AP genetics notes
advertisement

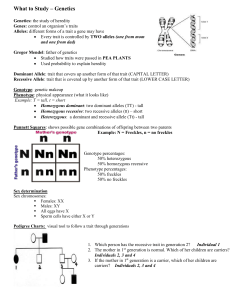
CHAPTER 14 The Science of genetics has ancient roots Greek: Hippocrates Hypothesis: pangenesis: pangenes from each part of the body travel to sperm or egg Aristotle rejected his hypothesis Experimental genetics began in abbey garden Heredity- the passing of traits from parent to offspring Genetics- is the science of heredity 1. Gregor Mendel- 1860s monk who was the first to study genetics a. b. c. d. e. 2. Worked with pea plants, discovered how traits are passed from one generation to the next Some traits that were studied: seed shape, seed color, flower color, height etc. Pea plant reproduce sexually, with both sex organs in the same flower, usually self-fertilize Mendel mated (crossed) different offspring, cross-fertilize When he mated different types (example Short and Tall), the trait that was shown in the offspring was called the dominant trait (all offspring =Tall) Offspring of a parent (P generation) cross are called F1 generation, offspring of the second cross are called the F2 generation Mendel’s principle of segregation describes the inheritance of a single characteristic 1. Traits a. Dominant Traits- Form of the trait that dominates, and prevents the showing of the recessive trait b. Recessive trait-Trait that is hidden by the dominant one 2. Genes: a. Allele: each form of a trait (Example: eye color- blue and brown are alleles for that trait) a. Symbols: i. Dominant Trait is represented by a capital letter 1. Brown eyes = B ii. Recessive Trait is represented by a lower case letter 1. Blue eyes= b b. Each gamete (sex cell) has one allele for each gene i. Ex: Sperm has one allele for eye color and egg has one allele for eye color c. Three possible gene combinations i. Homozygous dominant= two dominant alleles (BB) ii. Homozygous recessive= two recessive alleles (bb) iii. Heterozygous or Hybrid = one dominant and one recessive allele (Bb) d. Genotype: Gene combination of any given trait (genes that one has (BB)) e. Phenotype: expression of that gene (Trait being expresses(Brown Eyes)) Example: Genotype: Phenotype BB= Brown eyes Bb= Brown eyes bb= Blue eyes Principle of segregation: During gamete (sex cell) formation the pair of genes responsible for each trait separates so that each gamete receives only one allele for each trait. Example: Monohybrid Cross: parents differ in only one characteristic. Let’s cross a homozygous brown eyes (BB) with a homozygous blue eyes (bb). What is the genotypic and phenotypic ratio of each cross? Punnette square to predict F1 Generation: The principle of independent Punnette square to predict the F2 Generation assortment is revealed by tracking two characteristics at once Example: Dihybrid Cross Parents differ in two characteristics. RRYY (yellow round) x rryy (green shrivel) What is the genotype of all offspring or F1? ______ What is the phenotype of all offspring or F1?______ What are the four types of gene combinations that can be found in the gametes? ___ ____ ____ ____ Use a 4 box by 4 box grid to find the F2 generation. Conclusion: Principle of independent assortment: each pair of alleles segregates independently during gamete formation Geneticists use the testcross to determine unknown genotypes Define Testcross: Problem: Miss Lyon owns a purebred long haired Jack Russell Terrier named Brodie. JRTs are more valuable if they have long hair (L) as opposed to short hair (l). Recently, the breeder Miss Lyon got her dog from has been charged with selling dogs that are not purebred long haired terriers! Now, Miss Lyon wants to find out if the breeder charged her for a purebred long haired dog and got a heterozygous long haired one instead! How can Miss Lyon find out if she was cheated? Create the two possible punnette squares. If one of the offspring to the testcross has short hair, was Ms. Lyon cheated?______ Mendel’s principles reflect the rules of probability Rule of Multiplication DefinitionRule of Addition DefinitionProblem: If a golden retriever Bb is crossed with a golden retriever Bb. 1.Show mathematically how to determine the probability that the offspring will be BB. Rule Used:____ Probability BB:___ Calculations: 2.Show mathematically how to determine the probability that the offspring will be Bb. Rule Used:____ Probability Bb:___ Calculations: 3.Show mathematically how to determine the probability that the offspring will be bb. Rule Used:____ Probability bb:___ Calculations: Draw the Punnette square to check your answer: Challenge: In this cross, three genes are present: A, B and C. If one parent is AABbCC and the other parent is AaBbCc, what is the probability that the offspring from this cross