Evolution_Glossary
advertisement

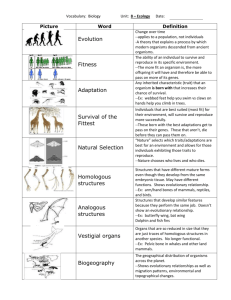
Word Definition 1 Evolution The slow ad gradual process of change over a log period of time that has given rise to the diverse organisms around us today. This theory was first created by Charles Darwin Natural Selection The process by which traits that make it more likely for an organism to survive and reproudce. The traits become more common in a population over successive generations Natural selection occurs because: 1) Variation existas within a population of organisms. 2) All organisms face a daily struggle to survive and reproduce, whether it is to find mates, to seek shelter, to find food or to avoid predators. 3) Those organisms with features that best suit their environment have the best chance of survival and reproduction. 4) Over time, the population will become better suited to its environment. DNA Hybridisation Refers to a molecular biology technique that measures the degree of simalarity in the DNA code of species. Comparitive Anatomy The study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of organisms. Biogeography The study of geographic distribution of a species using present day observations and fossil records. Takes into account the existence of supercontinents and Gondwana and Laurasia and how the developement of species during this period evolved. Gondwana Southern half of the world. Opposite of laurasia Pangea The supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras Sagittal Crest Ridge of bone running lengthwise running along the middle of the top of the skull of many mammals and reptiles Neanderthal An extinct human species or subspecies living during the late Pleistocene Epoch throughout most of Europe and parts of Asia and northern Africa and associated with Middle Paleolithic tools. hominid The group consisting of all modern and extinct Great Apes (that is, modern humans, chimpanzees, gorillas and orang-utans plus all their immediate ancestors). hominin The group consisting of modern humans, extinct human species and all our immediate ancestors (including members of the genera Homo, Australopithecus, Paranthropus and Ardipithecus. cro-magnon An early form of modern human inhabiting Europe in the late Paleolithic Period and characterized by a broad face and tall stature. Cro magnon is homo sapien. Australopithecus A genus of hominids that are now extinct. First human-like species present on Earth. bipedal Two footed animal cranium Top of the skull foramen magnum Hole for the spine underneath the skull Homo Man fossil The remains of a plant or animal that existed in the past that has been dug up from the soil. There are several types of fossils depening on how they are formed e.g. imprints, casts, moulds... artificial selection Selevtively breeding of an animal/plant for a desired characteristics/trait E.g. breeds in dogs and other domestic animals have been created in this way. palaeontology The study of prehistoric life. species A common definition is that of a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring of both sexes adaptation The variation in structure, form or trait of an organism that is most suited to the environment. The trait can be either structural, physiological or behavioural. homologous Corresponding in structure and in origin, but not necessarily in function: The wing of a bird and the foreleg of a horse are homologous. species A common definition is that of a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring of both sexes variation Differences in structure, form ot trait that is recognised from the more common trait analogous similar or alike in function but not in structure and evolutionary origin e.g. fin in a fish and in a whale. era A division in geological time brow ridge The bone structure above the eyes Fossils preserved remains or traces of animals, plants or other organisms. Relative Dating determining the age of fossils by the order of enents such as the order of rock layers in the Earth. Fossils found in that layer are considered to be of the same age Absolute dating / carbon dating / radio-isotopic dating Determining the exact lage of fossils (by a number) from radioactive chemicals found in matter (e.g. rocks) Carbon dating Using living matter (containing original carbon) to determine the exact date of the material. As most fossils are formed by replacing of organic matter by sediments fossils cannot be dated in this way. coprolite fossilised faeces Missing Link A transitional species i.e. a fossil that exhibits traits common to two different species e.g. archaepteryx is a dinosaur (related to reptiles) that has bird like features and believed to be a common ancestor of birds. Direct descendent They are directly related on the evolutionary tree. common ancestor A relation that is a direct descendent for both species on the evolutionary tree characteristic/trait Physical attributes of an organism organism A living thing. Can be animal, plant, animal or fungi Sedimentation The formation of fossils by the following process: 1)For a fossil to form animals or plants first fall into mud or silt in water to settle. Over time, more layers of silt or mud, covered the remains compressing them between the layer below and the one above. 2) TheThe lack of oxygen in the sediments prevents the fossil from decomposing. Pressure from additional layers of sediment that formed above the remains compressed them flat, forming an impression between the layers of silt. 3) Pressure and heat eventually changed the silt into layers of finely grained rock, such as shale and slate, commonly called sedimentary rock. Over many centuries, the matter in the remains was slowly dissolved, with the resulting space acting as a mold that filled with minerals, preserving the impression as a fossil. 4) As time passed and the waters receded from geological changes, the once-wet regions became dry land. Further geological changes exposed the rock surface, making it possible to see the fossils within. 5) Many people hunt fossils in geological formations. Removing large sections of rock, then split them along the layers, hoping to reveal the fossil of a fern, fish, trilobite or other life that existed millions of years ago. Convergent Evolution when different species (organisms not closely related) have a similar trait (analogous traits) Divergent Evolution when similar organisms (same species) have very different traits but the organisms can be traced back to a common ancestor. (homologous traits) Parallel evolution when related species evolve similar traits but independently i.e. cannot be linked to a common ancestor. This is usually because they have similar environmental pressures.