Review Answer key
advertisement

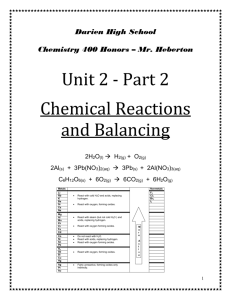
Honors Chemistry Chemical Reactions Review – Ch. 11 ANSWER KEY synthesis 2Sb + 3I2 2SbI3 single replacement 2Li + 2H2O 2LiOH + H2 decomposition 2AlCl3 2Al + 3Cl2 combustion C6H12 + 9O2 6CO2 + 6H2O double replacement 2AlCl3 + 3Na2CO3 Al2(CO3)3 + 6NaCl Neutralization 2HNO3 + Ba(OH)2 Ba(NO3)2 + 2H2O single replacement 2Al + 3Pb(NO3)2 2Al(NO3)3 + 3Pb double replacement 2NH4Cl(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) PbCl2(s) + 2NH4NO3(aq) combustion CS2(s) + 3O2(g) CO2(g) + 2SO2(g) single replacement Fe(s) + 3AgNO3(aq) Fe(NO3)3(aq) + 3Ag(s) decomposition 2KNO3(s) 2KNO2(s) + O2(g) synthesis Ca(s) + Cl2(g) CaCl2(s) single replacement F2(g) + 2KCl(aq) 2KF(aq) + Cl2(g) comb, synthesis P4(s) + 5O2(g) 2P2O5(s) single replacement 3Mg(s) + Al2O3 (aq) 3MgO + 2Al combustion C2H4(g)+ 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) double replacement FeCl2(aq)+ K2S(aq) FeS(s) + 2KCl(aq) Neutralization H2S (aq) + 2KOH(aq) K2S + 2H2O double replacement NH4NO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) N.R. single replacement Cl2(g) + MnBr4(s) MnCl4(s) + Br2(l) 1 atom of solid magnesium reacts with 2 molecules of aqueous hydrochloric acid to form 2 units of aqueous magnesium chloride and 1 molecule of hydrogen gas 22. 1 unit of solid iron (II) sulfide reacts with 2 molecules of aqueous hydrochloric acid to form 1 molecule of hydrogen sulfide gas and 2 units of aqueous iron (II) chloride 23. 1 unit of aqueous potassium bromide reacts with 1 unit of aqueous silver nitrate to form 1 unit of solid silver bromide and 1 unit of aqueous potassium nitrate 24. 1 unit of solid mercury (II) oxide breaks down 1 atom of liquid mercury and 1 molecular of 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. gaseous oxygen. 25. 2 molecules of gaseous tetracarbon decahydride reacts with 13 molecules of oxygen gas to form 8 molecules of gaseous carbon dioxide and 10 molecules of water vapor. 26. 1 molecule of aqueous sulfuric acid reacts with 1 unit of aqueous calcium hydroxide to form 1 unit of aqueous calcium sulfate and 2 molecules of liquid water 27. Cu2+ + OH- Cu(OH)2(s) 28. Ni2+ + PO43- Ni3(PO4)2(s) 29. Zn(s) + Sn4+ Sn(s) + Zn2+ 30. Cl2(g) + I- I2(s) + Cl31. Soluble 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. Insoluble Soluble Soluble Insoluble Insoluble Insoluble Soluble Insoluble