7 th Grade Midterm Study Guide – Language Arts
advertisement

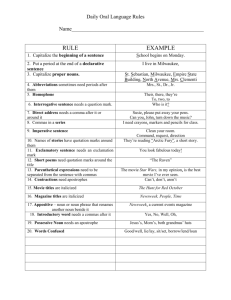
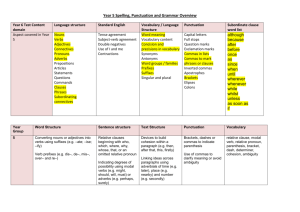
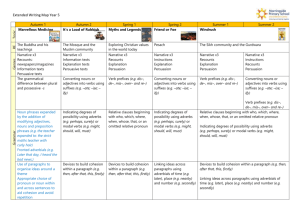
7th Grade Midterm Study Guide – Language Arts Spelling principles to review: Compound Words: Closed compounds: briefcase, granddaughter, Hyphenated compounds: far-fetched, three-fourths, brother-in-law Double Consonants: embarrass, exaggerate, unnecessary Words with Silent Letters: guarantee, wrestle, knoll, spaghetti The Rule -- I before e except after c, or when in sounds like a long a as in neighbor and weigh: believe, piece, receive, vein, weight Grammar Lessons to Review: Identifying Subjects and Predicates in a sentence Subjects are the people, places and things in a sentence Predicates can be action verbs or verb of being – is, was, am, has been Identifying complete sentences versus fragments Direct and Indirect Objects and Subject Complements Direct Objects receive the action of the verb. They also follow an action verb. The quarterback threw the ball. Indirect objects receive the action of the direct object. It is almost always a person. The quarterback threw the receiver the ball. Subject complements are either adjectives or nouns. They always follow a being verb. Subject complements used as adjectives are called Predicate Adjectives. My Mom was selfless. Subject complements used as nouns are called Predicate Nominatives. Correct use of commas Commas in a series of three or more things Commas are used to separate the date and year from the rest of the sentence Commas used to set off an introductory phrase or words such as yes, no and well in the beginning of a sentence Commas used to set off a noun of direct address or the name of a person spoken to Commas used to separate “interrupters” like of course and in fact from the rest of the sentence Commas used before conjunctions, words like and, or, but in a compound sentence Commas used to separate a direct quotation from the rest of a sentence Semicolons and colons Use a semicolon to join independent clauses in a compound sentence when you do not use coordinating conjunctions. The bake sale will be in the cafeteria; parents should bring donations tomorrow. Use a colon to introduce a list of items. The bake sale will include: muffins, cupcakes and cookies. Quotation Marks versus Italics Use italics for the titles of books, movies, newspapers, works of art and the names of airplanes and spacecraft Use quotation marks to enclose the titles of short works like poems, songs, short stories, parts of books, and articles Capitalization Rules All proper nouns The first letter of a direct quotation The first and last words in titles of works such as books, songs, stories, poems, paintings or newspapers Historical events and documents Monuments and buildings Organizations, teams, businesses and brands Awards Government agencies First word in the greeting and closing of a letter Terminology for the Writing Process: Prewriting – the act of coming up with a topic Drafting – the act of writing or typing your essay for the first time Editing – the act of making corrections to your essay Revising – the act of rewriting the final draft Publishing – the act of printing a neat final copy of your essay Terminology for the 6+1 Writing Traits: Ideas – the piece’s central message and details that support it Organization – the internal structure of the piece Voice – the tone and tenor of the piece; the stamp of the writer Word Choice – the specific vocabulary the writer uses Sentence Fluency – the way words and phrases flow through a piece Conventions – the mechanical (spelling/grammar) correctness of the piece Presentation – the physical appearance of the piece