lesson 2 adaptaion in plants
advertisement

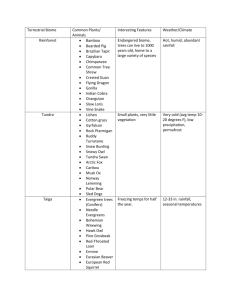
Buds Public School- Dubai 2015- 2016 Lesson 2 – adaptation in plants A. Knowledge and understanding 1. Adaptation: The process of adjustment to their surroundings by animals and plants. 2. Floating plants: Some plants floating on surface of water in ponds and lakes. (Ex: Water hyacinth, duck weed) 3. Fixed plants: Some aquatic plants have roots fixed to the soil under water. (Ex: lotus, water lily) 4. Terrestrial plants: Some plants grow on land. They are called terrestrial plants. (Ex: Neem, cactus, tea, coconut) 5. Insectivorous plants: Plants which trap and consume insects are called insectivorous plants. B. Give example for each 1. Terrestrial plants: Neem, Cactus, Tea, Coconut. 2. Aquatic plants: Water hyacinth, Lotus, Water lily, Pistia, Wolffia. 3. Fixed plants: Lotus, Water lily. 4. Underwater plants: Hydrilla, Vallisneria. 5. Insectivorous plants: Venus flytrap, Pitcher plant. 6. Floating plants: Water hyacinth, Duck weed. C. Fill in the blanks 1. The Cactus is a desert plant. 2. Coffee bushes require warm climate. 3. Plants of cold region have needle like leaves. 4. Aquatic plants grow in water. 5. Pond weed plants help small animals by giving them oxygen. 6. Water hyacinth has swollen leaves. 7. Mangrove trees grow in marshy areas. 8. Bamboo is a grass. 9. Desert plant are known as xerophytes. D. Name the following 1. Plants of the grass family which gives us food – wheat and rice. 2. Two house hold items made from Bamboo tree – mat and basket. 3. Two grasses whose leaves are used for thatching the huts – Bamboo and reed. 4. Two parasitic plants Mushroom and Amarbel. 5. Plants in marshy area- Mangroves. 6. Plants in hilly areas – Tea plants. 7. Plants in hot and humid region – Rubber and Coconut. 8. Plants in cold region – Pine trees and deoder 9. Plants in plains – Neem tree and Teak. E. Answer the following 1. Why do the plants of cold region have pointed leaves? Plants of cold region have pointed leaves which allow the rain water and snow to slide off easily. 2. Why do floating plants have air space in their root, stems and leaves? Air space in floating plants make the plants light and keeps them floating in water. 3. How plants of the grass family are useful to us? a. They provide cereals for humans and fodder for animals. b. Grasses are used for building purposes (ex: bamboo, reed) c. Many types of grasses are used for making paper. d. Some grasses used for medicine (ex: lemon grass). 4. How does pitcher plant catch it’s pray? The leaves of pitcher plants are in the form of hollow pitcher filled with nectar which attracts insects. The moment insects sits on the pitcher, the lid snaps shut, trapping the insect. The digestive juice present in them consume the insects. 5. How does a cactus survive in the desert? In cactus leaves are reduced to spines. This helps to conserve water and keep away animals. The stem is green and fleshy. The green stem contain chlorophyll and makes food instead of the leaves.