15T5m&fits-3to5m
advertisement

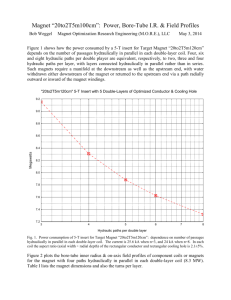
Field Profiles of Target Magnets with B(z>5m) = 1.5 T, 2 T, 2.5 T & 3 T Robert J. Weggel; Magnet Optimization Research Engineering (M.O.R.E.), LLC; 1/3/2014 Each of the magnets described below consists of a main coil, which may be notched on its inner surface to improve field homogeneity, plus downstream coils that achieve a field profile that ramps downward to 1.5, 2.0, 2.5 or 3.0 T at z = 5 m. The Excel spreadsheet used to design the system embodies the following goals and constraints: 1) 2) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Main-solenoid I.R. = 120 cm; current density = 18 A/mm2, as typical for SC#1 (~60% steel); Current density in solenoids #2 to #7 = 45 A/mm2 (~10% steel); I.R. = 60 cm for coils #5-#7; B(z), is 15 T at z = −0.5 m, Bmin at 5 m, and ~14.7 T (∆B = 0.3 T = 2% of 15 T) at 0 & −1 m; Field derivative B' ≡ dB/dz = 0 at z = −0.5 m & z = 5 m; B' < 0 from z = −0.5 m to 5 m; Goal function strongly penalizes ampere-meters of conductor usage, to reduce magnet cost; Penalized gently is I.R. < 120 cm for solenoid #2 and O.R. > 100 cm for solenoids #3 & #4; Penalized for z > 5 m is a weighted sum of the squares of ∆B ≡ B−Bmin, B', & B" ≡ d2B/dz2; Figs. 4 & 5 prolong the taper by constraining B' < 0.5 (5 − z/100) from z = −0.5 m to 5 m; Fig. 5 achieves a full-length taper by moving Coil #2 from Cryostat # 2 into Cryostat #1. Field Magnitude and Derivatives of Target Magnet 5m1+3+3 15.0 13.5 Field magnitude, |B| [T] 10 log10(field magnitude) First derivative, B' [T/m] nd 2 2 derivative, B" [T/m ] 12.0 10.5 9.0 See legend for units 7.5 6.0 4.5 3.0 1.5 0 -1.5 -3.0 -4.5 -6.0 -300 -200 -100 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 On-axis distance from downstream end of target [cm] Fig. 1a&b. Target Magnet 15to1.5T5m1+3+3. Left: Conductor cross sections and field direction (arrows) & magnitude (color & contours). Inner radius of successive coils is [1.20, 1.10, 1.03, 0.83, 0.60] m. Gap between coils #1 & #2 is 2.8 m; between triplets #1 & #2 is 0.56 m = 1/3 of sum of outer radii of flanking coils. Peak ambient field is 16.0 T. Right: Field profile, |B(z)| (blue);10 log10(|B|) (black); 1st derivative, dB/dz (turquoise); and 2nd derivative d2B/dz2 (green). B(−50 cm) = 15 T; B(500 cm) = 1.5 T. B(−100 cm) = B(0) = 14.7 T. Field Magnitude and Derivatives of Target Magnet 15to2.5T5m1+3+3 Field Magnitude and Derivatives of Target Magnet 15to2T5m1+3+3 15.0 15.0 13.5 13.5 10 log10(field magnitude) Field magnitude, |B| [T] First derivative, B' [T/m] nd 2 2 derivative, B" [T/m ] 12.0 10.5 9.0 9.0 7.5 7.5 6.0 4.5 3.0 6.0 4.5 3.0 1.5 1.5 0 0 -1.5 -1.5 -3.0 -3.0 -4.5 -4.5 -6.0 -300 Field magnitude, |B| [T] 10 log10(field magnitude) First derivative, B' [T/m] nd 2 2 derivative, B" [T/m ] 12.0 See legend for units See legend for units 10.5 -200 -100 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 -6.0 -300 1200 -200 -100 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 On-axis distance from downstream end of target [cm] On-axis distance from downstream end of target [cm] 2 2 Fig. 2a&b. On-axis field profile, |B(z)| (blue);10 log10(|B|) (black); dB/dz (turquoise); & d B/dz (green) of target magnets with B(−100 cm) = B(0) = 14.7 T and B = Bmin at z = 500 cm. Left: Bmin = 2 T. Right: Bmin = 2.5 T. Figure 3 compares the field profiles of the target magnets in Figs. 1 & 2 and also one with Bmin = 3 T. Only for Bmin = 1.5 T does the field profile extend nearly to z = 5 m; the other field profiles reach their asymptotic values prematurely, at ~4.2 m, ~3.8 m and 3.5 m, respectively. Field Profiles of Target Magnets 15toBmin5m1+3+3; Bmin= 1.5 T, 2.0 T, 2.5 T & 3.0 T 15.0 150 135 Bmin = 3.0 T Bmin = 2.5 T Bmin = 2.0 T Bmin = 1.5 T On-axis field [T] 12.0 120 10.5 105 9.0 90 7.5 75 6.0 60 4.5 45 3.0 30 1.5 15 0 -1.5 -300 B/Bmin – 1 [%] 13.5 0 -200 -100 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 -15 1000 1100 1200 On-axis distance from downstream end of target [cm] Fig. 3: On-axis field profiles of target magnets as in Figs. 1 & 2, with Bmin = 1.5 to 3 T. Upper set of curves