LIFE Skills Science II
advertisement
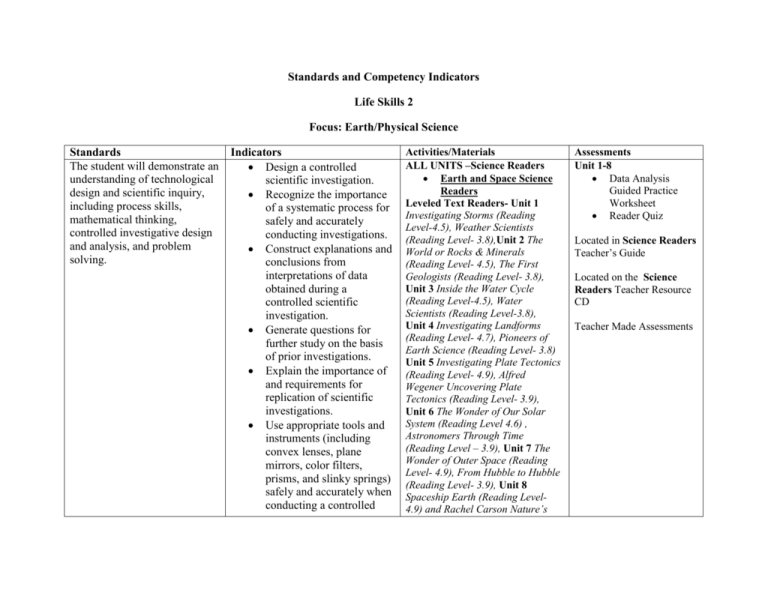
Standards and Competency Indicators Life Skills 2 Focus: Earth/Physical Science Standards The student will demonstrate an understanding of technological design and scientific inquiry, including process skills, mathematical thinking, controlled investigative design and analysis, and problem solving. Indicators Design a controlled scientific investigation. Recognize the importance of a systematic process for safely and accurately conducting investigations. Construct explanations and conclusions from interpretations of data obtained during a controlled scientific investigation. Generate questions for further study on the basis of prior investigations. Explain the importance of and requirements for replication of scientific investigations. Use appropriate tools and instruments (including convex lenses, plane mirrors, color filters, prisms, and slinky springs) safely and accurately when conducting a controlled Activities/Materials ALL UNITS –Science Readers Earth and Space Science Readers Leveled Text Readers- Unit 1 Investigating Storms (Reading Level-4.5), Weather Scientists (Reading Level- 3.8),Unit 2 The World or Rocks & Minerals (Reading Level- 4.5), The First Geologists (Reading Level- 3.8), Unit 3 Inside the Water Cycle (Reading Level-4.5), Water Scientists (Reading Level-3.8), Unit 4 Investigating Landforms (Reading Level- 4.7), Pioneers of Earth Science (Reading Level- 3.8) Unit 5 Investigating Plate Tectonics (Reading Level- 4.9), Alfred Wegener Uncovering Plate Tectonics (Reading Level- 3.9), Unit 6 The Wonder of Our Solar System (Reading Level 4.6) , Astronomers Through Time (Reading Level – 3.9), Unit 7 The Wonder of Outer Space (Reading Level- 4.9), From Hubble to Hubble (Reading Level- 3.9), Unit 8 Spaceship Earth (Reading Level4.9) and Rachel Carson Nature’s Assessments Unit 1-8 Data Analysis Guided Practice Worksheet Reader Quiz Located in Science Readers Teacher’s Guide Located on the Science Readers Teacher Resource CD Teacher Made Assessments scientific investigation. Use appropriate safety procedures when conducting investigations. Guardian (Reading Level- 3.9). Life Science ReadersLeveled Text Reader- Unit 7 Investigating the Human Body(Reading Level- 4) and Hippocrates Making the Way for Medicine (Reading Level-3) Physical Science Readers Leveled Text Reader- Unit 1 Inside the World of Matter (Reading Level4.5), Max Planck Uncovering The World of Matter (Reading Level3.8), Unit 2 Investigating the Chemistry of Atoms (Reading Level4.6), Marie Curie Pioneering Physicists (Reading Level- 3.8), Unit 3All About Energy (Reading Level-4.7), Albert Einstein Gentle Genius (Reading Level-3.9), Unit 4 Investigating Forces and Motion (Reading Level-4.8), Isaac Newton and the Laws of the Universe (Reading Level-3.9),Unit 5 Investigating Electromagnetism (Reading Level-4.9), Thomas Edison and the Pioneers of Electromagnetism (Reading Level3.9),Unit 6 All About Mechanical Engineering (Reading Level- 4.9), Making It Go: The Life and Work of Robert Fulton (Reading Level-3.9), Unit 7 All About Light and Sound (Reading Level-4.9), Pioneers of Unit 7 Life Science Reader and Unit 1-8 Physical Science Reader Data Analysis Guided Practice Worksheet Reader Quiz Located in Science Readers Teacher’s Guide Located on the Science Readers Teacher Resource CD Teacher Made Assessments The student will demonstrate an understanding of materials that determine the structure of Earth and the processes that have altered this structure. Summarize the three layers of Earth-crust, mantle, and core- on the basis of relative position, density, and composition. Explain how scientists use seismic waves-primary, secondary, and surface waves-and Earth’s magnetic fields to determine the internal structure of Earth. Infer an earthquake’s epicenter from seismographic data. Explain how igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks are interrelated in the rock cycle. Summarize the important of minerals, ores, and fossil fuels as Earth resources