ohsrm PART A
advertisement
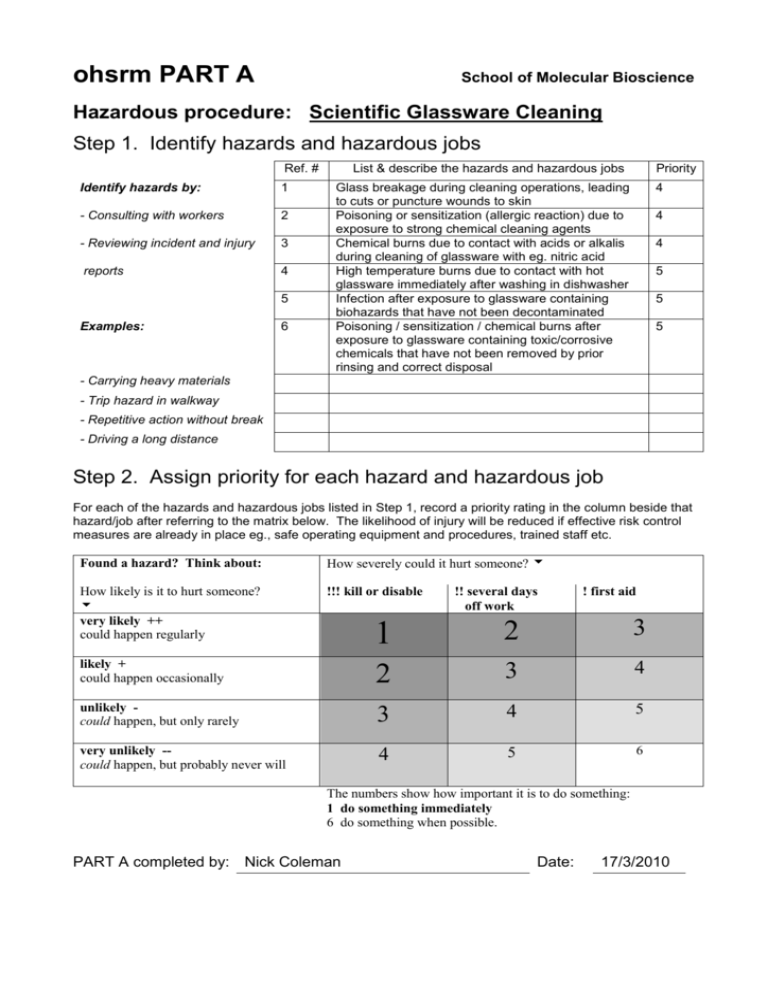
ohsrm PART A School of Molecular Bioscience Hazardous procedure: Scientific Glassware Cleaning Step 1. Identify hazards and hazardous jobs Ref. # Identify hazards by: 1 - Consulting with workers 2 - Reviewing incident and injury 3 reports 4 5 Examples: 6 List & describe the hazards and hazardous jobs Priority Glass breakage during cleaning operations, leading to cuts or puncture wounds to skin Poisoning or sensitization (allergic reaction) due to exposure to strong chemical cleaning agents Chemical burns due to contact with acids or alkalis during cleaning of glassware with eg. nitric acid High temperature burns due to contact with hot glassware immediately after washing in dishwasher Infection after exposure to glassware containing biohazards that have not been decontaminated Poisoning / sensitization / chemical burns after exposure to glassware containing toxic/corrosive chemicals that have not been removed by prior rinsing and correct disposal 4 4 4 5 5 5 - Carrying heavy materials - Trip hazard in walkway - Repetitive action without break - Driving a long distance Step 2. Assign priority for each hazard and hazardous job For each of the hazards and hazardous jobs listed in Step 1, record a priority rating in the column beside that hazard/job after referring to the matrix below. The likelihood of injury will be reduced if effective risk control measures are already in place eg., safe operating equipment and procedures, trained staff etc. Found a hazard? Think about: How severely could it hurt someone? How likely is it to hurt someone? very likely ++ could happen regularly !!! kill or disable !! several days off work ! first aid 1 2 3 likely + could happen occasionally 2 3 4 unlikely could happen, but only rarely 3 4 5 very unlikely -could happen, but probably never will 4 5 6 The numbers show how important it is to do something: 1 do something immediately 6 do something when possible. PART A completed by: Nick Coleman Date: 17/3/2010