File
advertisement

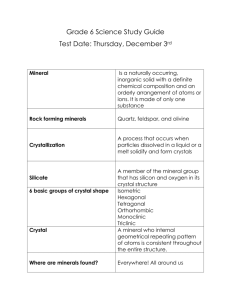
Name ______________________________ Minerals Atoms, Elements, Compounds, & Mixtures ________________- Basic unit of matter, smallest part of an element ________________- Consists of only one type of atom o Cannot be broken down by ____________ or ______________ means ________________- 2 or more elements chemically combined o Cannot be broken apart by ______________ means ________________- Two or more substance combined, but they each retain their own identity o Can be broken apart by ______________ means ____________ ________________ _______________ _______________ Characteristics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. ________________: An inorganic, naturally occurring solid with a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure. ________________: A solid with atoms arranged in a specific patterns Crystallization: Minerals can form in one of the following ways: 1. ___________________- Cooling and hardening of a molten material such as magma (igneous rock) 2. _______________: Water is turned into gaseous state leaving minerals behind (ex. salt) 3. __________________- When concentrations of mineral atoms is too much for water to hold, minerals will naturally form in water Properties of Minerals: Properties are based on physical features and the arrangement of atoms ________________ ________________ _____ ____________ is responsible for most properties!! These properties help us with the identification of various minerals 1. Color Easiest to _________________, but the____________ useful property This is because many different minerals may have the____________ color or one mineral may have many________________ colors (ex. Quartz) ________________ trapped in the mineral during formation cause various colors 2. Luster The way a mineral _______________ _________________: Shiny, appears like a______________ (ex. pyrite, graphite) _________________: Various appearances- can be shiny, glossy, greasy, pearly, etc., but will not look like a metal (ex. diamond, sulfur) 3. Hardness Based on ______________ _______________ __________ Minerals are rated 1-softest to 10- hardest This scale measures a mineral’s resistance to being scratched 4. Cleavage/Fracture A. _______________- Breakage of a mineral that retains a smooth plane or crystal shape Due to weakness in ____________ Results in ______________ sides/edges When broken, pieces of the mineral appear similar B. ________________- Breakage that does NOT occur on cleavage planes Can be uneven, jagged, smooth, etc. No two pieces will appear exactly the same after broken (think of glass) Cleavage types: There are repeatable shapes when minerals break along cleavage ____________ These shapes are based on their _____________ ____________ of atoms (crystalline structure) o Patterns how their atoms are arranged A. ________________ Cleavage Breaks into sheets Ex. Muscovite B. _________________ Cleavage Breaks into cubes Ex. Halite C. _________________Cleavage Breaks into rhombohedra shapes ( “slanted cube”) Ex. Calcite * DON’T MIX UP THE WAY A MINERAL BREAKS FOR THE WAY IT GROWS DUE TO IT’S CRYSTALLINE STRUCTURE! 6. Streak Color of the _______________ of a mineral Perform “streak test” by rubbing a mineral on a __________________ plate and examining the color left behind The streak color is often _______ the same as the color of the mineral, but a much better property to use when identifying Minerals in Earth’s Crust Of the approximate ______________ minerals on Earth, only about ______ are common Most minerals are ___________, ex. gold, diamonds, etc. Rocks are _____________ of minerals. On page 8 and 16 of your ESRT, the rocks and minerals that make up Earth’s crust are listed On page ______ of your ESRT, the most common _____________ in the earth’s crust are listed Only ______ elements make up 97% of earth’s crust The 2 most abundant elements are ______________ and ______________ Rock-Forming Minerals Silicates Most ______________ minerals in Earth’s crust Made of ______________ (Si) and ________________ (O) 90% of Earth’s minerals o Feldspar o Quartz o Micas Remember, on page 1 of your ESRT, there is a chart for Earth’s most abundant elements. The two most abundant are Oxygen and Silicon. ________________ __________________- Basic structure for silicate minerals (SiO4) One silicon bonded to four oxygen in a specific pattern Tetra= ________ in greek Carbonates 2nd most abundant group Mainly ________________ (CO3) Calcite (CaCO3) is common mineral Oxides Contain Oxygen ____________ _____________ (Fe2O3) Name _____________________________ Pd. ________ Minerals 1. What is a mineral? 2. What are the 5 characteristics of minerals? 3. What’s the difference between metallic and non-metallic luster? 4. What’s the difference between fracture and cleavage? 5. What’s the softest mineral on the Moh’s hardness scale? The hardest? 6. Why is relying on color a poor choice when identifying minerals? 7. What are 3 property TESTS you would perform when trying to identify a mineral? 8. What mineral has a hardness of 7, comes in many colors, and is used in glass, jewelry, and electronics? 9. What mineral is commonly found in pencil lead? 10. What mineral commonly has a brassy-yellow color, but leaves a green-black streak? 11. What mineral has a chemical composition of CaCO3? What is this mineral’s common use? 12. What 2 minerals are common ores of iron? Rock Forming Minerals 13. What are the 2 most abundant ELEMENTS in the earth’s crust? 14. What are the 2 most abundant MINERLAS in the earth’s crust? 15. Which mineral family contains the most minerals? 16. What’s the basic structure of silicate minerals? 17. The formula for Iron Oxide is Fe2O3. Keeping that in mind, what’s the common name for the process of oxidation? 18. What CHARACTERISTIC of a mineral is responsible for most of a minerals properties?