Biology SG unit 7 History of Life on Earth 2016 - Jones-Bio

Biology Name ____________________________ Per __
Study guide Unit 7
The History of Life on Earth
Please answer all questions in your own words, on a separate piece of paper and staple this sheet in front.
Due 1/14/16. Test is 1/15/16
1.Define biological diversity (also called biodiversity), episodic speciation, and mass extinction.
2.What percentage of potassium-40 remains after two half-lives?
3.How long is the half-life of carbon-14?
4.How old is the oldest fossil you could use carbon-14 to date?
5.What is carbon-14 most useful for dating?
6.As the amount of potassium-40 decreases, how does the amount of stable isotope formed change?
7.The early molecular catalyst that may have assisted in building the first proteins was
8.How did cyanobacteria change the young Earth’s atmosphere?
9.Eukaryotes first appeared when?
10.
What did pre-eukaryotic cells lack that eukaryotic cells do have?
11.
Chloroplasts are thought to be the result of an invasion of pre-eukaryotic cells by what process?
12.
The first eukaryotic kingdom was the Kingdom _____.
13.
What is a "RNA world" and why do most scientists think it is a valid theory?
14.
What does the biochemistry of diverse organisms compare?
15.
How does the age of fossils compare to their depth in the earth?
16.
On an evolutionary tree diagram, how to you tell when organisms last had a common ancestor?
17.
When did dinosaurs become extinct?
18.
What is the earliest fossil evidence of life?
19.
When did all of the major phyla of animals on Earth today evolve?
20.
Compare and contrast eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells.
21.
What are the eukaryotic kingdoms?
22.
What can scientists determine by comparing the DNA of two different species?
23.
If two organisms branch from the same point on an evolutionary tree diagram, what does the point that they branch from represent?
24.
What is the most diverse eukaryotic kingdom now?
25.
What is the most diverse group of animals now?
26.
What are angiosperms?
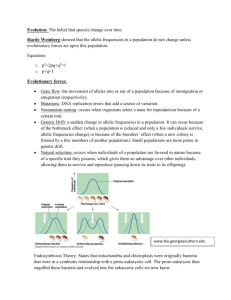
27.
Why have insects been very successful?
28.
What are the first animals to evolve wings?
29.
Describe the relationship between angiosperms and insects.
30.
The oldest known fossils of multicellular organisms were found in rocks that were how old?
31.
The kingdom that evolved from the protists was the kingdom
32.
Describe the history and characteristics of multicellularity?
33.
When did of the major phyla of animals on Earth today evolve?
34.
The fossil record indicates that Earth has experienced how many mass extinctions? When did they occur?
35.
The first organisms to populate the surface of the land were…?
36.
Why have insects have been very successful?
37.
From fossils, we know that insects were the first animals to evolve what feature?
38.
Flying insects were able to use the ability to fly to do what?
39.
What are the characteristics of arthropods?
40.
The most diverse group of animals on Earth is the…?
Unit 7: The History of Life on Earth Jones Biology
Biology Name ____________________________ Per __
Study guide Unit 7
The History of Life on Earth
41.
What do you use to show the theoretical evolutionary relationships among organisms?
42.
What is a clad? What is a taxon?
43.
The ability to fly led to partnerships between insects and what other organisms?
44.
What major problems were faced by moving onto land?
45.
What were the first vertebrates? What were the first vertebrates to move onto land like?
46.
Vertebrates that are adapted to life both on land and in the water are called…?
47.
What characteristics did the first vertebrates to successfully colonize land share?
48.
What are the characteristics of reptiles? Of amphibians?
49.
Describe the endosymbiosis theory including when it would have first occurred, what organisms were involved, what organelles were involved, and what evidence there is to support it.
50.
What is an evolutionary tree diagram? Explain how it is used
51.
What are some possible scientific explanations for aspects of the fossil record such as gaps and the sequential nature of fossils?
52.
What are the Eras and Periods of earth's history?
53.
The age of Earth is estimated at about …?
54.
What is the process of the creation of new species called?
55.
What is a fossil?
56.
What are examples of fossils
57.
Calculate how old a sample is by using absolute dating; specifically radioactive half-life.
58.
Describe how you find the date of a fossil using relative dating.
59.
Describe the 3 different theories from Discovery Techbook for how life began on earth.
60.
Describe the 5 mass extinctions and what they resulted in.
61.
How can you determine how closely related two different groups are to each other?
Unit 7: The History of Life on Earth Jones Biology