on the basis of their physical and chemical properties. Explain how the theory of Light and Sound (Reading Level3.9), Unit 8 The World of Elements and Their Properties (Reading Level- 4.9) and Antoine Lavoisier Founder of Modern Chemistry (Reading Level- 3.9) United Streaming Teacher Toolbox Science Readers Earth and Space Science Units 2,4,5 and 8 Leveled Text Readers- Unit 2 The World or Rocks & Minerals (Reading Level- 4.5), The First Geologists (Reading Level- 3.8), Unit 4 Investigating Landforms (Reading Level- 4.7), Pioneers of Earth Science (Reading Level- 3.8) Unit 5 Investigating Plate Tectonics (Reading Level- 4.9), Alfred Wegener Uncovering Plate Tectonics (Reading Level- 3.9), Unit 8 Spaceship Earth (Reading Level4.9) and Rachel Carson Nature’s Guardian (Reading Level- 3.9). AGS Earth Science AGS General Science Chapters 917 Steck Vaughn GED Skill Book Unit 2,4,5 and 8 Data Analysis Guided Practice Worksheet Reader Quiz Located in Science Readers Teacher’s Guide Located on the Science Readers Teacher Resource CD Teacher Made Assessments AGS Earth Science and General Science Assessments can be utilized throughout instruction PRE GED and GED Materials will be used by the teacher to develop assessments. The student will demonstrate an understanding of the relationship between Earth’s atmospheric properties and processes and its weather and climate. plate tectonics accounts for the motion of the lithospheric plates, the geologic activities at the plate boundaries, and the changes in landforms areas over geologic time. Illustrate the creation and changing of landforms that have occurred through geologic processes (including volcanic eruptions and mountainbuilding forces). Explain how earthquakes result from forces inside Earth. Identify and illustrate geologic features of South Carolina and other regions of the world through the use of imagery (including aerial photography and satellite imagery) and topographic maps. Compare the composition and structure of Earth’s atmospheric layers (including the gases and differences in temperature and pressure within the layers). Summarize the Science-Physical Science, Earth and Space Science Lesson 5 pages 15-17 United Streaming Teacher Toolbox Science Readers Earth and Space Science Units 1,3,5 and 8 Unit 1 Investigating Storms (Reading Level- 4.5),Weather Scientists (Reading Level- 3.8), Unit 3 Inside Water Cycle (Reading Level- 4.5), Water Scientists (Reading Level- 3.8) Unit 5 Unit 1,3, 5 and 8 Data Analysis Guided Practice Worksheet Reader Quiz Located in Science Readers Teacher’s Guide interrelationships among the dynamic processes of the water cycle (including precipitation, evaporation, transpiration, condensation, surface-water flow, and groundwater flow). Classify shapes and types of clouds according to elevation and their associated weather conditions and patterns. Summarize the relationship of the movement of air masses, high and low pressure systems, and frontal boundaries to storms (including thunderstorms, hurricanes, and tornadoes) and other weather conditions. Use appropriate instruments and tools to collect weather data (including wind speed and direction, air temperature, humidity, and air pressure). Predict weather conditions and patterns based on weather data collected from direct observations and measurements, weather maps, satellites, and radar. Investigating Plate Tectonics (Reading Level- 4.9), Alfred Wegener Uncovering Plate Tectonics (Reading Level- 3.9) Unit 8 Spaceship Earth (Reading Level- 4.9) and Rachel Carson Nature’s Guardian (Reading Level3.9) Steck Vaughn GED Skill Book Science-Physical Science, Earth and Space Science Lesson 2 and 3 pages 6-11 Steck Vaughn Pre GED Unit 4 Lesson 10 page 416 Unit 4 Lesson 11 page 419 United Streaming Teacher Toolbox Located on the Science Readers Teacher Resource CD Teacher Made Assessments PRE GED and GED Materials will be used by the teacher to develop assessments. The student will demonstrate an understanding of the characteristics, structure, and predictable motions of celestial