will be homozygous dominant for all three genes (AABBCC)? The relationship of genotype and phenotype is rarely simple Detailed Description from book Examples from the book Incomplete Dominance Codominance Pleiotrophy Epistasis Environmental Impact Polygenic Blood Type: Multiple alleles: a set of three or more different alleles controlling a trait a. Each individual only gets two alleles b. Example: Blood type is an example of multiple alleles and Co-dominance (More than one can be dominant) c. I A and I B are both dominant over i, but I A and I B are both expressed (Blood type AB) d. Antigens:_____________________________________________________________________ Example: Blood type A has A antigens e. Antibodies are______________________________________ ________________________ Example: Blood type A makes Anti-B antibodies Blood Type (Phenotype) A B AB O Genotypes Blood Type Challenge: USE PENCIL!!!!! Information we know about the family: John and Tom are brothers George is blood type O Bill’s Mother is Sally John and Harry are blood type A Mary is going to marry George next month Bill and Tom are brothers Bill is blood type AB Tom’s blood is homozygous recessive Mary is blood type B Mary’s father is Harry Mary and John are brother and sister Antigen Antibody Receive from Questions to Answer 1) What is John’s genotype?___ 2) What are the chances of George’s children being blood type O?____ 3) What is Sally’s blood type?___ 4) What is Sally’s genotype?___ 5) What is Mary’s genotype?__ Draw the pedigree Genetic Traits in humans can be tracked through family pedigrees Define the following words and draw a sample pedigree of your family and include their genotype for a specific trait (Hint: I will never know if it is your real family) Pedigree: Carrier: Drawing Many inherited disorders in humans are controlled by a single gene Describe the following words and diseases Recessive Disorders: Dominant disorders: Disorder Recessive: Albinism Cystic Fibrosis Galactosemia PKU Sickle Cell Homozygous Tay Sachs Dominant: Achrondroplasia Huntington’s Hypercholesterolemia Descriptions/Symptoms/Comments Incidence Fetal testing can spot many inherited disorders early in pregnancy Answer the following questions 1) Amniocentesis Steps: Why might a pregnant female choose to have this test done? 2) Chorionic villus sampling Steps: Advantage: 3) What are the risks of amniocentesis and CVS? 4) What is ultrasound imaging? 5) What else can be analyzed to determine the health of the baby? CHAPTER 15 Chromosome behavior accounts for Mendel’s Principles: Describe the following theory The Chromosomes theory of Inheritance: Genes on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together Define linked genes: Drawing: Crossing over produces new combinations of alleles Recombination frequency: Draw Example Geneticists use crossing over to map genes. Describe how geneticists use crossing over to map genes. If you have genes A B C and D on a chromosomes with the recombination frequencies A-B= 50% , A-C= 5%, B-D=10%, CD=20% , draw what the chromosome might look like. Chromosomes determine sex in many species Organism Human Grasshopper, crickets, roaches Fish, butterfly, bird Ants and bees Date, spinach Wild strawberry Define monoecious: Details about sex determination Female___ Male___ Sex of offspring determined by________________ ___________________________________________________________ Female___ Male___ Sex of offspring determined by________________ ___________________________________________________________ Female___ Male___ Sex of offspring determined by________________ ___________________________________________________________ Lack ________________, Females _____________________________ Males_____________________________________________________ System:______ System:______ Define hermaphroditic: 9.22 Sex-linked genes exhibit a unique pattern of inheritance What is a sex linked gene? Why are most sex linked genes found on the X? Draw a punnette square that crosses a white eyed female fruit fly and a red eyed male fruit fly. Write the female on the side and the male across the top of the punnette square. What percent of the offspring will have red eyes? ____ white eyes____ What percent of the males will have red eyes? ____ white eyes____ What percent of the female will have red eyes?______ white eyes____ 9.23 Sex-linked disorders affect mostly males Describe the following disorders 1) red-green color blindness 2) Hemophilia 3) Duchene muscular dystrophy Neither Sue nor Tom has Duchene muscular dystrophy, but their first son does. If the couple has a second child, what is the probability that he or she will also have the disease? Show the punnette square