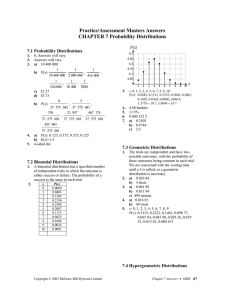
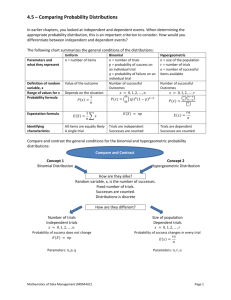
Probability Distribution Problem Bernoulli Trials Exactly x
advertisement

MDM 4U Probability Distributions Review Outline Review and be able to do the following: 1) Introduction to Probability Distributions: a) Define and understand the meaning of: random variable, discrete random variable, continuous random variable, expected value, probability distribution. b) Tabulate and graph probability distributions. c) Calculate the Expected Value of an experiment and interpret its meaning in the context of the problem. d) Know and use the formulas for calculating probability and expected value. P(X = x) = E(X) = Or E(X) = Where x = _______________________ 2) Uniform Distribution a) Define and recognize the characteristics of an experiment with a uniform distribution. b) Know and use the formulas for calculating probabilities and expected value for a uniform distribution. P(X = x) = E(X) = Or E(X) = Where x = _______________________ n = _______________________ c) Use E(X) to determine whether a game is fair or determine what to charge to make a profit. d) Tabulate and graph uniform probability distributions. 3) The Binomial Distribution a) Know and recognize the 3 Characteristics required for an experiment to consist of Bernoulli Trials. 1. _________________________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________________________________ b) Define a Binomial Distribution, repeated trials, independent events, success or failure outcomes. c) Know and use the formulas for calculating probabilities and expected value for a Binomial distribution. P(X = x) = E(X) = Where x = _______________________ n = _______________________ p = _________________________ q = _________________________ d) Use E(X) to determine whether a game is fair or determine what to charge to make a profit. e) Tabulate and graph Binomial probability distributions. f) Know the relationship to Binomial Theorem: (𝑝 + 𝑞)𝑛 = _________________________________________________________________________ = _________________________________________________________________________ 3) Geomentric Distributions (Waiting Times) a) Define waiting times and geometric distribution. b) Define the random variable X for geometric distribution. c) Know and use the formulas for calculating probabilities and expected value for a Geometric distribution. P(X = x) = E(X) = Where x = ________________________________________________ p = _________________________ q = _________________________ c) Use E(X) to determine whether a game is fair or determine what to charge to make a profit. d) Tabulate and graph Geometric probability distributions. 4) Hypergeometric Distributions a) Define the conditions necessary for a Hypergeometric Distribution. Experiment of repeated trials where: 1. __________________________________________________________________________ 2. __________________________________________________________________________ b) Know and use the formulas for calculating probabilities and expected value for a hypergeometric experiment with “success/failure” outcomes: P(X = x) = E(X) = Where x = ________________________________________________ n = ________________________________________________ a = ________________________________________________ b = ________________________________________________ c) Use E(X) to determine whether a game is fair or determine what to charge to make a profit. d) Tabulate and graph Hypergeometric probability distributions. e) Know and use the formulas for calculating probabilities for a hypergeometric distribution with more than 2 outcomes. 𝑃(𝑋1 = 𝑥1 , 𝑋2 = 𝑥2 , 𝑋3 = 𝑥3 , … ) = ( )( )( )… 𝑎+𝑏+𝑐+⋯ ( ) 𝑛 Where a = ________________________________________________ b = ________________________________________________ c = ________________________________________________ n = ________________________________________________ 𝑥1 , 𝑥2 , 𝑥3 , … = ___________________________________________________________________________________ Review Questions: Page 406 # 1 – 15, 17, 19, 20 MDM 4U Probability Distribution Questions Probability Distribution Problem Not Bernoulli Trials Bernoulli Trials Exactly x "successes" Binomial Waiting Time for first success Geometric Outcomes Equally Likely Uniform Sampling without Replacement Hypergeometric Not Obvious