Evidence of Evolution
advertisement

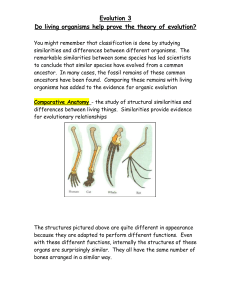
Evidence of Evolution Evidence of Evolution 1. Fossil Record 2. Homologous Body structures 3. Similarities in Embryology 4. Biochemical Evidence Evidence of Evolution: The Fossil Record • Fossil record provides evidence that living things have evolved • Fossils show the history of life on earth and how different groups of organisms have changed over time Relative vs. Absolute Dating Relative Dating • Can determine a fossil’s relative age • Performed by estimating fossil age compared with that of other fossils • Drawbacks – provides no info about age in years Absolute Dating • Can determine the absolute age in numbers • Is performed by radioactive dating – based on the amount of remaining radioactive isotopes remain • Drawbacks - part of the fossil is destroyed during the test • Radiometric dating uses decay of unstable isotopes. – Isotopes are atoms of an element that differ in their number of neutrons. – A half-life is the amount of time it takes for half of the isotope to decay. Primate Fossils Australopithecus Homo erectus Homo sapien Primate Bone Structure Evidence of Evolution: Homologous Body Structures – Turtle Structures that have different mature forms but develop from the same embryonic tissues Ex: Wing of bat, human arm, leg of turtle Alligator Bird Evidence of Evolution: Homologous Structures • Features that are similar in structure but appear in different organisms and have different functions. • Strong evidence for common ancestor. • Ex: forelimbs of humans, bats and moles. Human hand Mole foot Bat wing Analogous Structures • Structures that perform a similar function. • Not evidence of common ancestry. Vestigial Structures • Remnants of organs or structures that had a function in an early ancestor. • Ex: Ostrich wings, used for balance but not flight • Ex: Humans’ appendix Evidence of Evolution: Similarities in Embryology In their early stages of development, chickens, turtles and rats look similar, providing evidence that they shared a common ancestry. Embryological Development Evidence of Evolution: Biochemical Similarities • Scientists study nucleotide sequences in DNA and proteins in different organisms to determine ancestry. • If the organisms are closely related they will have similar sequences of nucleotides in their DNA and arrangement of amino acids in proteins. Evidence of Evolution: Biochemical Similarities Organism Amino Acid Differences Organism Amino Acid Differences Human beta chain 0 Mouse 27 Gorilla 1 Kangaroo 38 Rhesus monkey 8 Chicken 45 Dog 15 Frog 67 Cow 25 Soy bean 124 The more similar the amino acid sequence, the more closely related the organisms are.