1.1 Notes
advertisement

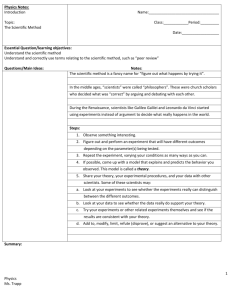
Name:_________________________ 1.1 Scientific Methodology Observing and Asking Questions There isn’t a single scientific method, but there is a style of investigation that can be called ___________________________________________. There are ____________ main parts that are described… 1. Observing and asking questions Scientific studies begin with observation, the act of _____________________________________________________________________. Observation leads to new questions 2. Inferring and Forming a Hypothesis After asking questions, scientists use further observations to make ________________________ . An inference is an ___________________________________________. Inference, along with imagination, can lead to a ______________________________________. A hypothesis is _________________________________________. 3. Designing Controlled experiments Testing a hypothesis often involves ___________________________________________, or the things that can change Whenever possible, only ____ variable should change when testing. All other variable should be left ______________________ Controlling variables: Variables are controlled so scientists can identify what caused the results The variable that is changed is called ________________________________________ The variable that is observed and that changes because of modifications ___________________________________________ Control and Experimental groups The control group ___________________________________________, except for one independent variable. 4. Collecting and Analyzing Data Scientists make detailed records of experimental observations by gathering data. Qualitative data: ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________: descriptions, observations Scientists use ___________________________________________ Ex: Sources of Error Scientists ___________________________________________ Sometimes errors are ___________________________________________ Tools have limited ___________________________________________ The more tests that are run (sample size), the ___________________________________________ 5. Drawing conclusions Scientists use ___________________________________________, change the hypothesis, or to draw a ___________________________________________ Scientists are able to make ___________________________________________based on the results of an experiment that was completed. The five parts of the Scientific method are? Complete the chart as an appropriate review of today’s lesson Parts of the Scientific Method 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Explanation/Purpose KEY 1.1 Scientific Methodology Observing and Asking Questions There isn’t a single scientific method, but there is a style of investigation that can be called scientific methodology. There are 5 main parts that are described… Observing and asking questions Scientific studies begin with observation, the act of noticing and describing what is happening in an orderly way. Observation leads to new questions Inferring and Forming a Hypothesis After asking questions, scientists use further observations to make inferences. An inference is an idea based on what is already known. Inference, along with imagination, can lead to a hypothesis. A hypothesis is a scientific explanation for a set of observations that can be tested Designing Controlled experiments Testing a hypothesis often involves an experiment that keeps track of variables, or the things that can change Whenever possible, only 1 variable should change when testing. All other variable should be left unchanged Controlling variables Variables are controlled so scientists can identify what caused the results The variable that is changed is called the independent variable The variable that is observed and that changes because of modifications is the independent variable Control and Experimental groups The control group is treated the same as the experimental group, except for one independent variable. Collecting and Analyzing Data Scientists make detailed records of experimental observations by gathering data. Qualitative data: descriptions, observations Quantitative data: NUMBERS Scientists use research tools to collect and analyze data Ex: Sources of Error Scientists must avoid error Sometimes errors are made using tools Tools have limited accuracy or can be read incorrectly The more tests that are run (sample size), the more sure scientists are about their data Drawing conclusions Scientists use data to support or refute the hypothesis, change the hypothesis, or to draw a valid conclusion Scientists are able to make new hypotheses based on the results of an experiment that was completed. The five parts of the Scientific method are? Complete the chart as an appropriate review of today’s lesson Be sure to include an explanation of each part We will be using this information for our upcoming experiment.