bodies. Explain how solar energy affects Earth’s atmosphere and surface (land and water). Explain how convection affects weather patterns and climate. Explain the influence of global winds and the jet stream on weather and climatic conditions. Summarize the characteristics and movements of objects in the solar system (including planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteors). Summarize the characteristics of the surface features of the Sun: photosphere, corona, sunspots, prominences, and solar flares. Explain how the surface features of the Sun may affect the Earth. Explain the motions of Earth and the Moon and the effects of these motions as they orbit the Sun (including day, year, phases of the Moon, eclipses, and tides). Science Readers Earth and Space Science Units 6,7 and 8 Leveled Text Readers- Unit 6 The Wonder of Our Solar System (Reading Level-4.6), Astronomers Through Time (Reading Level- 3.9), Unit 7 The Wonder of Outer Space (Reading Level- 4.9) From Hubble to Hubble Astronomers and Outer Space (Reading Level-3.9), Unit 8 Spaceship Earth (Reading Level-4.9) and Rachel Carson Nature’s Guardian (Reading Level- 3.9) Unit 6, 7 and 8 Data Analysis Guided Practice Worksheet Reader Quiz Steck Vaughn GED Skill Book Science-Physical Science, Earth and Space Science PRE GED and GED Materials will be used by the teacher to develop assessments. Lesson 1 pages 3-5 Lesson 3 pages 9-11 Lesson 6 pages 18-20 Steck Vaughn Pre GED Located in Science Readers Teacher’s Guide Located on the Science Readers Teacher Resource CD Teacher Made Assessments The student will demonstrate an understanding of the law of Explain how the tilt of Earth’s axis affects the length of the day and the amount of heating on Earth’s surface, thus causing the seasons of the year. Explain how gravitational forces are influenced by mass and distance. Explain the effects of gravity on tides and planetary orbits. Explain the difference between mass and weight by using the concept of gravitational force. Recall the Sun’s position in the universe, the shapes and composition of galaxies, and the distance measurement unit (light year) needed to identify star and galaxy locations. Compare the purpose of the tools and the technology that scientists use to study space (including various types of telescopes, satellites, space probes, and spectroscopes). Unit 4 Lesson 12 page 421 Unit 4 Lesson 13 page 424 Identify the sources and properties of heat, solar, Science Readers Physical Science Unit 1, 2, 3,4,5,7 &8 United Streaming Teacher Toolbox Unit 1,2,3,4,5,7 &8 Data Analysis conservation of energy and the properties of energy and work. (Physical Science) chemical, mechanical, and electrical energy. Explain how energy can be transformed from one form to another (including the two types of mechanical energy, potential and kinetic, as well as chemical and electrical energy) in accordance with the law of conservation of energy. Explain how magnetism and electricity are interrelated by using descriptions, models, and diagrams of electromagnets, generators, and simple electrical motors. Illustrate energy transformations (including the production of light, sound, heat, and mechanical motion) in electrical circuits. Illustrate the directional transfer of heat energy through convection, radiation, and conduction. Recognize that energy is the ability to do work (force exerted over a distance). Explain how the design of simple machines (including levers, pulleys, and inclined planes) helps reduce the amount of force required to do work. Illustration ways that simple Leveled Text Reader- Unit 1 Inside the World of Matter (Reading Level4.5), Max Planck Uncovering The World of Matter (Reading Level3.8), Unit 2 Investigating the Chemistry of Atoms (Reading Level4.6), Marie Curie Pioneering Physicists (Reading Level- 3.8), Unit 3All About Energy (Reading Level-4.7), Albert Einstein Gentle Genius (Reading Level-3.9), Unit 4 Investigating Forces and Motion (Reading Level-4.8), Isaac Newton and the Laws of the Universe (Reading Level-3.9),Unit 5 Investigating