+ H 2 (g) - North Salem High School Chemistry
advertisement
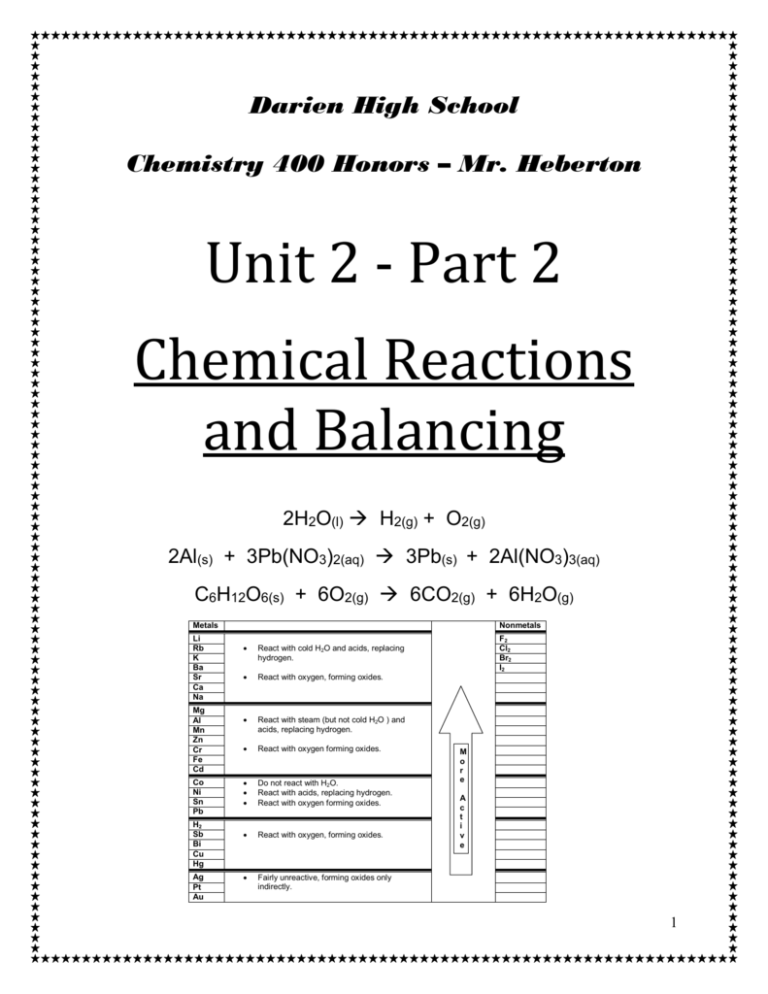
Darien High School Chemistry 400 Honors – Mr. Heberton Unit 2 - Part 2 Chemical Reactions and Balancing 2H2O(l) H2(g) + O2(g) SERIES (s) + 2Al(NO3)3(aq) 2Al(s) + 3Pb(NO3)2(aq) ACTIVITY 3Pb C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(g) Metals Li Rb K Ba Sr Ca Na Mg Al Mn Zn Cr Fe Cd Co Ni Sn Pb H2 Sb Bi Cu Hg Ag Pt Au Nonmetals React with cold H2O and acids, replacing hydrogen. React with oxygen, forming oxides. React with steam (but not cold H2O ) and acids, replacing hydrogen. React with oxygen forming oxides. Do not react with H2O. React with acids, replacing hydrogen. React with oxygen forming oxides. React with oxygen, forming oxides. Fairly unreactive, forming oxides only indirectly. F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 M o r e A c t i v e 1 Chemical Reactions Vocabulary Part I Chemical reaction- Reactants- Products- Word Equations- Chemical Equations- Coefficient- Aqueous Solution Part II Synthesis Reaction- Decomposition Reaction- Combustion Reaction- Single Replacement Reaction- Double Replacement Reaction- 2 1. Balance the following equations. Make sure that you use the lowest possible whole number coefficients. Example a. _3__C + _4__H2 → __1_C3H8 (but no need to write “1” as a coefficient) b. 2H2O + O2 → 2H2O2 c. S8 + 12O2 → 8SO3 d. N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 e. 4P + 5O2 → 2P2O5 f. 2CaO + MnI4 → MnO2 + 2CaI2 g. 2Ag2O → 4Ag + O2 h. CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O i. 2C6H6 + 15O2 → 6H2O + 12CO2 j. 4NaI + Pb(SO4)2 → PbI4 + 2Na2SO4 k. 2HNO3 + Mg(OH)2 → 2H2O + Mg(NO3)2 l. Fe2O3 + 3H2O → 2Fe(OH)3 m. C2H2 + 2H2 → C2H6 n. CF4 + 2Br2 → CBr4 + 2F2 o. 2NaBr + Ca(OH)2 → CaBr2 + 2NaOH p. 2NH3 + H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4 q. 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O r. Li3N + 3NH4NO3 → 3LiNO3 + (NH4)3N 3 Balance the following equations. Make sure that you use the lowest possible whole number coefficients. ALSO note the type of reaction to the right of the equation. Example: a. 2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2 Decomposition b. 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O Synthesis c. 2NaCl + F2 → 2NaF + Cl2 Single Replacement d. 2AlBr3 + 3K2SO4 → 6KBr + Al2(SO4)3 Double Replacement e. C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O Combustion f. 2NaBr + CaF2 → 2NaF + CaBr2 Double Replacement g. 4C5H9O + 27O2 → 20CO2 + 18H2O Combustion h. 2C8H18 + 25O2 → 16CO2 + 18H2O Combustion i. FeCl3 + 3NaOH → Fe(OH)3 + 3NaCl Double Replacement j. 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 Single Replacement k. H3PO4 + 3NaBr → 3HBr + Na3PO4 Double Replacement l. 2K + MgBr2 → 2KBr + Mg Single Replacement m. 2Fe(OH)3 → Fe2O3 + 3H2O Decomposition n. 2HCl + CaCO3 → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2 Double Replacement/Synthesis o. HNO3 + NaHCO3 → NaNO3 + H2O + CO2 Double Replacement/Synthesis p. 2VF5 + 10HI → V2I10 + 10HF Double Replacement q. H2SO4 + 2NaNO2 → 2HNO2 + Na2SO4 Double Replacement 4 Directions: 1. Write the skeletal formula equation showing all appropriate symbols (aq, s, l, g) 2. Name the type of reaction 3. Balance the equation Aluminum reacts in the air to form aluminum oxide. 