Supplementary Material - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement

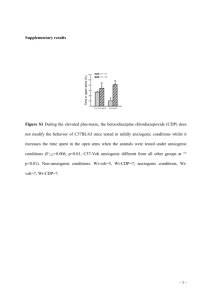
Supplementary Material Brain Structure & Function Cannabinoid receptor interacting protein Crip1a modulates CB1 receptor signaling in mouse hippocampus Stephan Guggenhuber1, Alan Alpar2,3,4, Rongqing Chen5, Nina Schmitz1, Melanie Wickert1, Tobias Mattheus1, Anne E. Harasta1,6, Martin Purrio1, Nadine Kaiser1, Maurice R. Elphick7, Krisztina Monory1, Werner Kilb5, Heiko J. Luhmann5, Tibor Harkany2,8, Beat Lutz1,*, Matthias Klugmann1,6,* 1Institute of Physiological Chemistry, University Medical Center of the Johannes Gutenberg University, D-55128 Mainz, Germany. 2Division of Molecular Neurobiology, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics, Scheeles väg 1:A1, Karolinska Institutet, SE-17177 Stockholm, Sweden. 3Research Group of Experimental Neuroanatomy and Developmental Biology, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Budapest, Hungary. 4Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary. 5Institute of Physiology, University Medical Center of the Johannes Gutenberg University, D-55128 Mainz, Germany. 6Department of Physiology & Translational Neuroscience Facility, School of Medical Sciences, UNSW, High Street, Randwick, NSW 2052, Sydney, Australia. 7School of Biological & Chemical Sciences, Queen Mary University of London, London E1 4NS, UK. 8Department of Molecular Neuroscience, Center for Brain Research, Medical University of Vienna, Spitalgasse 4, A-1090 Vienna, Austria. Correspondence should be addressed to Matthias Klugmann or Beat Lutz. Email: m.klugmann@unsw.edu.au or blutz@uni-mainz.de. Materials and Methods Behavioral testing Behavioral testing commenced at four weeks after vector injections, when AAV-mediated transgene expression has reached maximum and stable levels. AAV-CRIP1a and AAV-empty animals (n=21-25) were subjected to the tests in the order listed below. Animals were left undisturbed for at least 5 days between the different test sessions. The experimenter was blind to the treatment of the animals. Locomotor activity and anxiety-related behavior was tested using an open field box and the light/dark emergence test, respectively, as described (Schneider et al. 2007). Inherent anxiety was investigated using the elevated plus maze, consisting of two open arms (35 cm length, 6 cm width) and two enclosed black arms (35 cm length, 6 cm width, 20 cm height) at 1 m above the floor. The light on the floor of the open arms and the center had about 30 lux. At the beginning of the test, the mouse was placed in a close arm, and the behavior was video-monitored for 5 min. Recordings were used to determine the time spent in the different arms, the entire entries to the arms as well as head dips and risk assessment. References Schneider M, Spanagel R, Zhang SJ, Bading H, Klugmann M (2007) Adenoassociated virus (AAV)-mediated suppression of Ca2+/calmodulin kinase IV activity in the nucleus accumbens modulates emotional behaviour in mice. BMC neuroscience 8:105. doi:10.1186/1471-22028-105 Legends to Supplementary figures Figure 1. CRIP1a does not affect excitatory synaptic transmission. A, B, Amplitude and frequency of miniature EPSCs were not significantly different in CA1 pyramidal cells from AAV-empty and AAV-CRIP1a transfected animals. C, Typical current traces illustrating paired-pulse facilitation of the 2nd eEPSC. Note comparable paired-pulse facilitation between AAV-empty and AAVCRIP1a mice. D, Bar graph illustrating paired-pulse ratio of evoked EPSCs in AAV-empty and AAV-CRIP1a mice. n.s., non significant. Figure 2. CRIP1a overexpression did not affect locomotion and anxiety behavior. A, B, Animals were subjected to an open field test. The time spent in the center (p = 0.83) and the distance travelled (p = 0.42) did not differ between AAV-empty and AAV-CRIP1a mice. C, D, In the elevated plus maze, there was no significant difference in the time spent in the open arm (p = 0.59) or in the entries into the open arm (p = 0.36) between the two groups. E, F, The light/dark test revealed that AAV-empty and AAV-CRIP1a animals did not differ in the time spent in the lit compartment (p = 0.22) and in the entries into the lit compartment (p = 0.73). N = 21 to 25 mice per group. Data are expressed as means ± SEM.



![Historical_politcal_background_(intro)[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005222460_1-479b8dcb7799e13bea2e28f4fa4bf82a-300x300.png)