is B(z); lower set is ∆B/Bmin. One can prolong the taper by requiring that each field profile rapidly acquire a significant downward slope upstream of 5 m. Figure 4 introduces the constraint −dB/dz ≥ ½(5−z) T/m throughout the range 2.5 < z < 5 m. To achieve the full-length taper of Fig. 5 requires transforming the upstream coil of Cryostat # 2 into the downstream coil of Cryostat #1. The gap between cryostats shrinks from ~2.8 m to 1.041.10 m, which is one-third the sum of the maximum coil outer radius in each cryostat. Field Profiles of Extended-Taper Target Magnets 15toBmin5m1+3+3; Bmin= 1.5 to 3.0 T 15.0 150 135 Bmin=3.0 T Bmin= 2.5 T Bmin= 2.0 T Bmin= 1.5 T On-axis field [T] 12.0 120 10.5 105 9.0 90 7.5 75 6.0 60 4.5 45 3.0 30 1.5 15 0 B/Bmin – 1 [%] 13.5 0 -1.5 -300 -200 -100 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 -15 1000 1100 1200 On-axis distance from downstream end of target [cm] Fig. 4: On-axis field profiles that prolong the taper by requiring −dB/dz ≥ ½(5−z) T/m for 2.5 < z < 5 m. Upper set of curves is B(z); lower set is ∆B/Bmin. Field Profiles of Full-Taper Target Magnets 15toBmin5m2+2+3; Bmin= 1.5 to 3.0 T 15.0 150 135 Bmin= 1.5 T Bmin= 2.0 T Bmin= 3.0 T Bmin= 2.5 T On-axis field [T] 12.0 120 10.5 105 9.0 90 7.5 75 6.0 60 4.5 45 3.0 30 1.5 15 0 -1.5 -300 B/Bmin – 1 [%] 13.5 0 -200 -100 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 -15 1000 1100 1200 On-axis distance from downstream end of target [cm] Fig. 5: On-axis field profiles of full-taper Target Magnets with −dB/dz ≥ ½(5−z) T/m and d2B/dz2 ≥ 0 for 2 < z < 5 m, and two coils in each of Cryostats #1 and #2. Upper set of curves is B(z); lower set is ∆B/B min. Fig. 6a&b. Conductor cross sections and field direction (arrows) & magnitude (color & contours). Left: Target Magnet 15to2T5m1+3+3 (Fig. 4, blue curve); I.R. of successive coils is [1.20, 1.02, 1.14, 0.84, 0.60] m; gap between coils #1 & #2 is 2.25 m. Right: Target Magnet 15to2T5m2+2+3 (Fig. 5, blue); I.R. of coils is [1.20, 1.10, 1.02, 0.81, 0.60] m; gap between coils #2 & #3 is 1.04 m = 1/3 of sum of max. coil outer radii in flanking cryostats. Figure 7 plots the on-axis field profile of a magnet similar to that in Fig. 6a but with just a single coil from z = 5.23 m to 20 m. Also plotted are three curve fits of progressively greater simplicity. The blue-curve magnet employs twelve fitting parameters: the radius, upstream end, downstream end, and current-per-unit-length of each of three current-sheet solenoids. Its field profile duplicates that of the fitted curve so accurately as to mask it. The magenta-curve magnet employs only three parameters: the level of energization of a thickwalled solenoid flanking the target region, plus two current sheets downstream. The parameters of the thick-walled solenoid are: current density = 18.086 A/mm2, I.R. = 120 cm; O.R. = 208 cm; upstream end = −235 cm; and downstream end = 134 cm. The current sheets each have a radius of 1 m; the upstream one carries 9,957 A/mm and extends from 3 m to 5 m; the downstream one carries 15,616 A/mm and extends from 5.2 m to 20 m. With only three parameters, B(z=−50cm) is not exactly zero. The red-curve magnet consolidates its current sheets. Its solenoid carries 18.077 A/mm2; its current sheet, 12,220 A/mm. With only two parameters, B'(5m) differs somewhat from zero. Also, B(5m) is slightly greater than 2 T, so that B(z) does not fall too far below 2 T for z > 5 m. 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -300 -200 -100 0 100 200 300 400 15 14 On-axis field profile (4 coils to 20 m) 13 12 parameters (3 current-sheet coils) 12 3 current densities: 1 coil + 2 sheets 2 current densities: 1 coil + 1 sheet 11 Slope dB/dz: 1 thick coil + 2 sheets 10 Slope dB/dz: 1 thick coil + 1 sheet 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 On-axis distance from downstream end of target [cm] Fig. 7. On-axis field profile of Fig 6 Magnet and three curve-fits over length −3 m < z < 12 m. Blue: 12 parameters; magneta: 3 parameters; red: 2 parameters. Field slope dB/dz [T/m] On-axis field [T] Field Profile and Three Curve Fits of Target Magnet 15to2T5m1+2