4Al(s) + 3O2 (g) 2Al2O3 (s) Synthesis Sodium oxide reacts at room temperature with water to form sodium hydroxide. Na2O (s) + H2O (l) 2NaOH (aq) Synthesis Aqueous solutions of sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide react to form aqueous sodium sulfate and water. H2SO4 (aq) + 2NaOH (aq) Na2SO4 (aq) + 2H2O (l) Double Replacement or Neutralization Solid aluminum reacts with aqueous zinc chloride to produce solid zinc metal and aqueous aluminum chloride. 2Al (s) + 3ZnCl2 (aq) 3Zn (s) + 2AlCl3 (aq) Single Replacement Nitrogen gas reacts with oxygen gas to form dinitrogen monoxide gas. 2N2 (g) + O2 (g) 2N2O (g) Synthesis Potassium bromide decomposes to form potassium metal and bromine liquid. 2KBr (s) 2K(s) + Br2 (l) Decomposition Mercury (II) oxide when heated forms mercury and oxygen gas. Heat 2HgO (s) 2 Hg + O2 (g) Decomposition 5 Zinc reacts with aqueous sulfuric acid to form zinc sulfate and liberates hydrogen gas. Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g) Single Replacement Magnesium nitride and water combine to form magnesium hydroxide and aqueous ammonia. Mg3N2 (s) + 6H2O (l) 3Mg(OH)2 (s) + 2NH3 (aq) Double Replacement Propane gas (C3H8) burns in air to produce carbon dioxide gas and water vapor. C3H8 (g) + 5O2 (g) 3CO2 (g) + 4H2O (g) Combustion Nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen gas to form gaseous ammonia. N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2NH3 (g) Synthesis Calcium reacts with aqueous aluminum chloride to form aqueous calcium chloride and aluminum metal. 3Ca (s) + 2AlCl3 (aq) 3CaCl2 (aq) + 2Al (s) Single Replacement At high temperatures, aluminum oxide decomposes. Heat 2Al2O3 (s) 4Al (s) + 3O2 (g) Decomposition 6 Directions: For each problem, complete the following: 1. Use the Activity Series to determine if the reaction will occur 2. Write the formula equation showing all reactants and predicted products. 3. Balance the equation Solid nickel (II) reacts with aqueous copper (II) chloride. Ni (s) + CuCl2 (aq) NiCl2 (aq) + Cu (s) Aqueous iron (II) sulfate reacts with solid copper (II). FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s) NR (No Reaction) Calcium reacts with water at 50°C. Ca (s) + 2H2O (l) Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g) Zinc dust reacts with aqueous lead (II) nitrate. Zn (s) + Pb(NO3)2 (aq) Zn(NO3)2 (aq) + Pb (s) Tin (II) reacts with aqueous sulfuric acid. Sn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) SnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g) Solid manganese (II) reacts with water at 50°C. Mn (s) + H2O (l) NR (water needs to be in steam form, i.e. at 100oC) 7 Magnesium bromide + chlorine MgBr2 (s) + Cl2 (g) MgCl2 (s) + Br2 (g) Aqueous Silver nitrate + zinc chloride 2AgNO3 (aq) + ZnCl2 (aq) 2AgCl (s) + Zn(NO3)2 (aq) Sulfuric acid solution + sodium hydroxide H2SO4 (aq) + 2NaOH (s) Na2SO4 (aq) + 2H2O (l) Acetic acid + copper CH3COOH (aq) + Cu (s) NR Silver + copper(II) sulfate Ag (s) + CuSO4 (aq) NR Nitric acid + iron(III) hydroxide 6HNO3 (aq) + 2Fe(OH)3 (s) 2Fe(NO3 )3 (aq) + 6H2O (l) Magnesium chloride + silver nitrate MgCl2 (aq) + 2AgNO3 (aq) Mg(NO3)2 (aq) + 2AgCl (s) 8