Enter Topic Title in each section above
advertisement

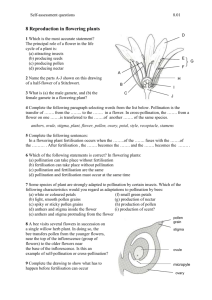
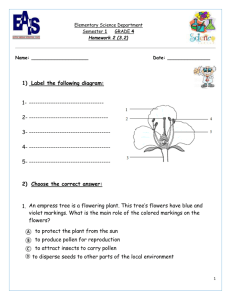
A. Increases variation; Reduces chance of genetic problems A. Anther; Stamen Q. What happens to the two polar nuclei? Q. To which part of a flower is pollen carried? A. Fuse with male gamete nucleus to form triploid endosperm nucleus A. Stigma of the carpel Q. What happens to the ovary after Q. What happens to the ovule after fertilisation? fertilisation? A. Becomes the seed A. Becomes the fruit Q. True or False. Endosperm is a food reserve in some seeds. Q. Give one location in a seed in which food is stored. A. TRUE A. Endosperm; Cotyledon; Nucellus Q. What is pollination? Q. What is fertilisation? A. Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma Q. From which structure in the seed did the root develop? A. Fusion of gametes; Formation of zygote Q. Name a carbohydrate that you would expect to be present in the food store of a seed. Page 1 of 4 A. Starch A. Radicle Q. How are wind-pollinated flowers adapted? A. No colours; No scent; No nectar; Small or no petals; Long stamens; Long feathery stigmas Q. Name a structure through which the pollen tube grows in order to reach the embryo sac. A. Stigma; Style; Ovary; Micropyle Q. In which part of a flower does a seed form? Q. Give two ways in which pollen may be transported to another flower. A. Wind; Insect; Artificial Q. What forms in the ovary of a flower after pollination and fertilization? A. Seed; Zygote; Embryo; Food reserve Q. What process follows pollination in the life cycle of a flowering plant? A. Carpel; Ovary A. Fertilisation Q. Some flowers have nectaries. How are these flowers pollinated? Q. Name the part of the flower where fertilisation occurs. A. Insects A. Embryo sac; Ovule; Ovary Q. What is the difference between Q. Suggest a substance that flowers self-pollination and crossproduce that may cause hay fever in pollination? some people. Page 2 of 4 A. Occurs on same plant or flower; Occurs between plants of same species A. Pollen Q. What is the function of the sepals? Q. Name two ways in which crosspollination happens. A. Wind; Insect A. Protection; Photosynthesis Q. Suggest why cross-pollination is preferable to self-pollination. Q. In which part of the flower is pollen produced? Page 3 of 4 Follow-me Quiz Follow-me Quiz 3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant 3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant Flower Structure, Gamete Formation, Pollination & Fertilisation Flower Structure, Gamete Formation, Pollination & Fertilisation Follow-me Quiz Follow-me Quiz 3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant 3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant Flower Structure, Gamete Formation, Pollination & Fertilisation Flower Structure, Gamete Formation, Pollination & Fertilisation Follow-me Quiz Follow-me Quiz 3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant 3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant Flower Structure, Gamete Formation, Pollination & Fertilisation Flower Structure, Gamete Formation, Pollination & Fertilisation Follow-me Quiz Follow-me Quiz 3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant 3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant Flower Structure, Gamete Formation, Pollination & Fertilisation Flower Structure, Gamete Formation, Pollination & Fertilisation Follow-me Quiz Follow-me Quiz 3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant 3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant Flower Structure, Gamete Formation, Pollination & Fertilisation Flower Structure, Gamete Formation, Pollination & Fertilisation Enter Topic Title in each section above Page 4 of 4