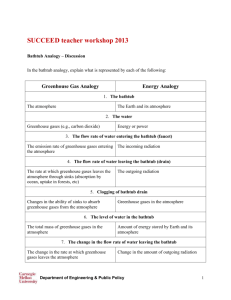
Lesson 2 Intro to greenhouse effect and carbon cycle
advertisement

What’s this climate stuff all about? Overview of Atmosphere, heat-trapping gases, and carbon cycle Part 1: Adapted from WWF lessons 1 and 2 Goals: Students will understand how heat-trapping gases work in the atmosphere and why they and carbon dioxide are necessary for life on Earth. Students will review the structure of atmosphere, the greenhouse effect, heat trapping gases in the atmosphere. Hook Climate pre-test from WWF lesson 1 Mini Lesson Show NASA video (first 2 min) Show ppt overview of atmosphere, the greenhouse effect, heat trapping gases in the atmosphere. Show npr video clip as part of ppt Practice Take notes on ppt: including a sketch of greenhouse effect and list of greenhouse gases Students can read lesson 1 text from facing the future for additional information on greenhouse effect and answer question 1 Debrief Revisit pre-test questions 1-8, students respond to statement Greenhouse gases are always bad for the environment. Part 2: (adapted from Facing the Future: lesson 1 The Carbon Link) Goals : Students will identify sources and sinks of the carbon cycle. Student will link carbon cycle dynamics to the greenhouse effect, i.e. students will make a connection between increasing atmospheric CO2 and increasing temperature. Hook Mini Lesson Practice Mini Lesson Pair-share: In relation to climate, what’s the big deal about carbon dioxide? Show npr video on carbon Explain that carbon lasts a long time in atmosphere Project carbon cycle diagram students use the diagram and background knowledge to answer carbon FAQs with a partner go over the FAQs with the whole class if necessary review cellular respiration and photosynthesis – just focus on where co2 is in the processes Explain carbon cycle, including sources and sinks Explain that students will be modeling the cycle (students = sources and sinks, ball of yarn = carbon) Pass out role cards Start with a student with an atmosphere card Students complete the activity as a fishbowl with half of the class tracking and recording the path carbon takes. If time, repeat the activity with the second group and change the Debrief scenario to model deforestation (half the students with plant cards step out) or model reduced automobile use (half the students with automobile cards step out of circle) Students discuss in small groups reflection questions 1 or 2, 3 Students write a short story about a day in the life of a carbon molecule. If time, students can share their story with a partner or with the whole class. Resources: Powerpoint includes several weblinks Atmosphere poster from NCAR Carbon cycle game http://reti.ucar.edu/mod/resource/view.php?id=290 WWF: Lesson 1 pre-assessment questions WWF lesson 2: our unique atmosphere Facing the future lesson 1: The carbon link Carbon cycle diagram http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/earth/Water/co2_cycle.html— importance of carbon http://www.npr.org/news/specials/climate/video/ see video 5 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rDYqlTsZfgw&feature=PlayList&p=D7BEC5371B22BD (8 min overview of climate change and gases role in increasing temp) https://www.planetseed.com/node/15226 (interactive of carbon cycle) https://www.planetseed.com/node/15223 (CO2 interactive) The Carbon Link Record the path carbon takes. Round 1 Where it started Where it went How it got there Round 2: Scenario ______________________ Where it started Where it went How it got there Round 3: Scenario _______________________ Where it started Where it went How it got there Discussion Questions: 1. Choose one scenario and explain how it affected the carbon cycle? (hint: how was the carbon cycle different when we removed half the plants or half the cars?) 2. What do you think will happen to the carbon stored in fossil fuels as the world population increases? In your opinion, why would increased population change create this change in the carbon cycle? Journal prompt: Write a short story from the perspective of a carbon atom as it travels through the carbon cycle. List the places you travel and how you move from place to place until you return to where you started.