Electromagnetism (Reading Level-4.9), Thomas Edison and the Pioneers of Electromagnetism (Reading Level3.9), Unit 7 All About Light and Sound (Reading Level-4.9), Pioneers of Light and Sound (Reading Level3.9), Unit 8 The World of Elements and Their Properties (Reading Level- 4.9) and Antoine Lavoisier Founder of Modern Chemistry (Reading Level- 3.9) Steck Vaughn GED Skill Book Science-Physical Science, Earth and Space Science Lesson 12-14 pages 36-44 Guided Practice Worksheet Reader Quiz Located in Science Readers Teacher’s Guide Located on the Science Readers Teacher Resource CD Teacher Made Assessments PRE GED and GED Materials will be used by the teacher to develop assessments. AGS Physical Science and General Science Assessments can be utilized throughout instruction machines exist in common tools and in complex machines. Steck Vaughn Pre GED Unit 4 Lesson 14 page 430 Unit 4 Lesson 15 page 434 Unit 4 Lesson 16 page 437 AGS Physical Science AGS General Science Chapters 1-8 United Streaming Teacher Toolbox The student will demonstrate an understanding of the effects of forces on the motion of an object. Use measurement and time-distance graphs to represent the motion of an object in terms of its position, direction, or speed. Use the formula for average speed, v=d/t, to solve real-world problems. Analyze the effects of forces (including gravity and friction) on the speed and direction of an object. Predict how varying the amount of force or mass will affect the motion of an object. Analyze the resulting effect of balanced and unbalanced forces on an object’s motion in terms of magnitude and direction. Summarize and illustrate the concept of inertia. Science Readers Physical Science Unit 3,4 & 6 Leveled Text Reader-Unit 3 All About Energy (Reading Level-4.7), Albert Einstein Gentle Genius (Reading Level-3.9), Unit 4 Investigating Forces and Motion (Reading Level-4.8), Isaac Newton and the Laws of the Universe (Reading Level-3.9), Unit 6 All About Mechanical Engineering (Reading Level-4.9) and Making It Go: The Life and Work of Robert Fulton.(Reading Level-3.9) Steck Vaughn GED Skill Book Science-Physical Science, Earth and Space Science Lesson 11 pages 33-35 Steck Vaughn Pre GED Unit 4 Lesson 17 page 441 United Streaming Teacher Toolbox Unit 3,4 &6 Data Analysis Guided Practice Worksheet Reader Quiz Located in Science Readers Teacher’s Guide Located on the Science Readers Teacher Resource CD Unit Test will be developed by the teacher. PRE GED and GED Materials will be used by the teacher to develop assessments. The student will demonstrate an understanding of the properties and behaviors of waves. Recall that waves transmit energy but not matter. Distinguish between mechanical and electromagnetic waves. Summarize factors that influence the basic properties of waves (including frequency, amplitude, wavelength, and speed). Summarize the behaviors of waves (including refraction, reflection, transmission, and absorption). Explain hearing in terms of the relationship between sound waves and the ear. Explain sight in terms of the relationship between the eye and the light waves emitted of reflected by an object. Explain how the absorption and reflection of light waves by various materials result in the human perception of color. Compare the wavelength and energy of waves in various parts of the electromagnetic spectrum (including visible light, infrared, and ultraviolet radiation). Source for Standards: SC Science Standards 6-4,6-5,8-1,8-3,8-4,8-5 and 8-6 Science Readers Physical Science Unit 7 Leveled Text Readers - Unit 7 All About Light and Sound (Reading Level-4.9), Pioneers of Light and Sound (Reading Level- 3.9). Steck Vaughn GED Skill Book Science-Physical Science, Earth and Space Science Lesson 7 and 8 pages 21-26 Unit 7 Data Analysis Guided Practice Worksheet Reader Quiz Located in Science Readers Teacher’s Guide Located on the Science Readers Teacher Resource CD Teacher Made Assessments United Streaming Teacher Toolbox PRE GED and GED Materials will be used by the teacher to develop assessments.