delivery was 12.6 g/dl and increased to 13.0 g/dl after delivery, blood values should return to prepregnant state at the end of the postpartum period. A decrease in levels should alert to further assessment because this can be related to bleeding/hemorrhage. Saunders p 364, Olds 997 Outcome is met hemoglobin reached desired level. Plan is ongoing. 11. Patients hematocrit will trend towards 37-47% assessed as ordered Monitor Hematocrit values as ordered Hematocrit levels may be difficult to interpret in the first 2 days after birth because of the changing blood volume. This blood loss in the first 24 hrs accounts for half of the RBC blood volume gained during the course of pregnancy. This patient’s hematocrit was, before birth at 35.5% and increased to 38.4% after delivery. A 3-4% drop in hematocrit equals a blood loss of 500 ml. A drop greater than that would indicate further bleeding and potential for hemorrhage. Blood values should return to prepregnant state at the end of the postpartum period. Olds 997,998 Outcome is met hematocrit reached desired level. Plan is ongoing. Outcome Criteria Interventions Scientific Rationale Evaluation 12. Patients uterus will contract preventing uterine atony, decreasing blood loss to moderate amount of lochia rubra postpartum as assessed Oxytocin in LR 20 units/1000ml IV 250ml/hr one time only Oxytocin is a hormone and oxytocic. Postpartum this helps with control of bleeding after expulsion of the placenta. Oyxtocin stimulates uterine contraction after delivery and there by controls uterine atony which leads to decreased risk of hemorrhage. Olds 733 Outcome is met. Plan is resolved. Outcome Criteria Interventions Scientific Rationale Evaluation