Click Here to Access Science Anchor Charts

Physical Science
An Object is the Sum of its Parts
Physical Change
Chemical Change
Electricity
Magnetism
Physical Science
The Mass on an Object
Equal to the Sum of its
Parts
Some Things are too small to be seen without
Magnification
Physical Changes
Separating Mixtures
Manipulating Paper
(cutting, tearing, folding)
Physical Changes
of Water
Water Vapor
Steam
Liquid
Ice
Chemical Changes
A Substance
Combines with
Another to Form a
New Substance
(Chemical Reactions)
Static Electricity
An Accumulation of
Electric Charge on an
Insulated Object
An Electric Circuit
Electrons Flow from the Source to the Load and then Back to the
Source
The Battery is the Source that
Supplies Energy to the Circuit.
The Light Bulb is the Load Where
Energy Leaves the Circuit.
Insulators of
Electricity
Does not Respond to an
Electric Field & Resists the
Flow of Electric Charges
Conductors of
Electricity
Are Materials that
Contain Movable
Electric Charges
.
The Bar Magnet
Has Magnetic Poles at
Each End
An
Electromagnet
A Magnet Consisting of an Iron or Steel Core
Wound with a Coil of
Wire, Through Which a
Current is Passed
Earth Science
Constructive Processes
(Deposition, Earthquakes,
Volcanoes, Faults)
Destructive Processes
(Erosion, Weathering, Impact of Organisms, Earthquakes,
Volcanos)
Seismological Studies
Flood Control
Beach Reclamation
Constructive
Processes
Are Things that Happen to the Earth that Build it up or make Positive Changes
Depositions
(Deltas, Sand Dunes, etc.)
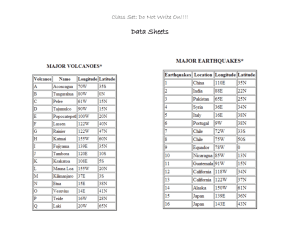
Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Faults
Destructive Processes
Are When Things Happen to the Earth that Destroy or
Break Down Parts of it
Erosion
(Water-Rivers, Oceans, Wind)
The Impact of Organisms,
Weathering, Earthquakes,
Volcanos
Technological
Intervention
Seismological Studies
Seismology is the Study of
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves that Move Through and Around the Earth. A Seismologist is a
Scientist who Studies
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves.
Human Intervention
Flood Control
(Dams, Levees, Storm
Drain Management)
Refers to all Methods used to
Reduce or Prevent the
Detrimental Effects of Flood
Waters
Human Intervention
Beach Reclamation
(Georgia Coastal Islands)
Is the Act of Reclaiming a
Beach from Erosion by
Adding Sand and Dirt
Life Science
Vertebrates
(fish, amphibian, reptile, bird, mammal)
Invertebrates
Plants
Inherited Traits
Learned Behaviors
Cells
Microorganisms
Vertebrates
Animals with Backbones
(Fish, Amphibian, reptile, bird, mammal)
Invertebrates
Animals Without
Backbones
(97% of all Animal
Species)
Plants
Vascular Plants have
Tissues that Transport
Water, Minerals, and
Other Materials
Throughout the Plant.
Plants
Non-vascular Plants are
Unable to Absorb
Moisture Through Their
Roots. Moisture is
Absorbed Through its top Surface Area
.
Cells
Are the Smallest Unit in the Structure of an
Organism
People Must use
Microscopes or Hand
Lenses to Observe Cells and Their Structure.
Parts of a Plant Cells
Membrane
Cell Wall
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Chloroplasts
Parts of an Animal
Cell
Membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Multi-Celled
Organisms
Multicellular Organisms are Organisms that
Consist of More than
One Cell.
Single-Celled
Organisms
Consists of Only One
Cell
Beneficial
Microorganisms
Are Useful to People and Help Promote
Good Health. Many
Aid in Digestion,
Others are used in
Food and Medicine.
Harmful
Microorganisms
Are Capable of
Causing Diseases,
They Can Make you
Sick